 |
| Part of a series on the |
| Military of ancient Rome |
|---|
|
|
The following is a list of Roman external wars and battles[1] fought by the ancient Roman Kingdom, Roman Republic and Roman Empire against external enemies, organized by date. For internal civil wars, revolts and rebellions, see List of Roman civil wars and revolts.
8th century BC
The city of Rome in 753 BC
- Wars with the Latins and the Sabines (for the Rape of the Sabine Women)
- Conquest of Cameria
- War with Fidenae and Veii
7th century BC
6th century BC
508 BC Siege by Etruscans (forces in blue) of Rome (forces in red).
- Roman-Sabine wars
- War with the Volsci
- War with Gabii
- War with the Rutuli
- Roman-Etruscan wars
- c. 509 BC – (legendary) Overthrow of the Roman monarchy[2] – According to the traditional account, Roman aristocrats expel Etruscan king Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, abolish the Roman Kingdom and establish the Roman Republic. Many details are generally accepted to be fictional, but scholars disagree about the degree to which the legendary narratives may or may not have a foundation in historical fact.
- 509 BC – Battle of Silva Arsia – The Romans defeated the forces of Tarquinii and Veii led by the deposed king Lucius Tarquinius Superbus. One of the Roman consuls, Lucius Junius Brutus, is killed in battle.
- c. 508 BC – War between Clusium and Aricia – According to Livy, King Lars Porsena of the Etruscan city of Clusium besieged Rome on behalf of Tarquinius Superbus. The outcome is debated, but tradition states that it was a Roman victory. The Clusians then besieged the Latin town of Aricia, which received support from the Latin League as well as the Greek colony of Cumae and destroyed the Clusian army. Livy doesn't say whether the Romans participated as allies of Aricia, but defeated and surviving Etruscan soldiers were given refuge and medical treatment in Rome. He claimed some who stayed behind were given homes in a neighbourhood later known as the 'Tuscan quarter'.[3]
- Pometian Revolt (503–502 BC)
- 502 BC – Battle of Pometia – The Romans put down the revolt of Pometia and Cora.
5th century BC
- First Latin War (498–411 BC)
- 497 BC – Battle of Lake Regillus – Aulus Postumius Albus Regillensis defeats Tarquinius Superbus.
- 495 BC – Battle of Aricia – consul Publius Servilius Priscus Structus defeats the Aurunci.
- Wars with the Volsci and the Aequi (495 - 446 BC)
- 493 BC – Battle of Corioli – the Volscian army is defeated thanks to the vigilance of Gnaeus Marcius.
- 482 BC – Battle of Antium – the Volsci defeat consul Lucius Aemilius Mamercus.
- 482 BC – Battle of Longula – consul Lucius Aemilius Mamercus defeats the Volsci the day after his defeat in the Battle of Antium.
- 458 BC – Battle of Mount Algidus – Cincinnatus defeats the Aequi
- 446 BC – Battle of Corbio – Titus Quinctius Capitolinus Barbatus leads Roman troops to defeat the Aequi and the Volsci.
- 480 BC – Battle of Veii (480 BC) – Consuls Marcus Fabius Vibulanus and Gnaeus Manlius Cincinnatus win a heavy battle against Veians and their Etruscan allies. Gnaeus Manlius Cincinnatus and former consul Quintus Fabius are slain.
- 477 BC –
- Battle of the Cremera – All the Fabii except Quintus Fabius Vibulanus are killed in battle with the Veii|Veians.
- Battle of the Temple of Hope – Consul Gaius Horatius Pulvillus fights indecisive battle with the Etruscans.
- Battle of Colline Gate (477 BC) – Consul Gaius Horatius Pulvillus has indecisive victory over the Etruscan civilization soon after the Battle of the Temple of Hope.
4th century BC
- Roman-Etruscan Wars
- 396 BC – Battle of Veii – Romans complete conquest of Veii
- 390 BCE – Battle of the Allia – Gauls defeat the Romans, then sack Rome.[2]
- First Samnite War (343–341 BC)
- 342 BC – Battle of Mount Gaurus – Roman general Marcus Valerius Corvus defeats the Samnites.
- 342 BC – Battle of Saticula – Roman general Aulus Cornelius Cossus Arvina barely escapes disaster and manages to defeat the Samnites.
- 341 BC – Battle of Suessula – Roman consul Marcus Valerius Corvus defeats the Samnites once more.
- Latin War (340–338 BC)
- 339 BC – Battle of Vesuvius – Romans under P. Decius Mus and T. Manlius Imperiosus Torquatus defeat the rebellious Latins.
- 338 BC – Battle of Trifanum – Roman general T. Manlius Imperiosus Torquatus decisively defeats the Latins.
- Second Samnite War (326–304 BC)
- 321 BC – Battle of the Caudine Forks – Romans under Spurius Postumius Albinus and T. Verturius Calvinus are defeated by the Samnites under Gaius Pontius.
- 316 BC – Battle of Lautulae – Romans are defeated by the Samnites.
- 305 BC – Battle of Bovianum – Roman consuls M. Fulvius and L. Postumius decisively defeat the Samnites.
- 310 BC – Battle of Lake Vadimo – Romans, led by dictator Lucius Papirius Cursor, defeat the Etruscans.
3rd century BC
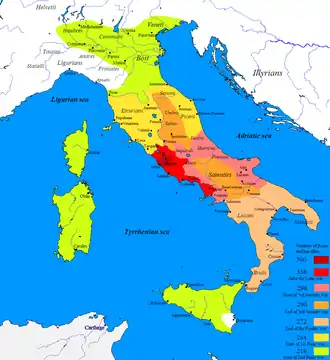
Roman expansion in Italy from 500 BC to 218 BC through the Latin War (light red), Samnite Wars (pink/orange), Pyrrhic War (beige), and First and Second Punic War (yellow and green). Cisalpine Gaul (238-146 BC) and Alpine valleys (16-7 BC) were later added. The Roman Republic in 500 BC is marked with dark red.
