 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.232.871 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
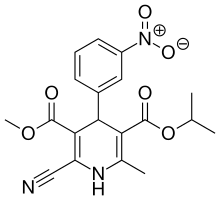
| Formula | C19H19N3O6 |
| Molar mass | 385.376 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Nilvadipine is a calcium channel blocker (CCB) used for the treatment of hypertension and chronic major cerebral artery occlusion.
Pathohistochemical studies have revealed that the volume of the infarction in the middle cerebral artery occlusion model could be decreased by nilvadipine.
Experimental research
Nilvadipine was tested in clinical trial as a possible treatment for Alzheimer's disease in Ireland by the Roskamp Institute, Florida, USA and Trinity College, Ireland.[1] Following this study, an international research consortium led by Trinity College Dublin (Ireland) in May 2011 announced the selection for funding of a large-scale European clinical trial of nilvadipine. More than 500 Alzheimer's disease patients will participate in the multicenter phase III clinical trial designed to study the effectiveness of nilvadipine.[2] In 2018, researchers analyzing data from the trial came to the conclusion that treatment with nilvadipine did not benefit the trial participants, who had suffered from mild to moderate Alzheimer disease.[3]
References
- ↑ "Roskamp Nilvadipine Clinical Trial Questions and Answers" (Press release). Roskamp Institute.
- ↑ "Roskamp Nilvadipine Clinical Trial Press Release" (Press release). Roskamp Institute.
- ↑ Lawlor B; Segurado R; Kennelly S; Olde Rikkert MGM; Howard R; Pasquier F; et al. (2018). "Nilvadipine in mild to moderate Alzheimer disease: A randomised controlled trial". PLOS Medicine. 15 (9): e1002660. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1002660. PMC 6152871. PMID 30248105.