Sir Henry Macandrew | |
|---|---|
 Macandrew in 1910s | |
| Birth name | Henry John Milnes Macandrew |
| Born | 7 August 1866 Inverness, United Kingdom |
| Died | 16 July 1919 (aged 52) Aleppo, Syria |
| Buried | Beirut War Cemetery |
| Allegiance | United Kingdom |
| Service/ | British Army British Indian Army |
| Years of service | 1884–1889 (British Army) 1889–1919 (British Indian Army) |
| Rank | Major-General |
| Commands held | 5th Bengal Cavalry 9th (Sirhind) Brigade 53rd Brigade 2nd Indian Cavalry Division 5th Cavalry Division |
| Battles/wars | |
| Spouse(s) | Esther Ritchie Cooper |
Major-General Sir Henry Macandrew KCB DSO (7 August 1866 – 16 July 1919) was a British Indian Army officer. Predominantly serving in the cavalry and also as an intelligence officer, Macandrew fought through the Tirah and Mohmand campaigns in India in 1897 and 1898, and then served as a staff officer during the Boer War, for which service he received the Distinguished Service Order.
After serving again on the staff Macandrew was given command of his regiment, the 5th Bengal Cavalry, in 1914, and upon the outbreak of the First World War travelled to France as GSO1 of the 1st Indian Cavalry Division. Soon afterwards he was promoted to become Brigadier-General General Staff for the Indian Cavalry Corps. He served at the Battle of Neuve Chapelle before in 1916 he assumed command of the 2nd Indian Cavalry Division, leading it during the Battle of the Somme and Battle of Cambrai. In 1918 he was given command of the newly created 5th Cavalry Division for the Sinai and Palestine campaign. He commanded the division throughout the campaign, including at the Capture of Damascus and Battle of Aleppo. Staying with his division after the war, Macandrew died of wounds received in an accidental explosion of petrol fumes in Aleppo.
Military career
Early service
Henry John Milnes Macandrew was born on 7 August 1866, the son of Sir Henry Macandrew of Aisthorpe, Inverness.[1] Macandrew was educated at The Inverness College before he joined the British Army on 6 August 1884 as a lieutenant in the 2nd Battalion, Cameron Highlanders.[1][2][3] Two years later he transferred to the Lincolnshire Regiment on 10 November 1886.[1][4]
Macandrew began an eighteen-month period of probationary service in the Bengal Staff Corps on 30 March 1888, serving as an officiating squadron officer in the 5th Bengal Cavalry of the British Indian Army. On 22 November 1889 he was admitted to the Bengal Staff Corps, having completed his probationary period, as a lieutenant and continued with the 5th Bengal Cavalry.[1][5]
Macandrew served as brigade transport officer to the 2nd Brigade involved in the Tirah campaign of 1897, and was promoted to captain on 10 November that year.[6][7] He continued his role as a transport officer into the following year, this time as part of the Mohmand campaign in the Khyber Pass. For his service in these campaigns, Macandrew was subsequently awarded the India Medal with two clasps and mentioned in dispatches.[6]
Boer War
Macandrew continued in India until 1900 when he moved to fight in the Boer War. Serving in Kitchener's Horse, from February he operated in the Orange Free State. He was present at the Battle of Paardeberg between 17 and 26 February, the Battle of Poplar Grove on 7 March, and the Battle of Driefontein on 10 March. After several other skirmishes, Macandrew moved to serve in the Transvaal in May, seeing action at the Battle of Doornkop on 29 May and being present at the occupation of Pretoria on 4 June.[6][8][9]
Macandrew was subsequently appointed intelligence officer on the Delagoa line, east of Pretoria, in July, in which role he continued until September. At this stage he was assigned as the Deputy Assistant Adjutant-General Intelligence (DAAGI) to Major-General Ralph Arthur Penrhyn Clements's column, serving in the Transvaal and to the west of Pretoria.[6][9] On 29 November Macandrew was awarded the Distinguished Service Order; he continued as DAAGI into 1901, moving in February to serve Major-General Neville Lyttelton in the same position.[6][10]
Having served in operations in the Transvaal, Orange River Colony, and Cape Colony, Macandrew was then promoted to serve Major-General Bruce Hamilton as DAAGI Army Headquarters Staff in May. He stayed in this role until the end of the war, relinquishing his position on 31 May 1902.[6][9] For his services in the Boer War Macandrew received the Queen's South Africa Medal with four clasps, the King's South Africa Medal with two clasps, and was mentioned in dispatches a further two times.[1]