- Third Samnite War (298–290 BC)
- 298 BC – Battle of Camerinum – Samnites defeat the Romans under Lucius Cornelius Scipio Barbatus.
- 297 BC – Battle of Tifernum – Romans under Quintus Fabius Maximus and Lucius Cornelius Scipio Barbatus defeat the Samnite army led by Gellius Statius
- 295 BC – Battle of Sentinum – Romans under Fabius Rullianus and Publius Decimus Mus defeat the Samnites and their Etruscan and Gallic allies, forcing the Etruscans, Gauls, and Umbrians to make peace
- 293 BC – Battle of Aquilonia – Romans decisively defeat the Samnites.
- Wars with Gauls and Etruscans (285–282 BC)
- 284 BC – Battle of Arretium – A Roman army under Lucius Caecilius is destroyed by the Gauls.
- 283 BC – Battle of Lake Vadimo – A Roman army under P. Cornelius Dolabella defeats the Etruscans and Gauls.
- 282 BC – Battle of Populonia – Etruscan resistance to Roman domination of Italy is finally crushed.
- Pyrrhic War (280–272 BCE)[2]
- 280 BC – Battle of Heraclea – First engagement of Roman and Greek armies, the latter led by Pyrrhus of Epirus, who is victorious, but at great cost.
- 279 BC – Battle of Asculum – Pyrrhus again defeats the Romans but once again suffers significant casualties in the process.
- 275 BC – Battle of Beneventum – Inconclusive encounter between Pyrrhus and the Romans under Manius Curius.
- 265 BCE – Rome completed the occupation of the Italian Peninsula[2] (except Northern Italy)
- First Punic War (264–241 BCE)[2]
- 261 BC – Battle of Agrigentum – Carthaginian forces under Hannibal Gisco and Hanno are defeated by the Romans, who attain control of most of Sicily.
- 260 BC -
- Battle of the Lipari Islands – A Roman naval force is defeated by the Carthaginians.
- Battle of Mylae – A Roman naval force under C. Duillius defeats the Carthaginian fleet, giving Rome control of the western Mediterranean.
- 258 BC – Battle of Sulci – Minor Roman victory against the Carthaginian fleet near Sardinia.
- 257 BC – Battle of Tyndaris – Naval victory of Rome over Carthage in Sicilian waters.
- 256 BC –
- Battle of Cape Ecnomus – A Carthaginian fleet under Hamilcar and Hanno is defeated in an attempt to stop a Roman invasion of Africa by Marcus Atilius Regulus.
- Battle of Adys – Romans under Regulus defeat the Carthaginians in North Africa
- 255 BC – Battle of Tunis – Carthaginians under Xanthippus, a Greek mercenary, defeat the Romans under Regulus, who is captured.
- 251 BC – Battle of Panormus – Carthaginian forces under Hasdrubal are defeated by the Romans under L. Caecilius Metellus.
- 250 BC - Siege of Lilybaeum - Siege on the Carthaginian city of Lilybaeum by Roman army under Gaius Atilius Regulus Serranus and Lucius Manlius Vulso Longus. Carthaginian victory.
- 249 BC – Battle of Drepana – Carthage under Adherbal defeat the fleet of Roman admiral Publius Claudius Pulcher.
- 241 BC – Battle of the Aegates Islands – Roman sea victory over the Carthaginians.
- 238 BCE – Roman conquest of Sardinia[2]
- First Illyrian War (229–228 BCE)[2]
- Roman-Gallic wars (225–200 BC)
- 225 BC – Battle of Faesulae – Romans are defeated by the Gauls of Northern Italy.
- 225 BC – Battle of Telamon – Romans under Aemilius Papus and Gaius Atilius Regulus defeat the Gauls.
- 222 BC – Battle of Clastidium – Romans under Marcus Claudius Marcellus defeat the Gauls.
- 216 BC - Battle of Silva Litana - Roman army under Lucius Postumius Albinus is ambushed by the Boii and crushed under falling trees.
- Gaulish invasion of northern Italy (200–191 BCE)[2]
- 200 BC – Battle of Cremona – Roman forces defeat the Gauls of Cisalpine Gaul
- 220–219 BCE Second Illyrian War[2]
- Second Punic War (218–201 BCE)[2]
- 218 BC –
- Battle of Lilybaeum – First naval clash between the navies of Carthage and Rome during the Second Punic War; Roman victory.
- Battle of Cissa – Romans defeat Carthaginians near Tarraco and gain control of the territory north of the Ebro River.
- Battle of the Ticinus – Hannibal defeats the Romans under Publius Cornelius Scipio the elder in a cavalry fight.
- Battle of the Trebia – Hannibal defeats the Romans under Tiberius Sempronius Longus with the use of an ambush.
- 217 BC -
- Battle of Ebro River – In a surprise attack, Romans defeat and capture the Carthaginian fleet in Hispania.
- Battle of Lake Trasimene – In another ambush, Hannibal destroys the Roman army of Gaius Flaminius, who is killed.
- Battle of Ager Falernus – Avoiding destruction with deceit, Hannibal escapes Fabius' trap in this small skirmish.
- 216 BC –
- Battle of Cannae – Hannibal destroys the main Roman army of Lucius Aemilius Paulus and Publius Terentius Varro in what is considered one of the great masterpieces of the tactical art.
- Battle of Silva Litana - The Boii ambushed and destroyed a Roman army of 25,000 men
- First Battle of Nola – Roman general Marcus Claudius Marcellus holds off an attack by Hannibal.
