| Old Xiang | |
|---|---|
| Lou-Shao | |
| Native to | People's Republic of China |
| Region | Hunan |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | None (mis) |
| ISO 639-6 | louo |
| Glottolog | luos1238 |
| Linguasphere | 79-AAA-eab |
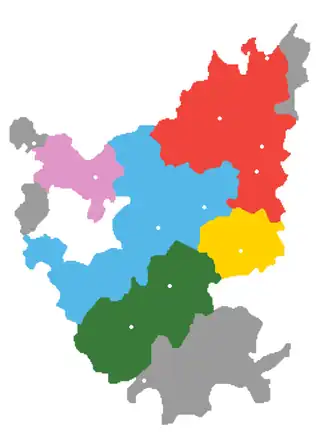 Old Xiang is in blue. It is in contact with New Xiang (red), Ji-Xu Xiang (pink), Southwestern Mandarin, Gan, and Yong-Quan Xiang (dark green, south). | |
Old Xiang, also known as Lou-Shao (娄邵片 / 婁邵片), is a conservative Xiang Chinese language. It is spoken in the central areas of Hunan where it has been to some extent isolated from the neighboring Chinese languages, Southwestern Mandarin and Gan languages, and it retains the voiced plosives of Middle Chinese, which are otherwise only preserved in Wu languages like Shanghainese. See Shuangfeng dialect for details. Mao Zedong was a speaker of Old Xiang with his native Shaoshan dialect.
Dialects and regions
The Shuangfeng dialect is representative.
| Subdialect | Main Counties | |
|---|---|---|
| Xiang-Shuang | Xiangtan, Shuangfeng, Shaoshan, Urban Loudi, Anhua*, Hengshan* | |
| Lian-Mei | Lianyuan, Lengshuijiang*, Anhua, Ningxiang* | |
| Xinhua | Xinhua, Lengshuijiang | |
| Shao-Wu | Urban Shaoyang, Wugang, Shaodong, Shaoyang County, Xinshao, Longhui*, Xinning, Chengbu, Dongkou* | |
| Sui-Hui | Suining*, Huitong | |
| *Small part of this territory is Hunanese-speaking. | ||
Laba Miao (喇叭苗话) is an Old Xiang dialect spoken by the Laba Miao people of western Guizhou. In Guizhou, it is spoken in Qinglong County 晴隆县 (including in Changliu Township 长流乡), Pu'an County 普安县, Liuzhi County 六枝县, Shuicheng County, 水城县, and Panzhou 盘州.[1]
Matanghua (麻塘话) is a variety of Old Xiang that is spoken in Matang Ethnic Miao Township (麻塘苗族乡), Suining County, Hunan.[2][3]
References
- ↑ Wu, Weijun 吴伟军 (2019). Guizhou Qinglong Changliu Laba Miaorenhua 贵州晴隆长流喇叭苗人话. Beijing: The Commercial Press. OCLC 1137079712.
- ↑ Yang, Zaibiao 杨再彪. 2011. Húnán xībù sìzhŏng bīnwēi yŭyán diàochá: Tujiayu, Xiaozhang Miaoyu, Guanxia Pinghua, Matanghua 湖南西部四种濒危语言调查:土家语、小章苗语、关峡平话、麻塘话 [A survey of four endangered languages of western Hunan]. Beijing: Minzu Chubanshe 民族出版社.
- ↑ Glottolog reference 324002.
Further reading
- Zeng, Ting (2020). "The Xiangxiang dialect of Chinese". Illustrations of the IPA. Journal of the International Phonetic Association. 50 (2): 258–281. doi:10.1017/S002510031800035X, with supplementary sound recordings.