Return to India
Macandrew's lengthy service as a staff officer during the Boer War led him to be considered qualified for formal staff employment after his return to India.[9] On 2 May 1903 he was appointed a Station Staff Officer, 1st Class, but he stayed in this position for only a short while.[11] Later in the year he was appointed brigade major to the Inspector-General of Cavalry in India, Major-General Douglas Haig. Haig chose Macandrew because he had worked with him in the Boer War and been impressed by his intelligence work. The appointment was meant to be for only one year, but Haig had Macandrew stay on until 1905.[6][12][13] He was promoted to major on 10 November 1904.[14]
After his appointment with Haig ended, Macandrew continued on as a staff officer, becoming a Deputy Assistant Quartermaster-General on 6 January 1906.[15] Still with the 5th Bengal Cavalry, Macandrew was subsequently promoted to lieutenant-colonel on 10 November 1912 and assumed command of the 5th on 16 February 1914.[16][17]
Western Front
Staff work
When the First World War began, Macandrew was assigned to serve on the Western Front in France as the GSO1 to Major-General Michael Rimington, commander of the 1st Indian Cavalry Division. They arrived on 7 November and subsequently the Indian Cavalry Corps was formed on 18 December, with Rimington in command. He brought Macandrew with him to the corps, as his Brigadier-General General Staff (BGGS).[18] In April 1915 Macandrew visited Haig, who was now a general, at his headquarters; Macandrew criticised how his cavalry had been utilised during the recent Battle of Neuve Chapelle and disagreed with the view of other staff officers that the war would continue and be won through trench warfare.[12] He believed that the ability to correctly utilise cavalry was a key facet to any successful general officer.[19]
Macandrew's position as a brigadier-general was a temporary rank, and he was still a substantive lieutenant-colonel, until he was promoted to brevet colonel on 3 June.[17][20] The historian Simon Robbins argues that Macandrew's staff work for the corps was sub-par, with his requirement that all orders to divisions be personally approved by him stifling initiative and creating backlogs.[21] The historian Geroge Morton-Jack, however, argues that his work improved, and he succeeded in creating an operational headquarters for the corps from very little.[22]
Command
Macandrew fell out with Rimington in September and left his staff on 7 October.[23][22] He thus relinquished his temporary rank, reverting to his brevet colonelcy.[24][23] Macandrew was still well thought of by Haig, who quickly had him appointed to a new command.[22] On 16 November he was re-promoted to temporary brigadier-general and given the 9th (Sirhind) Brigade, replacing the newly promoted Major-General William George Walker.[24][25][26] He stayed with the 9th only briefly, moving to the 53rd Brigade on 28 November.[27] The brigade, part of 18th (Eastern) Division, did not participate in any battles during Macandrew's command.[28]
Macandrew left 53rd Brigade on 27 April 1916 and on 7 May was promoted to temporary major-general and given command of the 2nd Indian Cavalry Division at Haig's behest.[29][30][27][22] The division contained the 3rd (Ambala) Cavalry Brigade, the 9th (Secunderabad) Cavalry Brigade, and the Canadian Cavalry Brigade.[31]
The Somme

Macandrew participated in the Battle of the Somme in July; his division was tasked by Fourth Army to advance through any gaps created by its advance beginning on 1 July. Little occurred for the cavalry in the next two weeks, before a push from Fourth Army on 14 July opened a route for the strategically important High Wood to be taken. In mid-morning, Macandrew took his division forward to capture High Wood, but the ground was too slippery and Macandrew fell twice during the advance.[32] It was called off and infantry were brought in to make the attack instead.[29] On 7 September the Cavalry Corps was re-established in France and all the cavalry divisions were put under its orders. As this occurred, Macandrew's division was renamed the 5th Cavalry Division.[33]