- Battle of Cornus -
- Battle of Hibera -
- Battle of Cumae -
- 215 BC – Second Battle of Nola – Marcellus again repulses an attack by Hannibal.
- 214 BC – Third Battle of Nola – Marcellus fights an inconclusive battle with Hannibal.
- 212 BC –
- First Battle of Capua – Hannibal defeats the consuls Q. Fulvius Flaccus and Appius Claudius, but the Roman army escapes
- Battle of the Silarus – Hannibal destroys the army of the Roman praetor M. Centenius Penula.
- Battle of Herdonia – Hannibal destroys the Roman army of the praetor Gnaeus Fulvius.
- 211 BC –
- Battle of the Upper Baetis – Publius and Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio are killed in battle with the Carthaginians under Hasdrubal Barca
- Second Battle of Capua – Hannibal is not able to break the Roman siege of the city.
- 210 BC –
- Second Battle of Herdonia – Hannibal destroys the Roman army of Fulvius Centumalus, who is killed.
- Battle of Numistro – Hannibal defeats Marcellus once more
- 209 BC – Battle of Asculum – Hannibal once again defeats Marcellus, in an indecisive battle
- 208 BC – Battle of Baecula – Romans in Hispania (Iberia) under P. Cornelius Scipio the Younger defeat Hasdrubal Barca.
- 207 BC –
- Battle of Grumentum – Roman general Gaius Claudius Nero fights an indecisive battle with Hannibal.
- Battle of the Metaurus – Hasdrubal is defeated and killed by Nero's Roman army.
- Battle of Carmona – Romans under Publius Cornelius Scipio besiege the city of Carmona and take it from Hasdrubal Gisco
- 206 BC –
- Battle of Ilipa – Scipio again decisively defeats the remaining Carthaginian forces in Hispania.
- Battle of the Guadalquivir – Roman army under Gaius Lucius Marcius Séptimus defeats a Carthaginian army under Hannón at Guadalquivir.
- Battle of Carteia – Roman fleet under Gaius Laelius defeats a Carthaginian fleet under Adherbal
- 204 BC – Battle of Crotona – Hannibal fights a drawn battle against the Roman general Sempronius in Southern Italy.
- 203 BC – Battle of Bagbrades – Romans under Scipio defeat the Carthaginian army of Hasdrubal Gisco and Syphax. Hannibal is sent to return to Africa.
- 202 BC, 19 October – Battle of Zama – Scipio Africanus Major decisively defeats Hannibal in North Africa, ending the Second Punic War.
- 218 BC –
- First Macedonian War (214–205 BCE)[2]

Expansion of Rome by 200 BC
2nd century BC
- Second Macedonian War (200–197 BCE)[2]
- 198 BC – Battle of the Aous – Roman forces under Titus Quinctius Flamininus defeat the Macedonians under Philip V
- 197 BC – Battle of Cynoscephalae – Romans under Flamininus decisively defeats Philip in Thessaly
- Roman-Spartan War (195 BC)
- 195 BC – Battle of Gythium – With some Roman assistance, Philopoemen of the Achaean League defeats the Spartans under Nabis
- Battle of Placentia (194 BC) – Roman victory over the Boian Gauls
- Battle of Mutina (193 BC) – Roman victory over the Boii, decisively ending the Boian threat.
- Roman–Seleucid War (192 BCE – 188 BCE)[2] (not to be confused with the Syrian Wars between the Seleucid Empire and the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt)
- 191 BC – Battle of Thermopylae – Romans under Manius Acilius Glabrio defeat Antiochus III the Great and force him to evacuate Greece
- 190 BC –
- Battle of the Eurymedon – Roman forces under Lucius Aemilius Regillus defeat a Seleucid fleet commanded by Hannibal, fighting his last battle.
- Battle of Myonessus – Another Seleucid fleet is defeated by the Romans
- December, Battle of Magnesia – (near Smyrna) Romans under Lucius Cornelius Scipio and his brother Scipio Africanus Major defeat Antiochus III the Great in the decisive victory of the war.
- Aetolian War (191–189 BC)
- Galatian War (189 BC)
- Battle of Mount Olympus – Romans under Gnaeus Manlius Vulso allied with Attalus II of Pergamum deliver a crushing defeat to an army of Galatian Gauls
- Battle of Ancyra – Gnaeus Manlius Vulso and Attalus II defeat the Galatian Gauls again before Ancyra, in what was an almost identical repeat of the Battle of Mount Olympus.
- First Celtiberian War (181–179 BC)
- 181 BC – Battle of Manlian Pass – Romans under Fulvius Flaccus defeat an army of Celtiberians.
- Third Macedonian War (171–168 BCE)[2]
- 171 BC – Battle of Callicinus – Perseus of Macedon defeats a Roman army under Publius Licinius Crassus.
- 168 BC, 22 June – Battle of Pydna – Romans under Lucius Aemilius Paullus Macedonicus defeat and capture Macedonian King Perseus.
- Third Illyrian War (169–167 BC)
- Lusitanian War (155–139 BC)
- Numantine War or Second Celtiberian War (154–133 BC)
- 134 BC – Siege of Numantia – Roman forces under Scipio Aemilianus Africanus defeat and raze the Celtiberian city of Numantia.
- Fourth Macedonian War (150–148 BCE)[2]
- 148 BC – Second battle of Pydna – The forces of the Macedonian pretender Andriscus are defeated by the Romans under Quintus Caecilius Metellus Macedonicus.
- Third Punic War and destruction of Carthage (149–146 BCE)[2]
- 147 BC -
- Battle of the Port of Carthage - Roman forces under Lucius Hostilius Mancinus are defeated by the Carthaginians.
