 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
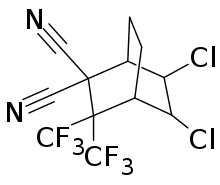
| IUPAC name
5,6-dichloro-3,3-bis(trifluoromethyl)bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-2,2-dicarbonitrile | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H6Cl2F6N2 | |
| Molar mass | 351.07 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Extremely toxic |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
0.1 mg/kg (intraperitoneal, mice)[1] |
LDLo (lowest published) |
0.2 mg/kg (oral, rats)[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Cloflubicyne is a chemical compound which is a chlorinated derivative of BIDN. It's an irreversible GABA receptor antagonist with powerful convulsant effects.[3][4][5][6]
See also
References
- ↑ Fetisov, V.I.; Maslov, A.A.; Panarin, V.A.; Trefilov, N.V. (August 1992). "Fluoro-containing 'cage' convulsants: inhibition of gamma-aminobutyric acid induced Cl−currents". Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. 58 (2–3): 368. doi:10.1016/S0022-1139(00)80833-7.
- ↑ Middleton, W.J; Bingham, E.M (May 1982). "Fluorine-containing 1,1-dicyanoethylenes: their preparation, diels-alder reactions, and derived norbornenes and norbornanes". Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. 20 (3): 397–418. doi:10.1016/S0022-1139(00)82232-0.
- ↑ Golovko, A. I.; Sofronov, G. A.; Klyuntina, T. V. (April 1996). "Norbornan, a new irreversible ligand of the GABAA-receptor chloride channels". Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 121 (4): 404–406. doi:10.1007/BF02446741. S2CID 35092380.
- ↑ Golovko, A. I.; Sofronov, G. A.; Klyuntina, T. V.; Suftin, S. G.; Garbuz, L. A. (July 1996). "Norbornane-induced changes in the density of chloride-ion channels in the brain of rodents". Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 122 (1): 660–662. doi:10.1007/BF02446014. S2CID 46036353.
- ↑ Golovko, A. I.; Ivanov, M. B.; Klyuntina, T. V.; Sofronov, G. A.; Sviderskii, O. A.; Shilov, V. V. (January 1997). "Development of increased convulsibility in mice after a single norbornan injection". Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 123 (1): 52–54. doi:10.1007/BF02764378. S2CID 27826524.
- ↑ Golovko, A. I.; Ivanov, M. B.; Sviderskii, O. A.; Sofronov, G. A.; Shilov, V. V. (June 1998). "Mechanisms of kindling induced by norbornan intoxication". Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 125 (6): 579–581. doi:10.1007/BF02445245. S2CID 26207399.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.