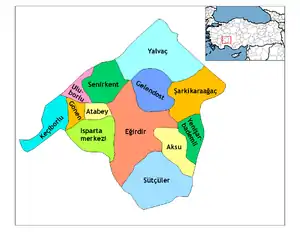
Isparta Province
Isparta ili | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Location of the province within Turkey | |
| Country | Turkey |
| Seat | Isparta |
| Government | |
| • Vali | Aydın Baruş |
| Area | 8,946 km2 (3,454 sq mi) |
| Population (2022)[1] | 445,325 |
| • Density | 50/km2 (130/sq mi) |
| Time zone | TRT (UTC+3) |
| Area code | 0246 |
| Website | www |
Isparta Province (Turkish: Isparta ili) is a province in southwestern Turkey. Its adjacent provinces are Afyon to the northwest, Burdur to the southwest, Antalya to the south, and Konya to the east. Its area is 8,946 km2,[2] and its population is 445,325 (2022),[1] up from 434,771 in 1990. The provincial capital is Isparta.
The province is well known for its apples, sour cherries, grapes, roses and rose products, and carpets. The best fertile lands are in the area named Uluborlu. The province is situated in the Göller Bölgesi (Lakes Area) of Turkey's Mediterranean Region and has many freshwater lakes.
Districts
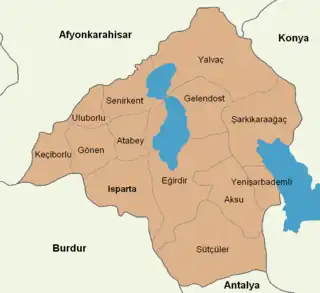
Isparta province is divided into 13 districts (capital district in bold):
Sites of interest

Kovada Lake and Kızıldağ National Parks, Isparta Gölcüğü, Çamyol and Kuyucak forest recreation areas, Eğirdir oak and Sütçüler forest conservation areas, Eğirdir, Uluborlu and Yalvaç castles, Antiochia in Pisidia and Apollonia antiquity cities, Ertokuş and Dündar Bey old theological schools (medrese), Isparta Hızır Bey, Kutlu Bey, Firdevs Bey, İplik, Eğirdir Hızır Bey, Barla Çaşnigir, Uluğbey Veli Baba mosques, Firdevs Bey Bazaar, Eğirdir Inn (caravansary), Ertokuş Hanı Inn, Baba Sultan Mousoleum, Isparta and Yalvaç Museums.
In 2020, the ancient 10 meters height rock mass of symbolic importance, which was in a village in Yalvaç district, was blown by treasure hunters.[3]
Geography
Isparta lies in the northernmost part of the Pamphylian basin, wedged between the continental Bey Dağları and Anatolian blocks.[4]: 134 This area is known as the Isparta Angle.[4]: 134 The Isparta Angle is a result of the Anatolian Plate's rotation from the early Paleocene to the early Pliocene.[5] This is a very seismically active area.[5]
Economy
As of 2012, there are 178,162 hectares of agricultural land in Isparta province, of which 28.8% (37,184 ha) is used for fruit growing.[6]: 5
Isparta province accounts for 23.4% of all apple production in Turkey as of 2012.[6]: 5 The majority of the province's apple production is done in three districts: Eğirdir, Gelendost, and Senirkent.[6]: 5 Together, these three districts account for 73.2% of the province's apple production.[6]: 5
Notable people
Gallery
 Köprülü Canyon in Sütçüler district
Köprülü Canyon in Sütçüler district Ancient Roman inscriptions in Yalvaç
Ancient Roman inscriptions in Yalvaç Antioch, Pisidia in Yalvaç district
Antioch, Pisidia in Yalvaç district Lake Eğirdir in Eğirdir district
Lake Eğirdir in Eğirdir district
See also
References
- 1 2 "Address-based population registration system (ADNKS) results dated 31 December 2022, Favorite Reports" (XLS). TÜİK. Retrieved 19 September 2023.
- ↑ "İl ve İlçe Yüz ölçümleri". General Directorate of Mapping. Retrieved 19 September 2023.
- ↑ Ancient symbolic rocks detonated by treasure hunters in Isparta
- 1 2 Poisson, André; Orszag-Sperber, Fabienne; Kosun, Erdal; Bassetti, Maria-Angella; Müller, Carla; Wernli, Roland; Rouchy, Jean-Marie (May 2011). "The Late Cenozoic evolution of the Aksu basin (Isparta Angle; SW Turkey). New insights". Bulletin de la Société Géologique de France. 182 (2): 133–48. doi:10.2113/gssgfbull.182.2.133. Retrieved 10 February 2023.
- 1 2 Şahin, Şakir; Abubakar, Ibrahim; Özçelik, Mehmet; Abdelwahed, Mohamed Farouk; Oksum, Erdinç (2019). "Neotectonic structures imaged by seismic velocity along the Isparta Angle". Arabian Journal of Geosciences. 12. Retrieved 10 February 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 Yilmaz, Hasan (2014). "Analysis in terms of apple producers of government supported crop insurance policies as a risk management tool in Turkey". Acta Scientiarium Polonorum, Hortorum Cultus. 13 (5): 3–12. Retrieved 10 February 2023.
External links
- (in Turkish) Isparta governor's official website
- (in Turkish) Isparta municipality's official website
- (in English) Isparta weather forecast information
- (in Turkish) Isparta city guide
- (Turkish) Isparta info website
37°57′24″N 30°57′39″E / 37.95667°N 30.96083°E