Macandrew was promoted to substantive major-general on 1 January 1917.[34] The Germans began to retreat to the Hindenburg Line in March, with the British following up behind them.[35] The cavalry were very active in these operations, with Haig singling out an action of Macandrew's division where on 27 March it drove the Germans out of Villers-Faucon and several surrounding villages.[36] With the retreat having come to a halt, by June Macandrew's division had returned to trench warfare, based around Le Verguier. The obstacles put up by it were complimented by Lieutenant-General Sir William Pulteney, commander of III Corps, as the best he had seen in the country.[35] In October the division marched into Belgium to take part in the Battle of Passchendaele but was not used.[35]
Cambrai
Macandrew's division next saw action on 20 November with the start of the Battle of Cambrai. The cavalry divisions were expected to break through gaps in the German line caused by attacking British infantry and tanks.[37] 5th Cavalry Division was allotted to cross the Dunkirk-Scheldt Canal at Masnieres and Marcoing to capture river crossings over the Sensée near Paillencourt.[38] By the afternoon Macandrew's brigades had reached both Masnieres and Marcoing, and small parts of the division succeeded in crossing the canal.[39] In many cases the infantry had not pushed back the German defenders as expected and the cavalry were too cumbersome to react to new weaknesses in the enemy lines. Unable to advance further, Macandrew's division stayed near the canal overnight and in the afternoon of 21 November attempted to make crossings again. These were, however, broken up by German counter-attacks and in the morning of 22 November the division was withdrawn to Fins.[40]
The advance was called off on 27 November, although the cavalry saw further service defending against the subsequent German counter-attack.[37] On 30 November, Macandrew's division returned to Villers-Faucon, near where the Germans had attacked and retaken Gauche Wood. Macandrew worked with the Guards Division and tank support to push the Germans back out of the heavily defended wood, succeeding on 1 December; it was intended to capture Villers-Guislain beyond the wood as well, but this was not done because of the heavy German defences around it, and the British instead fortified Gauche Wood.[41][42]
Macandrew, who had observed the 1st Cavalry Division as it failed to break through during the earlier British advance, wrote a report to Haig criticising the communications between the different British units in the attack, and identified a lack of "vigour and determination" in the cavalry brigade and regimental commanders. Haig agreed with Macandrew's assessment.[43] On 1 January 1918 Macandrew was created a Companion of the Order of the Bath.[44]
Divisional reforms
At conferences towards the end of 1917 the British prime minister Lloyd George, impacted by the failure at Cambrai, argued that the continued use of cavalry on the Western Front was useless, and that the cavalrymen would be of more use in other roles.[43] Internal army politics made it impossible for any cavalry division to be outright disbanded, and instead on 13 January Haig was ordered to send all his Indian cavalry to Palestine in return for yeomanry that could be converted into machine gunners.[45]
Simultaneously to this, Haig was reviewing the cavalry generals in the army, and on 15 January the commander of the Cavalry Corps, Lieutenant-General Charles Kavanagh, requested that Macandrew stay on the Western Front as commander of the 1st Cavalry Division instead of going with his men to Palestine. When the German spring offensive began in March the commander of 1st Cavalry Division, Major-General Richard Mullens, who Macandrew had been expected to replace, did well enough that Haig decided not to fire him.[46] As such in the same month Macandrew travelled to Palestine with the Indian portion of his division and the 1st Indian Cavalry Division, which had since been renamed 4th Cavalry Division.[45]
Joining the Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) for service in the Sinai and Palestine campaign, Macandrew was initially going to take over command of the Yeomanry Mounted Division as the previous commander was forming the new XXIV Corps. On 29 March the nascent corps was dissolved and Macandrew's orders for the Yeomanry Mounted Division were cancelled on 9 April.[47]
Macandrew's men were used to form the new 1st and 2nd Mounted Divisions, and he instead took command of the latter on 31 May. In an attempt to continue the legacy of the Indian cavalry from the Western Front, on 23 July the two divisions were respectively renamed the 4th and 5th Cavalry Divisions.[48][45][49] Macandrew's new division consisted of the 13th and 14th Indian Cavalry Brigades and the 15th (Imperial Service) Cavalry Brigade.[50]
