Monument in 2021 (view from the southwest) | |
 | |
| 37°58′30.2″N 23°43′20.5″E / 37.975056°N 23.722361°E | |
| Length | more than 16 m |
|---|---|
| Dedicated to | Eponymous Heroes |
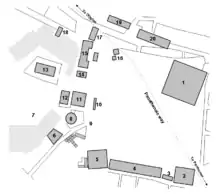
The Monument of the Eponymous Heroes, located in the Ancient Agora of Athens (No. 10 on the map on the right), Greece and adjacently situated near the Metroon (old Bouleuterion, No. 11), was a marble podium that bore the bronze statues of the heroes representing the phylai (tribes) of Athens. The monument was surrounded by a wooden fence on stone posts. All that remains on the modern agora are pieces of a long (over 16 m (52 ft)) statue base with the space for ten statues and two tripods at the ends[1] with partially restored fence. Large size and prominent position make the monument into a landmark for the agora visitors.[2]
Bulletin board
Being an important information center for the ancient Athenians, the place was used as an ancient bulletin board where proposed legislation, decrees and announcements were posted on wooden tablets.[1][3][4]
Evolution
The remaining base is from the mid-4th century BC.[5] The earliest known mention of the monument is almost a century older: Aristophanes in 424 BC refers to it as "place where lawsuits are displayed".[1] No remains of an earlier monument were found at the current spot.[5] A smaller, 9.7 m (32 ft) long, base was located about 50 m (55 yd) to the south under the Middle Stoa. While it can be argued that this was the site of the earlier monument,[6] the identification is uncertain.[1]
Cleisthenes had set up a new system of ten (instead of four) phylai around 508–507 B.C.[7] (see Deme). The version of monument of mid-4th century BC (so called Period I) therefore included ten statues, one for each hero designating a phyle.[1]
The late 4th century BC saw two statues added, representing Macedonian kings Antigonus I and Demetrius I Poliorcetes (two new tribes were added at this so-called Period II). Ptolemy III was added to the group some 80 years later (Period III). The Period II addition was reversed after the next 20 years, when Philip V of Macedon besieged Athens during the Second Macedonian War, followed by adding a sculpture of Attalos I[1] (Period IV). Finally, in the 2nd century A.D., a statue of Hadrian was installed[1] (Period V).
Identification
The archeologists unearthed the unusual structure during the excavation of 1931;[2] this was one of the first major finds.[8] While not immediately identified (for tens of years the researchers referred to it as "Periphragma" or "Fenced Peribolos",[2] the original report simply stated that this was not the Stoa of the Herms[8]), the importance of the monument was clear due to its large size (the length of the fenced area was over 21 m (23 yd) long at the maximum, apparently during Period V[9]), location next to Bouleuterion, and openness to the center of agora.[2]
It appears that there was no quick breakthrough in the monument identification. Instead, as the archeologists understood the layout of agora better and better, the fact that "peribolos" represent the ruins of the Monument of the Eponymous Heroes became "increasingly clear".[9] Several post-Second World War excavation maps routinely marked the location as such since at least 1947.[2] T. Leslie Shear, Jr. attributes the first detailed explanation of the identification to the 1949 article[10] by Eugene Vanderpool, where the author, among other considerations, had dealt with the remark by Pausanias that the monument was located above the Tholos (No. 8 on the map). This remark, if interpreted literally, would have placed the Eponymous Heroes out of the main area of the agora. Vanderpool suggested to read Ancient Greek: άνωτέρω (anōterō), 'above' as Ancient Greek: άπωτέρω (apōterō), 'further away'. Vanderpool also explains the words of unknown commenter of Aristophanes' Peace that the monument was close to Prytaneion (Pausanius places the latter on the northern slope of the Acropolis). Vanderpool agreed with earlier commenters that there was a confusion between Prytaneion and Prytanikon, a section of Tholos.[11][8]
Exploration
The monument was the first major discovery of the first archeological season in 1931, with a detailed study of foundation of the still unidentified structure published in 1933 by Richard Stillwell.[8] Few pieces of stone posts and capping blocks were used to reconstruct the fence panels on the western side in 1951. An additional major probing of the fill in the area dates back to 1967.[2]
Description

The monument was placed almost parallel to the porch of the Bouleuterion, on the east side a major road that formed the eastern boundary of the market area of agora. The sill of the peribolos, quite well preserved with only few pieces missing, is a rectangle 18.40 m × 3.56 m (60.4 ft × 11.7 ft) in size formed by a course of narrow blocks made of hard light-gray poros stone.[12] The overall construction exhibits a "surprising" lack of precision and regularity, with the peribolos being 12 cm (4.7 in) wider at the north end than at the south one.[12] Only the north end of the sill has any semblance of a foundation, while the rest was placed onto a shallow layer of earth spread across the rough surface packed by the previous intensive traffic. There are no clamps holding the sill blocks together, so the blocks have shifted exposing significant gaps (up to 5 cm (2.0 in)).[13] The ground under the monument slopes down to the north, so the builders tried to set the blocks to compensate for the slope by exposing just 18 cm (7.1 in) of the sill blocks at the south end (as indicated by better dressing of the stone) versus 30 cm (12 in) at the north end. But the sill course is still 7 cm (2.8 in) lower at the north end.[14]
Some of the periodic cutouts in the blocks contain remnants of the leaded-in marble fence posts.[12]
Each sill block has cutouts at either end for a pair of metal dowels that were used in the original (Period I) design of the fence, with posts spaced at approximately 1.27 m at the north end and 1.02 m at the south end. (Fifteen posts on each long side, and four posts on each short side.) A single post through these dowels joined adjacent sill blocks; the builders considered other clamps were unnecessary.[15] The fence itself consisted of three wooden rails inserted into the slots on the posts.[16]
Very little is left from the superstructure of the monument, though enough to permit a reconstruction:[17]
- five blocks of euthynteria at the north end;
- traces of foundation, again at the north end;
- two small fragments of the marble steps of the crepidoma;
- two pedestal caps, one for the statue and one for the bronze tripod.