- Second Battle of Neferis - Roman forces under Scipio Aemilianus win a decisive victory against Carthage marking the turning point in the Third Punic War.
- 146 BC – Battle of Carthage ends: Scipio Africanus Minor captures and destroys Carthage.
- 147 BC -
- Achaean War (146 BC)
- 146 BC – Battle of Corinth – Romans under Lucius Mummius defeat the Achaean League forces of Kritolaus, who is killed. Corinth is destroyed and Greece comes under direct Roman rule.
- First Transalpine War (125–121 BCE)[4]
- Cimbrian War (113–101 BC)
- 112 BC - Battle of Noreia - Roman force under Gnaeus Papirius Carbo are defeated by the Cimbri
- 107 BC – Battle of Burdigala – Roman forces under Lucius Cassius Longinus are defeated by the Helvetii
- 105 BC, 6 October – Battle of Arausio – Cimbri inflict a major defeat on the Roman army of Gnaeus Mallius Maximus
- 102 BC - Battle of Aquae Sextiae - Romans under Gaius Marius defeat Teutons, with mass suicides among the captured women.
- 101 BC - Battle of Vercellae – Romans under Gaius Marius defeat the Cimbri, who are entirely annihilated.
- Jugurthine War (112–105 BC)
- 108 BC – Battle of the Muthul – Roman forces under Caecilius Metellus fight indecisively against the forces of Jugurtha of Numidia
1st century BC

Expansion of Rome from 200 BC (green) to 100 BC (orange).

Roman holdings in the East (red), clients (pink), and other states.
- First Mithridatic War (89–85 BCE)[5]
- 89 BC – Battle of Protopachium – Manius Aquillius loses against Archelaus, general of the Pontic army.
- 88 BC – Battle of Mount Scorobas – Manius Aquilius is defeated by Archelaus and captured.
- 88 BC – Siege of Rhodes – Mithridates fails to capture Rhodes, defended by the proconsul Lucius Cassius.
- 87–86 BC – Siege of Athens and Piraeus – Sulla takes Athens, which had sided with Mithridates.
- 86 BC – Battle of Tenedos – Lucullus defeats the Pontic general Neoptolemus in a sea battle.
- 86 BC – Battle of Chaeronea – Sulla defeats Archelaus.
- 85 BC – Battle of Orchomenus – Sulla again defeats Archelaus in the decisive battle of the war.
- Second Mithridatic War (83–81 BCE)[5]
- 82 BC – Battle of Halys – Roman general Lucius Licinius Murena fights Mithridates and Gordius after launching several raids, to which the Romans lose.
- Third Mithridatic War (73–63 BCE)[5]
- 73 BC – Battle of Cyzicus – Roman forces under Lucullus defeat the forces of Mithridates.
- 72 BC – Battle of Cabira or the Rhyndacus – Lucullus defeats the retreating forces of Mithridates, opening way to Pontus.
- 69 BC – Battle of Tigranocerta – Lucullus defeats the army of Tigranes II of Armenia, who was harbouring his father-in-law Mithridates.
- 68 BC – Battle of Artaxata – Lucullus again defeats Tigranes.
- 66 BC – Battle of the Lycus – Pompey decisively defeats Mithridates, effectively ending the War.
- 65 BC – Caucasian campaign of Pompey – Roman victory, vassalisation of the Kingdom of Iberia
- 63 BC – Siege of Jerusalem – Pompey captured Jerusalem
- Gallic Wars (58–51 BCE)[5]
- 58 BC –
- June – Battle of the Arar (Saône) – Caesar defeats the migrating Helvetii
- July – Battle of Bibracte – Caesar again defeats the Helvetians, this time decisively.
- September – Battle of Vosges – Caesar decisively defeats the forces of the Germanic chieftain Ariovistus near modern Belfort
- 57 BC –
- Battle of the Axona (Aisne) – Caesar defeats the forces of the Belgae under King Galba of Suessiones.
- Battle of the Sabis (Sambre) – Caesar defeats the Nervii.
- Battle of Octodurus (Martigny) – Servius Galba defeats the Seduni and Veragri.
- 56 BC –
- Battle of Morbihan – Caesar defeats the Veneti in a sea battle.
- 55 BC –
- Caesar's first invasion of Britain – Caesar crosses the English Channel, winning a battle against the Celtic Britons, but achieves little else.
- 54 BCE
- Caesar's second invasion of Britain[5] – Caesar returns to Britain, and defeats Cassivellaunus. He extracts tribute from the Brittonics, but fails to incorporate Britain as Roman territory.
- 52 BC – Battle of Alesia – Caesar defeats the Gallic rebel Vercingetorix, completing the Roman conquest of Gallia Comata.
- 58 BC –
- Roman–Parthian war of 54–53 BCE. This conflict resulted from the Parthian war of succession (57–54 BCE) between Mithridates IV and his brother Orodes II after killing their father, king Phraates III. The Roman invasion of Parthia, commencing in 54 BCE and ending catastrophically at the Battle of Carrhae in 53 BCE, was partially motivated by or justified as supporting Mithridates' claim to the Parthian throne.[6]
- 53 BCE – Battle of Carrhae – Roman army commanded by triumvir Crassus is disastrously defeated by the Parthians.[6]

The extent of the Roman Republic in 40 BC after Caesar's conquests.
- Roman–Parthian Wars – period c. 44–34 BC
- 44 BC - Julius Caesar's planned invasion of the Parthian Empire - Aborted due to the Assassination of Julius Caesar.