Palestine campaign
Jordan Valley
Macandrew's division joined the Desert Mounted Corps (DMC) on 2 July.[51] It then participated in the occupation of the Jordan Valley. Macandrew, whose units were all equipped as traditional cavalry, ordered his patrols to always charge upon sighting Ottoman Empire soldiers. This had a negative affect on desertion rates amongst Ottoman soldiers because they were too scared of Macandrew's lancers to attempt to surrender to them.[52]
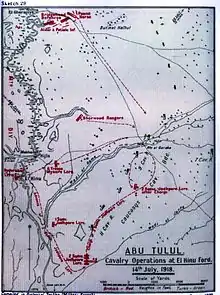
A joint Ottoman-German force attacked a weak point of the British line in the Jordan Valley on 14 July at the Battle of Abu Tellul, being defeated by a counter-charge by the ANZAC Mounted Division.[53] While this attack was ongoing an Ottoman force of 1,200 cavalry made contact with two of Macandrew's regiments, based between Ghorniye and the Dead Sea. With the British on the other side of the River Jordan to the Turkish force, Brigadier-General Cyril Harbord of the 15th suggested to Macandrew that his two regiments, the Mysore and Jodhpore Lancers, could attack the Ottomans in a pair of flanking manoeuvres. This Macandrew agreed to.[53][54]
The Jodhpores crossed the Jordan at El Hinu to the south of the Ottoman force while the Mysores did similarly to the north. Supported by machine gun fire, both regiments charged portions of the Ottoman force in the scrubland around the river. Over thirty Turkish soldiers were killed in the charges with more captured before the two Indian regiments withdrew, exhausted by the mid-day heat.[55][56] The Ottomans afterwards entrenched themselves along the crossings of the river, but a portion of the 34th Poona Horse came up as reinforcements and charged across a ford, forcing the Ottomans to abandon their positions and ending the Battle of El Hinu. The three Indian regiments killed around ninety Turkish soldiers and took a further ninety-one prisoner.[57][58]
Battle of Sharon
General Sir Edmund Allenby, the commander-in-chief of the EEF, began in July to plan a large operation to destroy the Ottoman Army Group F which faced him.[59] XXI Corps was assigned to break through the Ottoman defences around Sharon plain, which would allow Macandrew's and two other divisions to charge into the flat terrain beyond the defences and cut off the line of retreat of the Turkish Seventh and Eighth Armies.[60] To avoid alarming Ottoman intelligence, the cavalry divisions formed up in secret behind XXI Corps, only moving at night as they took their positions.[61] By 17 September Macandrew's division was in place, hiding in an orange grove 8 miles (12.9 kilometres) behind the front line.[62] Macandrew's force was to advance behind the attack of the 60th (2/2nd London) Division, attacking along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea, and he spent the night sleeping at the headquarters of Major-General John Shea, who commanded the 60th and had served with Macandrew in the Indian cavalry.[63]
XXI Corps' attack began in the night of 18 September.[63] The push forward was highly successful, with 60th Division capturing Tulkarm in the early evening on 19 September.[64] Macandrew's division had passed through the Turkish lines in the morning and ran along the beaches, hidden from Turkish fire by the cliffs. At around mid-day the division began to engage Turkish defences as it charged across Sharon plain; by 3 p.m. it had reached Liktera.[65][66] The division rested there for several hours while preparing to move on to fight the pre-planned Battle of Nazareth in which elements of Macandrew's division were to make a raid on and then capture Nazareth.[67] This was the headquarters of the Ottoman commander-in-chief, General Otto Liman von Sanders, with the goal of the attack being his capture.[68] Slowed by poor guides and long searches of small villages, the 13th Brigade sent to Nazareth attacked only in the early morning of 20 September. It captured 1,200 Ottoman soldiers before it was forced to withdraw, Macandrew unable to send reinforcements because his horses were too exhausted. Liman remained uncaptured, escaping from Nazareth around an hour after Macandrew had ordered the withdrawal of his force.[69][70]
