| Hylobates[1][2] | |
|---|---|
_-_Female.jpg.webp) | |
| A pileated gibbon (Hylobates pileatus) female hanging from tree | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Haplorhini |
| Infraorder: | Simiiformes |
| Family: | Hylobatidae |
| Genus: | Hylobates Illiger, 1811 |
| Type species | |
| Homo lar [1] Linnaeus, 1771 | |
| Species | |
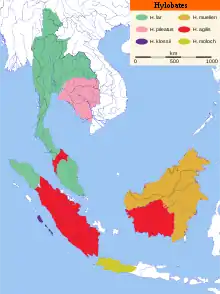 | |
| Distribution of Hylobates and its species (note: Bornean population formerly included in H. agilis is now generally considered a separate species, H. albibarbis; H. muelleri is now split into H. muelleri, H. abbotti, and H. funereus) | |
The genus Hylobates /ˌhaɪloʊˈbeɪtiːz/ is one of the four genera of gibbons. Its name means "forest walker", from the Greek hūlē (ὕλη, "forest") and bates (βάτης, "one who treads").[3][4]
It was once considered the only genus, but recently its subgenera (Hoolock [formerly Bunopithecus], Nomascus, and Symphalangus) have been elevated to the genus level.[1][5] Hylobates remains the most species-rich and widespread of gibbon genera, ranging from southern China (Yunnan) to western and central Java.
Individuals within this genus are characterized by 44 chromosomes and often have a ring of white fur around their faces.[2]
Classification
- Family Hylobatidae: gibbons[1][2]
- Genus Hylobates
- Lar gibbon or white-handed gibbon, Hylobates lar
- Malaysian lar gibbon, Hylobates lar lar
- Carpenter's lar gibbon, Hylobates lar carpenteri
- Central lar gibbon, Hylobates lar entelloides
- Sumatran lar gibbon, Hylobates lar vestitus
- Yunnan lar gibbon, Hylobates lar yunnanensis
- Bornean white-bearded gibbon, Hylobates albibarbis
- Agile gibbon or black-handed gibbon, Hylobates agilis
- Western grey gibbon or Abbott's grey gibbon, Hylobates abbotti
- Eastern grey gibbon or northern grey gibbon, Hylobates funereus
- Müller's gibbon or southern grey gibbon, Hylobates muelleri
- Silvery gibbon, Hylobates moloch
- Western silvery gibbon or western Javan gibbon, Hylobates moloch moloch
- Eastern silvery gibbon or central Javan gibbon, Hylobates moloch pongoalsoni
- Pileated gibbon or capped gibbon, Hylobates pileatus
- Kloss's gibbon or Mentawai gibbon, bilou or dwarf siamang, Hylobates klossii
- Lar gibbon or white-handed gibbon, Hylobates lar
- Genus Hoolock
- Genus Symphalangus
- Genus Nomascus
- Genus Hylobates
Hybrids
Hybrids between Müller's gibbon (H. muelleri) and the Bornean white-bearded gibbon, (H. albibarbis) have been reported in areas of Borneo.[6] A gibbon born at the Kujukushima Zoo in Japan to a female lar or white-handed gibbon (H. lar) was determined to have been fathered by a male agile gibbon (H. agilis).[7]
References
- 1 2 3 4 Groves, C. P. (2005). "Genus Hylobates". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 178–181. ISBN 0-801-88221-4. OCLC 62265494.
- 1 2 3 Geissmann, Thomas. "Gibbon Systematics and Species Identification". Retrieved 2006-04-13.
- ↑ βάτης. Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert; A Greek–English Lexicon at the Perseus Project: "one that treads or covers"
- ↑ Craig, John (1848). A new universal etymological technological, and pronouncing dictionary of the English language. p. 962.
- ↑ Mootnick, A.; Groves, C. P. (2005). "A new generic name for the hoolock gibbon (Hylobatidae)". International Journal of Primatology. 26 (4): 971–976. doi:10.1007/s10764-005-5332-4. S2CID 8394136.
- ↑ Payne, J.; Francis, C. (2005). A Field Guide to the Mammals of Borneo. Kota Kinabalu, Sabah, Malaysia: Sabah Society. p. 230. ISBN 967-99947-1-6.
- ↑ Watanuki, Hiroshi (31 January 2023). "Mystery solved: Father of gibbon at Nagasaki Pref. zoo identified through DNA analysis". The Mainichi. Retrieved 10 February 2023.