- 40–38 BC - Pompeian–Parthian invasion of 40 BC
- 36 BC - Antony's Atropatene campaign
- 34 BC - Antony's campaign against Armenia
- Roman-Kushite Wars (31–22 BC)
- 24–25 BC - Kushite Invasions of Roman Egypt - Kingdom of Kush from Meroë launched a series of attacks and incursions on south Roman Egypt, successful in taking Syene, Elephantine, and Philae, sacking them, slaving inhabitants and destroying the bronze statues of Caesar Augustus.
- 25–22 BC - Gaius Petronius' expeditions against Nubia - Roman forces managed to reach Qasr Ibrim and northern Nubia, capturing several cities, including Pselcis, Primis, Abuncis, Phthuris, Cambusis, Attenia, and Stadissias, then destroyed the city of Napata (kushite capital) and other cities in retaliation while taking captives. Kushites Kandake earns a favorable peace treaty and Romans established a new frontier at Hiere Sycaminos (Maharraqa), halting Rome’s southward expansion in Africa.
- Cantabrian Wars (29–19 BC)
- 25 BC - Battle of Vellica - Roman forces under Augustus against the Cantabri people, Roman victory.
- 25 BC - Siege of Aracillum - Roman forces under Gaius Antistius Vetus against the Cantabri people, Roman victory.
- Roman attempt to Conquest Arabia Felix (26–24 BC)[7]
- 25 BC Siege of Ma'rib - After Romans easily defeated the Arab army of 10,000 soldiers, conquered a few towns (including Mecca and Medina) and took on supplies from Nejran, Aelius Gallus besieged Ma'rib unsuccessfully for a week, before being forced to withdraw and unnable to secure Incense trade route in land (the Nabateans, apparent allies, wanted the Romans to fail otherwise they would loose their monopoly over the spice trade). Rome is unable to conquest Sabaean kingdom of Ancient Yemen or coercing the incense states (Himyarite Arab kingdoms) of the Arabian Peninsula to become Roman client states.
- 25 BC Siege of Eudaemon - The supporting Roman fleet, after crossing the Gulf of Aqaba, occupied and sacked the port of Aden, securing the Roman merchant route to India in Red Sea. However, Roman interests wouldn't be served by a second expedition, becoming clear that certain fringes of the empire (like Nubia or Arabia) could not be won except at greater costs, being careful of further military adventures.
- Roman expeditions to Lake Chad and the Niger River (19 BC–90 AD): Roman expeditions (two in the western Sahara, two in the central Sahara, and one in the area of Lake Chad) to subdue warring tribes in the area (like the warlike nomadic tribe of the Garamantes who lived in the current region of Fezzan) or to achieve the elimination of taxes on the nomads of the Sahara and plan possible routes of conquest to Sub-Saharan Africa, or at least control the Trans-Saharan caravan routes and penetrate into the kingdoms of the pygmies.
 Sub-Saharan Roman expeditions-explorations
Sub-Saharan Roman expeditions-explorations - Roman campaigns in Germania (12 BC – AD 16) (16–11 BC period)
- Clades Lolliana (16 BC) – The troops of Consul Marcus Lollius are defeated by West Germanic warriors in Gaul.
- Battle of Arbalo (11 BC) - Romans under Nero Claudius Drusus defeat the Germans
- Battle of the Lupia River (11 BC) – Roman forces under Augustus's stepson Drusus win a victory in Germany.
1st century

The Roman Empire under Augustus: The Republic in 31 BC (yellow) and Augustus's conquests (shades of green). Client states are in pink.
- Roman campaigns in Germania (12 BC – AD 16) (9–16 AD period) – Campaigns in Germania (modern day Germany and the Low Countries) against various Germanic units and coalitions with the objective of establish the border of the empire on the Elbe river.
- Battle of the Teutoburg Forest (9) – Cherusci-born Roman commander Arminius defects to a coalition Germanic rebel groups, who jointly ambush and annihilate three Roman legions under Publius Quinctilius Varus, prompting retaliation campaigns by the Romans. Germania Antiqua roman province is abandoned with all their settlements such as the Waldgirmes Forum .
- Battle at Pontes Longi (15) – Indecisive battle between a Roman army under Aulus Caecina Severus and Germanic troops led by Arminius.
- Battle of the Weser River (16) – Legions under Germanicus defeat Germanic troops of Arminius.
- Battle of the Angrivarian Wall (16) - Legions under Germanicus defeat the Germanic troops of Arminius, ending the campaigns.
- Roman conquest of Britain (43–96)
 British Campaigns of Agricola, 78 – 84
British Campaigns of Agricola, 78 – 84- 43 – Battle of the Medway – Claudius and general Aulus Plautius defeat a confederation of British Celtic tribes. Roman invasion of Britain begins
- 50 – Battle of Caer Caradoc – British chieftain Caractacus is defeated and captured by the Romans under Ostorius Scapula.
- 60–61 – Boudican revolt – Roman rule secured in Britain and submission of Celtic Britons (Iceni and Trinovantes lost independence).
- 60/61–77 Roman conquest of Anglesey – Anglesey in North West is left under Roman rule, being completed the conquest of Wales and northern England.
- 81 – Gnaeus Julius Agricola's planned invasion of Hibernia – Aborted Roman attempt of conquest Ireland due to other priorities.[8]
- 83/84 – Battle of Mons Graupius. Romans under Gnaeus Julius Agricola defeat the Caledonians and temporally expanded Roman rule north into Caledonia (modern Scotland), stablishing the northernmost Roman forts, like Cawdor, Tarradale and Portmahomack. Also, the fleet sailed north and made the first known circumnavigation of Britain, whereupon it was definitely discovered to be an island. It was proclaimed that Agricola had finally subdued all the tribes of Britain,[9] however, the costs of a drawn-out war outweighed any economic or political benefit and it was deemed more profitable to leave the Caledonians to themselves and dismantled roman fortifications after Southern Uplands.[10]
- Roman–Parthian War of 58–63 or War of the Armenian Succession[11]
- 58 – Sack of Artaxata by Gnaeus Domitius Corbulo.