Macandrew's commander, Lieutenant-General Harry Chauvel, was highly disappointed to not have captured Liman, although his headquarters and communications had been almost completely destroyed.[68][71] Macandrew heightened this disappointment by arriving to a meeting with Chauvel in Liman's staff car, only to announce that Liman was not in it. Allenby later on removed the direct commander of the operation, Brigadier-General Philip Kelly, from his command because of the failure to capture Liman.[72] Allenby decided on 22 September that the DMC would take Damascus, but to do this the port of Haifa had to be taken to allow supplies to be landed for the army. Macandrew's division was tasked with this, and to capture Acre 10 miles (16 kilometres) further on.[73] In the morning of 23 September Macandrew ordered the 13th Brigade to capture Acre, which was done without difficulty. 15th Brigade was tasked with the attack on Haifa, with the 14th in reserve.[74] The main attack on Haifa, orchestrated by Harbord, began at 2 p.m. in concert with two flanking attacks. Supported by machine gun fire, the cavalry squadrons completed the attack by 3 p.m. having captured 687 German and Ottoman soldiers.[75]
Capture of Damascus

With around 40,000 enemy soldiers retreating between Haifa and Damascus, the rate of the attack was increased by Allenby in order to ensure that German and Turkish soldiers did not reform and provide effective resistance to the British.[76] Macandrew's division was tasked with advancing on the most direct route to Damascus, through the Golan Heights, following behind the Australian Mounted Division (Ausdiv). The enemy units in front of them were the remnants of Seventh and Eighth Armies. Having begun on 27 September, the 5th and Ausdiv reached Quneitra on 28 September. The advance continued and on 30 September Macandrew's 14th Brigade encountered an Ottoman column near Al-Kiswah; it captured the front half of the column, around 2,000 men. The rear half of the column turned around but was intercepted by the 13th and 15th Brigades, which captured much of the rest and funnelled the survivors in the direction of Ausdiv.[77][78]
The DMC completed the surrounding of Damascus on 1 October, and Chauvel ordered that the city was not to be entered until 2 October.[79][80] Macandrew, however, entered Damascus in mid-morning on 1 October alongside the 14th Brigade and marched the length of the city.[81][80] Chauvel assumed temporary command of the city on 2 October and Macandrew ordered his staff to not mention the incursion of the previous day. The British subsequently organised a show of force, with a column consisting of one unit from each regiment in the DMC marching through the city. Chauvel headed the column, alongside Macandrew and Major-Generals George Barrow and Henry Hodgson.[82][80] This calmed the agitated local population and stopped some incipient looting.[83]
The advance through Ottoman territory continued after this, with Macandrew's division marching on 5 October.[84] Travelling slowly in the knowledge that the Ottoman armies had already left the area, Macandrew occupyed Rayak and Zahle on 6 October without resistance.[85] The division then began to advance on Homs, with Macandrew splitting his division into two columns. They reached the city on 16 October to find it also bereft of defences, and Macandrew was given a banquet by the local authorities.[86] Illness had by this point began to take a heavy toll on Allenby's troops, with the division following up behind Macandrew, the 4th Cavalry, having to stop its advance because of the amount of disease in its ranks. 5th Division, however, was the healthiest remaining. With horse artillery, armoured cars, and a Royal Air Force squadron also under his command, this meant that Macandrew commanded the strongest column available to the British, with 2,500 men.[87][88]
Pursuit to Haritan

Macandrew was given the task of capturing Aleppo, as part of the Pursuit to Haritan. He sent his armoured cars forward first, leaving Homs on 20 October.[89][88] Having pushed the Ottoman rearguard away on 22 October, Macandrew sent a request for surrender to Aleppo on the following day. Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, the commander there, declined, saying he did not "find it necessary to reply to your note".[89] Macandrew overestimated the condition of the Aleppo walls and defences, which had been maintained poorly, and chose to surround the city with his force rather than directly assault it.[90] 15th Brigade caught up with the armoured cars on 25 October, but on the same day the Arab force of Prince Faisal entered Aleppo and pushed Atatürk's forces out, completing the Battle of Aleppo.[89] Macandrew entered Aleppo in the morning of 26 October, the same date he had planned for his attack to begin.[91][92]
