 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
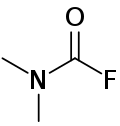
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dimethylcarbamoyl fluoride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H6FNO | |
| Molar mass | 91.085 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Soluble | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Highly toxic |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Dimethylcarbamoyl fluoride is a chemical compound that can be produced by fluorination of dimethylcarbamoyl chloride with potassium fluoride.[1] It's a colorless liquid that is soluble and stable in water.[2][3]
Dimethylcarbamoyl fluoride is highly toxic because it's a potent cholinesterase inhibitor and is lethal even at low doses.[2][3]
See also
References
- ↑ Cuomo, John; Olofson, R. A. (March 1979). "Efficient and convenient synthesis of fluoroformates and carbamoyl fluorides". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 44 (6): 1016–1017. doi:10.1021/jo01320a034.
- 1 2 Augustinsson, K.B.; Casida, J.E. (December 1959). "Enzymic hydrolysis of N:N-dimethylcarbamoyl fluoride". Biochemical Pharmacology. 3 (1): 60–67. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(59)90009-7. PMID 13795122.
- 1 2 MYERS, DK (April 1956). "Studies on cholinesterase. 10. Return of cholinesterase activity in the rat after inhibition by carbamoyl fluorides". The Biochemical Journal. 62 (4): 556–63. doi:10.1042/bj0620556. PMC 1215962. PMID 13315214.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.