- 59 – Capture of Tigranocerta by Corbulo.
- 62 – Battle of Rhandeia – Romans under Lucius Caesennius Paetus are defeated by a Parthian-Armenian army under King Tiridates of Parthia.
- Nero's exploration of the Nile (62–67) – Roman expeditions to Equatorial Africa with the objective to reach the origin of Nile river and recopile information for a possible Roman planned conquest of Ethiopia.
- Domitian's campaign against the Chatti across the Rhine (83)[5]
- Domitian's Dacian War (86–88)
- 87 – Dacian King Decebalus crushes the Roman army at Tapae (today Transylvania, Romania), Legio V Alaudae and general Cornelius Fuscus perish in battle.
- 88 – the Romans return and obtain a victory in the same battleground
2nd century
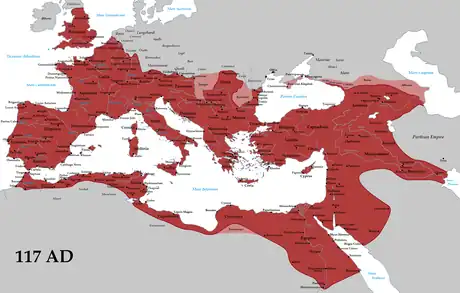
The extent of the Roman Empire under Trajan (117)
Empire
- First Dacian War (101–102)
- 101 – Second Battle of Tapae – Trajan defeated Decebalus, with heavy losses.
- 102 – Battle of Adamclisi - Roman forces led by Trajan annihilated a mixed Dacian-Roxolano-Sarmatae army, with heavy casualties on the Roman side.
- Second Dacian War (105–106)
- 106 – Battle of Sarmisegetusa – A Roman army led by Trajan conquered and destroyed the Dacian capital. Part of Dacia was annexed to the Roman Empire.
- Roman conquest of the Nabataeans (106) – The Third Cyrenaica legion moved north from Egypt into Arabia Petraea, while the Sixth Ferrata legion, a Syrian garrison unit, moved south to occupy Bostra.
- Trajan's Parthian campaign[13] (115–117) – Trajan invaded Parthia (planning its annexation) and occupied Ctesiphon while managed control of western Persia by a client ruler (Parthamaspates), but died. The Roman army withdrew, immediately abandoning the newly annexed provinces of Assyria, Mesopotamia and Armenia.
- Roman invasion of Southern Scotland (139-143) – Quintus Lollius Urbicus, by orders of Antoninus Pius, was sent to effect the reconquest of Lowland Scotland, winning some significant victories and building the Antonine Wall.
- Roman–Parthian War of 161–166 – Vologases IV invades Armenia, but is pushed back and Ctesiphon is sacked.
- Marcomannic Wars (166–180) – Roman Empire tried to expand in central Europe and stablish proposed roman province of Marcomannia (parts of the modern states and Slovakia and the Czech Republic) and Sarmatia (on Great Hungarian Plain).
- 170 – Battle of Carnuntum – Marcomannic King Ballomar defeats the Roman Army and invade Italy.
- 178-179 – Praetorian Prefect Teratenius Paternus defeats the Quadi.
- 179 or 180 – Battle of Laugaricio – Marcus Valerius Maximianus defeats the Quadi in Slovakia.
- 198 – Battle of Ctesiphon – Septimus Severus invaded, sacked Ctesiphon, and reinstated the province of Mesopotamia in northern Mesopotamia.
3rd century
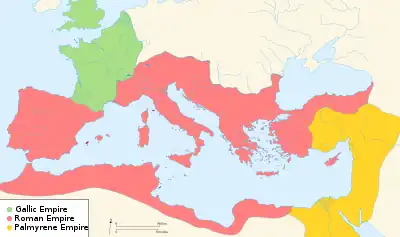
The Empires of Gaul (green), Rome (red), and Palmyra (yellow) in 271.
- Roman invasion of Caledonia (208-210) - Roman forces led by Septimus Severus invade Caledonia because massive increase in raids and attacks on Roman Britain, but romans are forced to withdraw to Hadrian's Wall after the emperor became ill and died at Eboracum (York) on 4 February 211, suffering heavy casualties. Romans never campaigned deep into Caledonia again.
- Parthian war of Caracalla (216–217)
- 217 – Battle of Nisibis – Bloody stalemate between the Parthians and the Roman army under Emperor Macrinus.
- Early Roman–Sasanian battles
- 231–232 - War between the Sassanids under Ardashir I and Severus Alexander; resulted in humiliating Roman defeat and withdrawal.
- 243 – Battle of Resaena – Roman forces under Gordian III defeat the Persians under Shapur I.
- 260 – Battle of Edessa – Emperor Shapur I of Persia defeats and captures the Roman Emperor Valerian
- 296 or 297 – Battle of Carrhae – Romans under the Caesar Galerius are defeated by the Persians under Narseh.
- 298 – Battle of Satala – Galerius secures a decisive victory against Narseh, following a peace treaty.
- Gothic and Alemannic wars
- 235 – Battle at the Harzhorn - Roman army under Emperor Maximinus Thrax defeats a German army while withdrawing back to Roman territory.
- 250 – Battle of Philippopolis – King Cniva of the Goths defeats a Roman army.
- 251, Summer – Battle of Abrittus – Goths defeat and kill the Roman Emperors Decius and Herennius Etruscus
- 259 – Battle of Mediolanum – Emperor Gallienus decisively defeats the Alemanni that invaded Italy
- 268 – Battle of Naissus – Emperor Gallienus and his generals Claudius and Aurelian decisively defeat the Goths.
