This is a list of planned, or proposed, high-speed rail projects by country. Although a number of countries have conducted preliminary feasibility studies, many lines are eventually shelved or postponed due to high costs; only a few nations are building high-speed rail lines. Planned (or proposed) lines are separated here from lines under construction, and some countries have both. High-speed rail is public transport by rail at speeds over 200 km/h (125 mph).[1]
Africa
Integrated network
.svg.png.webp)
In 2013, the African Union (AU) passed Agenda 2063: a 50-year development trajectory which includes a continental free trade zone, a common passport, an end to armed conflict, an annual African economic forum, a space program, a Great African Museum, establishment of e-universities, and a high-speed rail network.[2] Africa has the lowest rail density of any inhabited continents, with 16 countries lacking rail altogether (especially in Central Africa); most rail lines are single-track freight lines operating at 30|km/h, traveling from ports to industrial zones such as mines and forests.[3]
The AU signed a memorandum of understanding with China in 2014 for the 30– to 50-year development of a continental rail system connecting all African capitals with modern rail technology,[4] facilitating interoperability by using one gauge instead of the current nine.[3] The network's goal is to facilitate intra-African trade and lower shipping costs. Its initial timeline for 2022 was the completion of preparatory work; only 12.3 percent of the network was studied, however,[5] largely due to funding constraints.[3] Completed pre-feasibility studies include the 2,891-kilometre (1,796 mi) Cotonou-Niamey-Ouagadougou-Abidjan Railway, which would cost US$5.022 billion to build and rehabilitate and US$866 million to equip.[3] The Djibouti-Libreville corridor was estimated to be 2,366 kilometres (1,470 mi) long and cost $5.277 billion, and the Dakar-N'Djamena-Djibouti corridor was estimated to be 5,139 kilometres (3,193 mi) in length and cost $14.05 billion.[3] It has not yet been specified which rail lines would operate at 330 kilometres per hour (210 mph), 250 kilometres per hour (160 mph), or 160 kilometres per hour (99 mph).
A master plan for 2033 envisions 35,828 kilometres (22,262 mi) of rail construction with the following projects. The first three are accelerated pilot projects under study or construction. The objectives by 2033 are to connect 16 landlocked countries to seaports and connect regions with trans-Africa corridors.[6] The 2043 master plan would expand the network to connect Africa's political and economic capitals by rail.[7][6]
- Accelerated pilot projects:
- Kigali-Dar Es Salaam: 1,476 km (917 mi)
- Kampala-Bujumbura: 596 km (370 mi)
- Walvis Bay-Windhoek-Gaborone-Johannesburg: 1,643 km (1,021 mi)
- 2033 master plan:
- Nairobi-Mombasa: 459 km (285 mi)
- Bamako-Ouagadougou-Niamey-N'Djamena-Khartoum: 5,384 km (3,345 mi)
- Addis Ababa-Djibouti: 637 km (396 mi)
- Pointe Noire-Brazzaville-Kinshasa-Bujumbura: 1,755 km (1,091 mi)
- Johannesburg-Maputo: 524 km (326 mi)
- Pretoria-Durban: 626 km (389 mi)
- Algiers-Abuja-Lagos: 4,111 km (2,554 mi)
- Lobito-Lusaka: 2,253 km (1,400 mi)
- N'Djamena-Bangui-Brazzaville-Luanda: 2,240 km (1,390 mi)
- Addis Ababa-Nairobi-Dodoma-Lusaka-Gaborone: 4,812 km (2,990 mi)
- Khartoum-Addis Ababa
- Luanda-Windhoek: 1,882 km (1,169 mi)
- Mbeya-Lilongwe-Harare-Johannesburg-Maseru: 3,115 km (1,936 mi)
- Lilongwe-Nacala: 815 km (506 mi)
- Lamu-Juba: 1,547 km (961 mi)
- Bangui-Juba: 1,551 km (964 mi)
- Juba-Kampala: 672 km (418 mi)
- 2033 pilot projects:
- Tunis-Algiers-Casablanca: 1,981 km (1,231 mi)
- Douala-Bangui
- Kampala-Nairobi
- Dakar-Bamako 1,147 km (713 mi)
- Asmara-Addis Ababa: 771 km (479 mi)
- Lusaka-Beira
- Alexandria-Khartoum
- Ouagadougou-Abidjan: 1,120 km (700 mi)
- Niamey-Cotonou: 955 km (593 mi)
- 2043 master plan:
- Alexandria-Benghazi-Tripoli-Tunis: 2,770 km (1,720 mi)
- Casablanca-Laayoune-Nouakchott-Dakar: 2,733 km (1,698 mi)
- Dakar-Banjul-Conakry-Monrovia-Abidjan-Accra-Lagos-Douala: 7,595 km (4,719 mi)
- Yaoundé-Bata-Libreville: 594 km (369 mi)
- Mogadishu-Addis Ababa
- Windhoek-Cape Town: 1,632 km (1,014 mi)
- Maseru-Cape Town: 1,135 km (705 mi)
- Tripoli-N'Djamena: 2,437 km (1,514 mi)
Algeria