On 26 October the 15th Brigade advanced north to Haritan and encountered a force of Ottoman soldiers that outnumbered them, with around 3,400 men; Harbord attacked and was repulsed.[93] Macandrew relieved the 15th with the 14th Brigade on 27 October, and the Ottoman force fell back to a strong defensive position with around 7,000 men, outnumbering Macandrew's immediate force around seven to one. The same day Ausdiv was ordered to reinforce Macandrew and he settled to observe the enemy force until it arrived. Before Ausdiv could complete its march the Armistice of Mudros was signed on 31 October and hostilities ended.[94][95] This completed a campaign in which Macandrew's division had covered around 600 miles (970 kilometres) in thirty-eight days.[96]
Post-war and death
Macandrew was mentioned in dispatches several times for his services during the First World War, bringing his total number of mentions to eight.[1][97] He also received the Order of the Nile from the Sultanate of Egypt and was appointed colonel of the regiment to his old unit, the 5th Bengal Cavalry, on 13 March 1919.[97][98] Soon after this, on 3 June, he was created a Knight Commander of the Order of the Bath.[99] He continued with his division through this period, stationed at Aleppo. He was troubled by the increasing number of cases of malaria and influenza in his unit and was himself weakened by sickness.[100] In early July he was smoking a cigarette in his pyjamas when he entered a room where his uniform tunic was hanging to dry, having been recently cleaned with petrol. The cigarette flame ignited the petrol vapours which exploded, severely burning Macandrew.[101][102]

Macandrew was taken to hospital, and while undergoing treatment for his burns died of heart failure on 16 July.[101][102][100] He was buried in the Commonwealth War Graves Commission's Beirut War Cemetery.[97] The military historian Cyril Falls describes Macandrew as a vigorous and headstrong commander, arguing that at the time of his death he had:[89]
...lived to see his theories and the results of his life's work put into practice, and left behind him a record of achievement hardly equalled by any cavalryman of modern times[103]
An American cavalry officer attached as an observer to the British Army in Palestine and Syria, Lieutenant-Colonel Edward Davis, later recorded his opinion of Macandrew:[104]
...he was very unassuming, with an easy, genial, and most friendly manner...that a very bold spirit lay behind his placid, friendly manner was proved by the Aleppo operations[19]
Morton-Jack suggests that if Macandrew had not died prematurely his good war record would have seen him go on to hold more senior appointments within the British Indian Army, as other cavalry officers such as Barrow and Douglas Baird did, both eventually reaching the rank of general.[105] Macandrew's insignia of the Order of the Bath was presented by George V to his daughter, Esther Macandrew, on 5 December 1919.[106]
Personal life
Macandrew married Esther Cooper in a ceremony officiated by George James Cowley-Brown at St John's, Edinburgh on 9 August 1892.[107] She was the youngest daughter of Henry Ritchie Cooper, a justice of the peace from Ballindalloch, Stirlingshire. Together the couple had one son and one daughter.[6][8] Macandrew, who lived in Aisthorpe, was an enthusiastic horse rider in his spare time, riding both cross-country and on the flat. He was a member of the Cavalry Club.[6]
Citations
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Who Was Who (1967), pp. 656–657.
- ↑ Army List (1884), p. 791.
- ↑ "No. 25389". The London Gazette. 22 August 1884. p. 3832.
- ↑ Army List (1895), p. 558a.
- ↑ Gazette of India (1889), p. 646.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Who Was Who (1967), p. 657.
- ↑ Gazette of India (1898), pp. 120–121.
- 1 2 Burke & Burke (1909), p. 2203.
- 1 2 3 4 Indian Army List (1919), p. 327.
- ↑ Gazette of India (1901), pp. 313–314.
- ↑ "No. 27578". The London Gazette. 21 July 1903. p. 4594.
- 1 2 Sheffield & Bourne (2006), p. 114.
- ↑ Scott (2006), p. chap. 8.
- ↑ Gazette of India (1905), p. 167.
- ↑ "No. 27897". The London Gazette. 23 March 1906. p. 2067.
- ↑ Gazette of India (1913), p. 108.
- 1 2 Indian Army List (1915), p. 412.
- ↑ Anglesey (1996), pp. 222–223.
- 1 2 Davis (1924), p. 48.
- ↑ Indian Army List (1915), pp. 57–58.
- ↑ Morton-Jack (2014), p. 24.
- 1 2 3 4 Morton-Jack (2014), p. 278.
- 1 2 "No. 29372". The London Gazette (Supplement). 16 November 1915. p. 11455.