- 268 or 269 – Battle of Lake Benacus – Romans under Emperor Claudius II defeat the Alemanni
- 271 –
- Battle of Placentia – Emperor Aurelian is defeated by the Alemanni forces invading Italy
- Battle of Fano – Aurelian defeats the Alamanni, who begin to retreat from Italy
- Battle of Pavia – Aurelian destroys the retreating Alemanni army.
- 298 –
- Battle of Lingones – Caesar Constantius Chlorus defeats the Alemanni
- Battle of Vindonissa – Constantius again defeats the Alamanni
4th century

The Roman Empire in 337, showing the Empire under Constantine (shaded purple) and other Roman dependencies (light purple).
- Perso-Roman wars of 337–361
- 344 – Battle of Singara – Emperor Constantius II fights an indecisive battle against King Shapur II of Persia
- 359 – Siege of Amida – Sassanids capture Amida from Romans
- Julian's Persian expedition (March–July 363)
- 363, 29 May – Battle of Ctesiphon – Emperor Julian defeats Shapur II of Persia outside the walls of the Persian capital, but is unable to take the city.
- 363, June – Battle of Samarra (363) – Julian fights the Sassanids and is subsequently killed in battle. Though indecisive, the battle leads to massive losses for the Roman Empire through a forced peace treaty.
- Wars with Alemanni (356–378)
- 356 – Battle of Reims – Caesar Julian is defeated by the Alamanni
- 357 – Battle of Strasbourg – Julian expels the Alamanni from the Rhineland
- 368 – Battle of Solicinium – Romans under Emperor Valentinian I defeat yet another Alamanni incursion.
- 378 –
- May – Battle of Argentovaria – Western Emperor Gratianus is victorious over the Alamanni, yet again.
- Gothic War (376–382)
- 377 – Battle of the Willows – Roman troops fight an inconclusive battle against the Goths
- Summer -Battle of Dibaltum –Goths, Alans and Huns defeat Romans.
- 378 –
- 9 August – Battle of Adrianople – Thervings under Fritigern defeat and kill the Eastern Emperor Valens[14]
- 380 – Battle of Thessalonica – The new Eastern Emperor, Theodosius I, is also defeated by the Thervings under Fritigern.
- 377 – Battle of the Willows – Roman troops fight an inconclusive battle against the Goths
- 391 – Battle somewhere in Thrace: a band of Goths led Alaric I is defeated by Romans under Stilicho[15][16]
- Stilicho's Pictish War – 398(?)
5th century
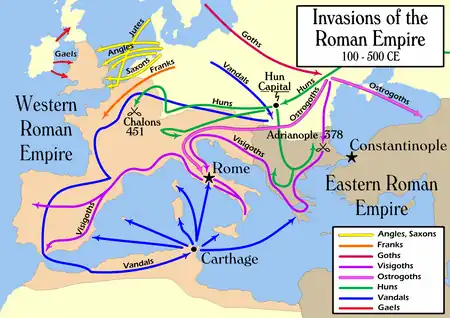
Map showing the paths of invasion by various groups into Eastern and Western Roman territory

Reconstruction of the 407–409 sack of Gaul, based on Peter Heather (2005)
The 5th century involves the final fall of the Western Roman Empire to Goths, Vandals, Alans, Huns, Franks and other peoples.
- Gothic War (c. 401–403), a Visigothic invasion of Italy led by Alaric I[16]
- 402
- Siege of Asti (402) – Visigoths besieged Western Emperor Honorius in Asti until March, when Stilicho sent reinforcements .
- 6 April – Battle of Pollentia – Stilicho defeated the Visigoths under Alaric.
- June – Battle of Verona – Stilicho defeated Alaric, who withdrew from Italy and settled in Illyricum.[16]
- 402
- War of Radagaisus: Invasion of Italy by a large groups of Goths, Vandals and Alans, gathered and led by Radagaisus (c. 405–410)
- c. c. 405/6: Siege of Florence - Stilicho defended the city from the Goths of king Radagaisus, but Florence was nearly destroyed.
- 406: Battle of Faesulae - Stilicho defeated the Visigoths and Vandals under Radagaisus.
- 406, 31 December – traditional date of the Crossing of the Rhine: a mixed group of barbarians, which purportedly included Vandals, Alans and Suebi, crossed into northern Gaul.[13]
- Another Visigothic invasion of Italy led by Alaric I (c. 408–410)[16][17]
- 409: Battle of Ostia – Visigoths under Alaric I defeated the Romans.
- 410, 24 August – Sack of Rome – Visigoths under Alaric sacked Rome.[17][16]
- 413 – Siege of Massilia – Visigoths under Ataulf were defeated by Romans under Bonifacius while trying to besiege the Roman city. They made peace with Rome soon after.
- 419 – Battle of the Nervasos Mountains – Western Romans and Suebi defeat Vandals and Alans.
- Roman–Sasanian War of 421–422 - The Eastern Roman Emperor Theodosius II declared war against the Persians and obtained some victories, but in the end, the two powers agreed to sign a peace on the status quo ante.
- 422 – Battle of Tarraco – The Vandal king Gunderic defeat the Western Romans, making the Vandals the undisputed masters of Hispania.
- 425 – Siege of Arles -The Roman general Aëtius defeats the Visigoths under Theodoric I.
- 431 - Siege of Hippo Regius – Vandals under Genseric establish a foothold in Africa, strategically defeating Rome. Saint Augustine dies during the siege.
- 432 – Battle of Ravenna – Bonifacius defeats rival Roman general Flavius Aetius, but is mortally wounded in the process.