Periods II and III, with their additions of statues, required a redesign of the pedestal. According to the reconstruction, the builders tried to alter the fence as little as possible while extending the pedestal. They went so far as to eliminate the marble steps on the narrow ends of the crepidoma.[18] Period IV saw a fairly haphazard repair of the peribolos.[19] Gates were installed to provide the officials with access to the pedestal for posting the notices.[20]
In the Period V, the peribolos was extended to the south by approximately 2.75 m (9.0 ft), as evidenced by the surviving foundations. At the same time, the fence construction on the eastern (apparently, more important) side, previously made of poros, was replaced by one of Pentelic marble, taller, but of "rather poor quality." The new fence terminated against the faces of the orthostates at the ends of the pedestal.[21]
Heroes and phylai
After the Cleisthenes reform, each Athenian phyle was no longer an actual kinship group,[22] but more of an administrative subdivision, symbolically designated by an eponymous "founder", originally a legendary hero, later an honorary figure.[8] Ancient Athenian documents listed the phylai in a particular order; historians frequently use Roman numerals to designate them.
| Order | Hero | Phyle[23] | Hero's identity |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Erechtheus | Erechtheis | Mythological king, founder of Athens |
| II | Aegeus | Aegeis | King of Athens, father of Theseus |
| III | Pandion | Pandionis | One of the two legendary kings of Athens, Pandion I or Pandion II |
| IV | Leos | Leontis | Son of Orpheus |
| V | Acamas | Acamantis | Son of Theseus |
| VI | Oeneus | Oineis | Calydonian king |
| VII | Cecrops | Kekropis | King of Athens |
| VIII | Hippothoon | Hippothontis | Mythical king of Eleusis |
| IX | Aias | Aiantis | Mythological hero that fought in Trojan War |
| X | Antiochus | Antiochis | Son of Heracles |
| XI | Antigonus | Antigonis | |
| XII | Demetrius | Demetrias | |
| XIII | Ptolemy | Ptolemais | |
| XIV | Attalus | Attalis | |
| XV | Hadrian | Adrianis |
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Mattusch 1996, p. 50.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Shear 1970, p. 146.
- ↑ Roisman, J.; Yardley, J.C. (2011). Ancient Greece from Homer to Alexander: The Evidence. Blackwell Sourcebooks in Ancient History. Wiley. p. 478. ISBN 978-1-118-30095-4. Retrieved 2023-09-17.
- ↑ Glowacki 2021, pp. 257–259.
- 1 2 Mattusch 1996, p. 52.
- ↑ Shear 1970, p. 205.
- ↑ phyle at the Encyclopædia Britannica
- 1 2 3 4 5 Vanderpool 1949, p. 129.
- 1 2 Vanderpool 1949, p. 132.
- ↑ Vanderpool 1949.
- ↑ Shear 1970, p. 147.
- 1 2 3 Shear 1970, p. 148.
- ↑ Shear 1970, pp. 149–150.
- ↑ Shear 1970, pp. 148–149.
- ↑ Shear 1970, pp. 150–151.
- ↑ Shear 1970, p. 158.
- ↑ Shear 1970, pp. 161–165.
- ↑ Shear 1970, pp. 171–176.
- ↑ Shear 1970, p. 176.
- ↑ Shear 1970, p. 180.
- ↑ Shear 1970, pp. 181–184.
- ↑ Gmirkin 2016, Kinship groups.
- ↑ Seyffert, Nettleship & Sandys 1895, p. 488.
Sources
- Shear, T. Leslie Jr. (1970). "The Monument of the Eponymous Heroes in the Athenian Agora" (PDF). Hesperia. 39 (3): 145–222. doi:10.2307/147592. JSTOR 147592.
- Mattusch, C.C. (1996). Classical Bronzes: The Art and Craft of Greek and Roman Statuary. Cornell University Press. ISBN 978-0-8014-3182-1. Retrieved 2023-09-16.
- Seyffert, O.; Nettleship, H.; Sandys, J.E. (1895). "Phyle". A Dictionary of Classical Antiquities: Mythology, Religion, Literature & Art. W. Glaisher, Limited. pp. 487–488. Retrieved 2023-09-17.
- Gmirkin, R.E. (2016). "Athenian and Pentateuchal Legal Institutions". Plato and the Creation of the Hebrew Bible. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-134-85458-5. Retrieved 2023-09-17.
- Glowacki, Kevin (2021-08-13). "The Athenian Agora". Meet the Philosophers of Ancient Greece. London: Routledge. pp. 257–259. doi:10.4324/9781315249223-65. ISBN 978-1-315-24922-3. S2CID 238682945.
- Vanderpool, Eugene (1949). "The Route of Pausanias in the Athenian Agora". Hesperia. American School of Classical Studies at Athens (ASCSA). 18 (1): 128–137. doi:10.2307/147000. ISSN 0018-098X. JSTOR 147000.