- 1 2 Creagh & Humphris (1924), p. 124.
- ↑ "No. 29409". The London Gazette. 21 December 1915. p. 12686.
- ↑ Robbins (2001), p. 456.
- 1 2 Becke (1938), p. 80.
- ↑ Becke (1938), p. 84.
- 1 2 Sheffield & Bourne (2006), p. 205.
- ↑ "No. 29625". The London Gazette. 16 June 1916. p. 5988.
- ↑ Gliddon (2016), p. 509.
- ↑ Gilbert (2006), p. 112.
- ↑ Badsey (2008), p. 275.
- ↑ Indian Army List (1919), p. 118.
- 1 2 3 Deccan Horse (1923), p. 189.
- ↑ Boraston (1979), p. 74.
- 1 2 Badsey (2008), pp. 290–291.
- ↑ Pitman (1923), p. 240.
- ↑ Pitman (1923), pp. 245–246.
- ↑ Pitman (1923), pp. 246–247.
- ↑ Rowcroft (1923), pp. 49–50.
- ↑ Miles (1948), pp. 238–240.
- 1 2 Badsey (2008), p. 292.
- ↑ Indian Army List (1919), p. supp. p. 3..
- 1 2 3 Badsey (2008), p. 293.
- ↑ Badsey (2008), p. 294.
- ↑ Becke (1945), p. 263.
- ↑ Falls (1930), pp. 414–415.
- ↑ Becke (1945), p. 42.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), p. 221.
- ↑ EEF Record (1919), p. 50.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), pp. 223–224.
- 1 2 Anglesey (1994), pp. 236–237.
- ↑ Falls (1930), p. 434.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), pp. 239–240.
- ↑ Falls (1930), p. 435.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), p. 240.
- ↑ Falls (1930), p. 436.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), p. 244.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), p. 246.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), p. 255.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), p. 257.
- 1 2 Anglesey (1994), p. 260.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), p. 263.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), pp. 266–267.
- ↑ Falls (1930), p. 523.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), pp. 268–269.
- 1 2 Anglesey (1994), p. 273.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), pp. 269–273.
- ↑ Falls (1930), pp. 524–527.
- ↑ Falls (1930), p. 527.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), p. 274.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), p. 295.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), p. 296.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), pp. 298–299.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), p. 316.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), p. 325.
- ↑ Falls (1930), pp. 575–576.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), p. 327.
- 1 2 3 Hughes (1999), p. 98.
- ↑ Falls (1930), p. 591.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), p. 329.
- ↑ Falls (1930), p. 593.
- ↑ Falls (1930), p. 601.
- ↑ Falls (1930), p. 602.
- ↑ Falls (1930), p. 606.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), p. 334.
- 1 2 Falls (1930), p. 610.
- 1 2 3 4 Anglesey (1994), p. 335.
- ↑ Palmer (1998), p. 264.
- ↑ Falls (1930), p. 616.
- ↑ Massey (1920), p. 308.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), pp. 335–338.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), p. 339.
- ↑ Falls (1930), p. 617.
- ↑ Anglesey (1994), p. 342.
- 1 2 3 "Major General Sir Henry John Milnes MacAndrew". Commonweath War Graves Commission. Retrieved 29 January 2023.
- ↑ Indian Army List (1919), p. 883.
- ↑ "No. 31395". The London Gazette. 6 June 1919. p. 7420.
- 1 2 Massey (1920), p. 313.
- 1 2 "General Sir Henry MacAndrew". The Times. London. 24 July 1919.
- 1 2 "General MacAndrew Killed by Petrol on Tunic". Daily Mail. London. 28 July 1919.
- ↑ Falls (1930), p. 624.
- ↑ Davis (1924), p. 47.
- ↑ Morton-Jack (2014), p. 280.
- ↑ "Court and Society". Belfast News-Letter. Belfast. 5 December 1919. p. 7.
- ↑ "Marriages". The Colonies and India. 13 August 1892. p. 36. Retrieved 4 February 2023.
References
- A Brief Record of the Advance of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force. London: His Majesty's Stationery Office. 1919. OCLC 17017063.
