
A dead heat is a rare situation in various racing sports in which the performances of competitors are judged to be so close that no difference between them can be resolved. The result is declared a tie and the competitors are awarded a joint ranking. Dead heats can occur in both head-to-head races and competitions where competitors race sequentially and are ranked by finishing time.
Photo finishes have been a long-standing method of resolving outcomes too ambiguous to be distinguished by the naked eye. Improvements in technology, including digital super-slow motion replay and pressure-sensitive digital timers, have increased precision in resolving dead heats. Consequently, dead heats are declared less often than they once were.
Etymology

The Oxford English Dictionary attributes the term to horse racing. Meets formerly had the same horses run several "heats" in a day, with victors being decided by the total number of wins. A heat which had no clear single winner was discounted from these tallies and was therefore "dead".[2]
Occurrence
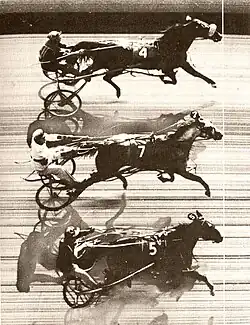
Dead heats are very rare, and situations with three (or more) competitors in a dead heat are exceptionally so. The frequency of dead heats varies between sports, depending on the typical variance in performances and the precision of the technology available. The use of the photo finish, first introduced in horse racing in second quarter of the 20th century, notably decreased the number of dead heats.[2] Both of the two recorded quadruple dead heats in horse racing occurred in England in the 1850s.[3]
Swimming has a relatively high number of dead heats because, under FINA rules (which includes Olympic events), positions are based on race timings which are limited in precision to hundredths of a second; this is despite the availability of technology that could provide further precision.[4][5] The reason for this is that the length of lanes can vary by up to 3 centimetres (1.2 in), with lower-precision timing compensating for the possible differences between the distances competitors have travelled.[6]
Occasionally racers will try to deliberately engineer a dead heat. During the mid-1940s, twin distance runners H. Ross Hume and Robert H. Hume became known as the "dead heat twins" for their practice of finishing their races hand-in-hand in intentional efforts to share victory.[7] At the 2002 United States Grand Prix auto racing teammates Rubens Barrichello and Michael Schumacher attempted to tie for first place, however Barrichello was adjudicated to have won by 0.011 seconds.[8]
Outcome
If a dead heat is declared, all tied competitors are considered to have jointly achieved the superior position (unless a tie-breaking method is used to separate them).[9] This does not affect awards for subsequent finishers. For example, in the final of the Women's 100 metre freestyle at the 2016 Summer Olympics, Penny Oleksiak and Simone Manuel finished in a dead heat for first place. Both were awarded gold medals, no silver medal was awarded, and the next finisher, Sarah Sjöström, received bronze.[10]
Prizes for the tied competitors may be divided. The rules of Formula 1, for example, specify that a dead heat in a race would result in the World Championship points for both the superior and inferior position being added together and divided equally between the tied competitors.[11] Complications can occur if the reward cannot be divided or duplicated: at the Women's 100 meters at the 2012 United States Olympic Track Trials, Jeneba Tarmoh and Allyson Felix finished in a dead heat for the third and final place in the US Olympic team, with there being no provision in the rules to resolve the situation (a head-to-head run-off was proposed, but Tarmoh eventually conceded the place).[12]
In Grand Prix motorcycle racing, joint rankings are resolved by using fastest lap times as a tiebreaker.[13] This rule resulted in Héctor Faubel winning the 125cc classification of the 2011 German motorcycle Grand Prix after a photo finish could not separate him and Johann Zarco.[14]
Special provision is made for dead heats in the rules of sports betting: punters' stakes are divided proportionally by the number of tied competitors.[15]
See also
References
- ↑ "The Boat Race yearly results - men". The Boat Race Limited. Archived from the original on 24 September 2014. Retrieved 26 March 2018.
- 1 2 Hammond, Gerald (2016). The Language of Horse Racing. Routledge. pp. 62–63. ISBN 9781135965020.
- ↑ Mazeppa, "Talk of the Day", Otago Witness, Issue 2083, 25 January 1894 ("At the Hoo races, held in Gorhambury Park, Hertfordshire, on April 26, 1851, four horses ran a dead heat for a race entitled the Omnibus or Open Hunters' Stakes— viz., Defaulter, The Squire of Malton, Reindeer, and Pulcherrima. In the deciding heat Reindeer and Pulcherrima were each backed at 6 to 4, but Defaulter won by half a length. Again in a sweepstakes at the Newmarket - Houghton meeting (October 22, 1855) five horses ran, and four of them — viz., Overreach, The Unexpected, Gamester, and Lady Golightly — could not be separated by the judge, the other horse, King of the Gipsies, being only half a length behind the quartet.")
- ↑ Burke, Timothy. "This Is Why There Are So Many Ties In Swimming". Deadspin. Retrieved 24 February 2018.
- ↑ "SW 11 TIMING | fina.org - Official FINA website". www.fina.org. Fédération internationale de natation. Retrieved 24 February 2018.
- ↑ Ward-Henninger, Colin (13 August 2016). "Rio Olympics: Here's the reason why there are so many ties in swimming". CBSSports.com. Retrieved 20 February 2018.
- ↑ Jimmy Jordan (27 May 1945). "Illinois Beats Michigan for Big Ten Track Crown: Three Illini Stars Win Six Events Among Them to Aid Most Stunning Upset in Years". Council Bluffs Nonpareil (AP wire service story).
- ↑ Clarke, Liz (30 September 2002). "Barrichello Wins Grand Prix With Schumacher's Assist". Washington Post. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
- ↑ See Mazeppa, op. cit.
- ↑ "Double gold medal joy as Oleksiak and Manuel finish in dead heat". International Olympic Committee. 11 August 2016. Retrieved 20 February 2018.
- ↑ 2018 FORMULA ONE SPORTING REGULATIONS. FIA. 19 December 2017. p. 4. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
- ↑ "Jeneba Tarmoh concedes 100m London Olympic spot to Allyson Felix". The Guardian. Associated Press. 2 July 2012. Retrieved 21 February 2018.
- ↑ FIM WORLD CHAMPIONSHIP GRAND PRIX REGULATIONS. Fédération Internationale de Motocyclisme. 17 February 2018. p. 61. Retrieved 22 February 2018.
In case of ties, the riders concerned will be ranked in the order of the best lap time made during the race.
- ↑ "Faubel victorious after photo finish". MotoGP.com. Dorna Sports. 17 July 2011. Retrieved 22 February 2018.
- ↑ "Exchange: What happens if there is a dead heat?". en-betfair.custhelp.com. Retrieved 20 February 2018.