- c. 445–450 – Battle of Vicus Helena – Romans under Aetius defeat Franks.
- Roman–Hunnic battles (447–452)
- 447 – Battle of the Utus – The Eastern Romans fought an indecisive battle with Huns led by Attila.
- 450 – Huns led by Attila invaded Gaul.[17]
- 451, 20 June – Battle of the Catalaunian Plains – The Romans with Flavius Aetius and the Visigoths with Theodoric, defend against Attila, ruler of the Hunnic Empire.
- 452 – Sack of Padua – Attila and his forces successfully capture and sack Padua.
- 452 – Siege of Mediolanum – Attila and his forces capture Milan and destroy the city.
- 452, 18 July –Sack of Aquileia – Aquileia is razed by the forces of Attila.
- 455
- Sack of Rome by Geiseric, King of the Vandals[17]
- Battle of Aylesford – Romano-Britons (under Vortimer) and Anglo-Saxons battle in Kent, victory is unclear.
- 457
- Battle of Garigliano (457) – The Western Roman Emperor Majorian surprised a Vandal-Berber raiding party which was returning with loot from Campania.
- Battle of Campi Cannini – Western Roman Emperor Majorian defeated an Alemanni invasion of Italy.
- Gothic War (457-458)
- 458
- Battle of Toulouse (458) – The Western Roman Emperor Majorian defeated the Visigoths.
- Battle of Arelate – The Western Roman Emperor Majorian, with the support of Aegidius and Nepotianus, defeated the Visigoths at Arlate. With a treaty, the Visigothic returned all territory in Hispania to the Romans.
- 461 – Battle of Cartagena – A Vandal fleet surprised and destroyed the Roman fleet.
- 463 – Battle of Orleans – Gallo-Roman and Salian Frank forces under the command of Aegidius defeated a force of Visigoths at Orleans.
- 464 – Battle of Bergamo – Romans under General Ricimer defeated Alan invasion of Italy and killed their king.
- 468 – Battle of Cap Bon - Failure of the invasion of the kingdom of the Vandals by the Western and Eastern Roman Empires.
- 469 – Battle of Déols - Visigoths defeated Bretons and Gallo-Romans under Riothamus.
- 471 – Battle of Arles - Visigothic king Euric defeated the Roman general Anthemiolus, captured Arles and much of southern Gaul
- 472 – Siege of Rome - Ricimer, having fallen out with his choice for Roman Emperor, allied with the Burgundians and Germans under Odoacer, defeated and killed the Western Roman Emperor Anthemius.
- 475 – Battle of Ravenna – Orestes deposes Julius Nepos and installs his son, Romulus Augustulus as emperor.
- 476
- Battle of Pavia – Odoacer captures and executes Orestes.
- Battle of Ravenna – The Germanic foederati led by Odoacer decisively defeated the Western Roman Empire and deposed Emperor Romulus Augustulus. Western Roman Empire dissolved. Odoacer declared himself King of Italy.
- 486 – Battle of Soissons – Clovis I defeated Syagrius, last Roman commander in Gaul, and annexed the Western Roman rump state known as the Kingdom of Soissons into Francia.
6th century and beyond
See also
References
- ↑ Jones 2013, p. 1–4.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Jones 2013, p. 1.
- ↑ Livy, Ab urbe condita, 2.14
- ↑ Webster, Jane (1996). "Ethnographic barbarity: colonial discourse and 'Celtic warrior societies'.". In Cooper, Nick (ed.). Roman Imperialism: Post-Colonial Perspectives (PDF). School of Archaeological Studies, University of Leicester. pp. 117–118. Retrieved 5 April 2023.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Jones 2013, p. 2.
- 1 2 De Ruggiero, Paolo (2014). Mark Antony: A Plain Blunt Man. Barnsley: Pen and Sword. pp. 44–45. ISBN 9781473834569. Retrieved 19 July 2019.
- ↑ "Aelius Gallus Attempts the Conquest of Arabia—and Reaches the Limits of Roman Power | Encyclopedia.com". www.encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 2023-05-30.
- ↑ Di Martino, Vittorio (2006). Roman Ireland. Cork: Collins. ISBN 978-1-905172-19-1
- ↑ Tacitus claims that Orkney was "discovered and subdued", but Thomson (2008) pp. 4–5 is as sceptical about Tacitus's claims on behalf of Agricola as he is about Claudius's earlier subjugation of Orkney (see above).
- ↑ Moffat (2005) p. 245.
- ↑ Lacey, James (2016). Great Strategic Rivalries: From the Classical World to the Cold War. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 120–121. ISBN 9780190620462. Retrieved 23 December 2016.
- ↑ Bennett, J. Trajan: Optimus Princeps. 1997. Fig. 1
- 1 2 Jones 2013, p. 3.
- ↑ "Valens, Flavius". Encarta Encyclopedie Winkler Prins (in Dutch). Microsoft Corporation/Het Spectrum. 2002.
- ↑ Boin 2020, p. 52–53.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Alarik I". Encarta Encyclopedie Winkler Prins (in Dutch). Microsoft Corporation/Het Spectrum. 2002.
- 1 2 3 4 Jones 2013, p. 4.
Sources
- Boin, Douglas (2020). Alaric the Goth: An Outsider's History of the Fall of Rome. New York: W.W. Norton & Co. ISBN 978-0-39363-569-0.
- Jones, Jim (2013). "Roman History Timeline" (PDF). West Chester University of Pennsylvania. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 April 2023. Retrieved 2 April 2023.
External links
- Milites. A Visual Analytics tool on Roman battles.
- Elton, Hugh and Christos Nüssli, "Imperial Battle Map Index". An Online Encyclopedia of Roman Emperors.
- "Roman Battles" map, platial.com
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.