- "A Short History of the Royal Deccan Horse II". The Cavalry Journal. 13: 187–194. 1923.
- Anglesey, Henry, Marquess of (1994). A History of the British Cavalry 1816 to 1919. Vol. 5. London: Leo Cooper. ISBN 0-85052-395-8.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Anglesey, Henry, Marquess of (1996). A History of the British Cavalry 1816 to 1919. Vol. 7. London: Leo Cooper. ISBN 0-85052-437-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Army List. London: John Murray. July 1884.
- Army List. London: Her Majesty's Stationery Office. July 1895.
- Badsey, Stephen (2008). Doctrine and Reform in the British Cavalry 1880–1918. Aldershot, Hampshire: Ashgate. ISBN 978-0-7546-6467-3.
- Becke, A. F. (1938). Order of Battle of Divisions: Part 3A New Army Divisions (9–26). London: His Majesty's Stationery Office. OCLC 656126891.
- Becke, A. F. (1945). Order of Battle: Part 4 The Army Council, G. H. Q.s, Armies, and Corps. London: His Majesty's Stationery Office. OCLC 493146775.
- Boraston, J. H. (1979). Sir Douglas Haig's Despatches. London: J. M. Dent & Sons. ISBN 0-460-04371-4.
- Burke, Sir Bernard; Burke, Ashworth P. (1909). A Genealogical and Heraldic History of the Peerage and Baronetage. London: Harrison & Sons. OCLC 28297274.
- Creagh, O'Moore; Humphris, E. M. (1924). The V.C. and D.S.O. Vol. 2. London: Standard Art Book Co. OCLC 779208523.
- Davis, Edward (January 1924). "The British Cavalry in Palestine and Syria". The Cavalry Journal. 33 (134): 47–51.
- Falls, Cyril (1930). Military Operations Egypt & Palestine. Vol. 2. London: His Majesty's Stationery Office. OCLC 1042348211.
- Gilbert, Martin (2006). The Battle of the Somme: The Heroism and Horror of War. Toronto: McClelland & Stewart. ISBN 978-0-7710-3547-0.
- Gliddon, Gerald (2016). Somme 1916: A Battlefield Companion. Stroud, Gloucestershire: The History Press. ISBN 978-0-7509-6732-7.
- Hughes, Matthew (1999). Allenby and British Strategy in the Middle East 1917–1919. London: Frank Cass. ISBN 0-7146-4473-0.
- Indian Army List. Calcutta: Government Printing, India. 1915.
- Indian Army List. Calcutta: Government Printing, India. 1919.
- Massey, William Thomas (1920). Allenby's Final Triumph. London: Constable and Company. OCLC 457411812.
- Miles, Wilfred (1948). Military Operations in France and Belgium 1917: The Battle of Cambrai. London: His Majesty's Stationery Office. OCLC 24954868.
- Morton-Jack, George (2014). The Indian Army on the Western Front. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-1392-2638-7.
- Palmer, Alan (1998). Victory 1918. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. ISBN 0-297-84124-6.
- Pitman, Thomas Tait (1923). "Surprise Attack on Cambrai". The Cavalry Journal. 13: 235–259.
- Robbins, Simon Nicholas (2001). British Generalship on the Western Front in the First World War, 1914–1918 (PhD). King's College London.
- Rowcroft, C. H. (1923). "The 9th Hodson's Horse at Cambrai, 1917". The Cavalry Journal. 13: 47–50.
- Scott, Douglas (2006). The Preparatory Prologue: Douglas Haig: Diaries & Letters, 1861–1914. Barnsley, South Yorkshire: Pen & Sword Military. ISBN 978-184415-404-3.
- Sheffield, Gary; Bourne, John (2006). Douglas Haig: War Diaries and Letters 1914–18. London: Phoenix. ISBN 978-0-7538-2075-9.
- The Gazette of India. Simla: Government Printing, India. 1889.
- The Gazette of India. Simla: Government Printing, India. 1898.
- The Gazette of India. Simla: Government Printing, India. 1901.
- The Gazette of India. Simla: Government Printing, India. 1905.
- The Gazette of India. Simla: Government Printing, India. 1913.
- Who Was Who 1916–1928. London: Adam & Charles Black. 1967. OCLC 1164573135.