In 2012, ANESRIF began building a double-track 142-kilometre (88 mi) electric high-speed railway reaching speeds of 220 kilometres per hour (140 mph) from Oued Tlélat (Oran) with stops in Sidi Bel-Abbès and Tlemcen. It was 80-percent completed by 2021, with 129 viaducts totaling 14 kilometres (8.7 mi) and three tunnels totaling 1.5 kilometres (0.93 mi). The project was scheduled for completion in 2019, but faced delays due to problems with land acquisition and COVID-19 and was scheduled to open by the end of 2021.[8] The administration began work on an extension from Tlemcen to Akkid Abbas (Maghnia) on the Moroccan border in 2015, a total of 56 kilometres (35 mi) designed for speeds of 220 kilometres per hour (140 mph). It was only seven percent completed by fall 2021, largely due to land-acquisition controversies in Tlemcen and Mansourah.[9][10] This section will contain Africa's largest viaduct: the 130-metre-high (430 ft), 1.8-kilometre-long (1.1 mi) M'dig Viaduct over the Isser River (near Aïn Fezza),[8] with a 600-metre (2,000 ft) tunnel into downtown Tlemcen and a renovated train station.[11] The 198-kilometre (123 mi) project is estimated to cost €2 billion.
Egypt
On 12 March 2018, Egyptian Transport Minister Hisham Arafat said that Egypt was in the process of launching a new high-speed railway linking the Mediterranean and the Red Sea in partnership with more than 10 international companies.[12][13] In September 2020, a Chinese-Egyptian consortium consisting of the China Civil Engineering Construction Corporation, the Egyptian Samcrete and the Arab Organization for Industrialization received US$9 billion to build a 543-kilometre-long (337 mi) high-speed railway capable of top speeds of 250 kilometres per hour (160 mph). The electric-powered trains would be manufactured in Port Said with a Chinese technology transfer to Egypt.[14]
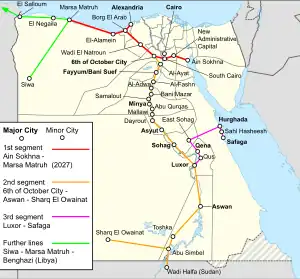
The first 660 kilometres (410 mi) was planned to begin in Mersa Matruh[15] on the Mediterranean Sea and pass through Al-Alamein, Borg El Arab, Wadi El Natroun and 6th of October through southern Cairo to the New Administrative Capital, ending in Ain Sokhna on the Red Sea's Gulf of Suez. Surveying and route planning were completed and construction began on bridges and track by January 2021.[16] This initial segment, intended for passengers and freight, is projected to cost $3 billion and has a completion date of 2023. On 14 January 2021, a memorandum of understanding was signed between Siemens Mobility and the Transportation Ministry's National Authority of Tunnels to design, install, and maintain Egypt's first high-speed rail system.[17][18] A second line between Alexandria and Borg El Arab was included in the contract, and both were under construction in 2022.[19] The Siemens-led consortium received a $4.5 billion contract to build the lines from Ain Sokhna to Marsa Matruh and to Alexandria in September 2021, which are scheduled for completion in 2027.[20] The lines will use Velaro high-speed passenger trains. The 660-kilometre (410 mi) segment will be designed to carry up to 30 million passengers annually, cut travel times in half, and reduce carbon emissions by 70 percent.[21] In February 2023, the French construction company NGE signed a contract to build 330 kilometres (210 mi) of the line between Ain Sokhna and Borg El Arab with 100 turnouts.[22]
A second line will run from the city of 6th of October through Fayoum, Minya, Aswan, and Abu Simbel over 1,100 kilometres (680 mi) along the west bank of the Nile.[23] Local stations will include Al-Ayat, Al-Fashn, Al-Adwa, Bani Mazar, Samalout, Abu Qurqas, Mallawi, and Dayrout.[24] Survey and construction work for the line began in March 2022 by Egyptian authorities, focusing on the area around 6th of October and Fayoum, with an anticipated design speed of 250 kilometres per hour (160 mph) and preliminary operation of express trains at 230 kilometres per hour (140 mph).[24] An extension of the line was announced in May 2022 from Aswan through Abu Simbel to Toshka and Sharq El Owainat in the Western Desert, as well as an extension to Wadi Halfa in Sudan.[25][26] The Kuwait Fund for Arab Economic Development signed a $2.45 million feasibility study for a 283.5-kilometre (176.2 mi) line from Aswan to Toshka and Abu Simbel, as well as an 80-kilometre (50 mi) extension to Sudan which includes a 6-kilometre (3.7 mi) bridge across Lake Nasser.[27][28] In early 2023, the Transport Ministry said that President Abdel Fattah al-Sisi approved the extension from Aswan to Abu Simbel with five high-speed rail stations and seven regional stations planned between Luxor and Abu Simbel.[29]
A third line is planned in the south from Safaga through Sahl Hasheesh, Hurghada, East Sohag, Qena, and Qus to Luxor at a total cost of $2.7 billion, with a construction time of two years.[30] Contracts for the second and third lines were planned to be signed by Siemens in March 2022; the €8.1 billion contract was signed on May 31, 2022, between the Egyptian government and Siemens (and its consortium partners Orascom Construction and Arab Contractors), and includes construction of the second and third lines, 41 Velaro eight-car high-speed passenger trains, 94 Desiro high-capacity four-car regional trainsets, 41 Vectron freight locomotives, a level-2 European Train Control System and a suitable power grid.[31] The network is projected to cost $23 billion and span over 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi).[18][23]
A planned extension eastwards from Marsa Matruh through El Negaila to Sallum on the Libyan border to Benghazi in Libya was announced by Egyptian Transport Minister Kamel Al-Wazir in November 2020, and was confirmed by the Libyan-Egyptian Chamber of Commerce on 18 January 2021.[32] An extension to Siwa was also cited.[26] Al-Wazir reiterated the Egyptian government's commitment to future extensions to Wadi Halfa in Sudan and Benghazi in Libya in March 2023 at the World High Speed Rail Conference in Marrakesh.[33] This is part of the Egyptian government's larger plan to build political and economic links with Libya and Sudan, including Wadi Halfa.[26][34]
Libya
Before the 2011 Libyan Revolution, the government of Muammar Gaddafi was building a high-speed rail line capable of 200-kilometre-per-hour (120 mph) operation from the Tunisian border to the Egyptian border at a total cost of $7.9 billion. Russian Railways had received the $2.9 billion contract for the section between Sirte and Benghazi, with an anticipated completion in 2012; at least 14 kilometres (8.7 mi) of the planned 554-kilometre (344 mi) line was laid.[35] China Railway had been working on a $2.6 billion link between Sirte and Khums, with plans for extension westwards to Tripoli. In 2010, the Libyan government proposed a feasibility study for a $2 billion high-speed rail line between Benghazi and Tobruk which was expected to be completed by 2012. Trains were to run on diesel fuel, with electrification planned. Dorsch Afrique was also involved in designing a 150-kilometre (93 mi) high-speed connection between Tobruk and Umm Saad, on the Egyptian border.[36] Three kilometers of high-speed track were finished, including a station in Tripoli and one kilometer of tunnels, and 30 kilometers had been cleared in 2003. The rail line's steel, however, was plundered during the civil war.[37]
The Libyan government has tried to resume the project several times. In 2015, Prime Minister Abdullah al-Thinni visited Moscow and set up a review commission.[38] The Libyan government approached Russia in 2018 to resume construction on the Sirte-Benghazi line, and Russian Railways responded that Tripoli would have to compensate the company for costs incurred after the project was halted in 2011.[39] In January 2021, the Egyptian government announced plans to extend its proposed high-speed link from Alamein through El Salloum to Benghazi.[40]
Morocco
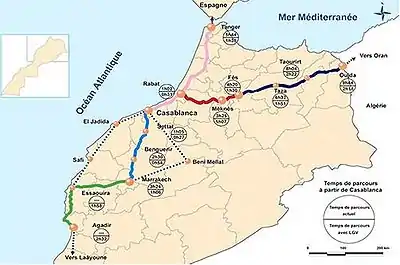
A trans-Maghreb high-speed rail line linking Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia is planned. The project is expected to begin in Morocco, move towards Algiers, and reach Tunis.[41] However, historical relations between Morocco and Algeria have delayed the project. Part of the line opened by November 2018, and Al Boraq (between Casablanca and Tangier) is Africa's first high-speed rail line.
By 2040, Morocco plans to build a route from Kenitra to Marrakech for 40 billion MAD (USD$4 billion) to upgrade the current Kenitra-Casablanca segment to high-speed, and to build a route from Marrakech to Agadir for 50 billion MAD (USD$5 billion).[42] China Railway expressed interest in the latter project to the Moroccan government in the summer of 2021.[43] In March 2022, after completion of design studies for the Marrakech-Agadir project, a Korea National Railway-led consortium secured a $32 billion contract with ONCF (Moroccan National Railways) for section three of the planned 230-kilometre (140 mi) line.
ONCF has announced plans to build high-speed rail between Rabat-Fez-Oujda, on the Algerian border, by 2040.[44] With initial feasibility studies completed, the company announced in July 2022 that the first section (Rabat-Khemisset-Meknes) had begun environmental and social review spurred by the success of the sections between Tangier and Casablanca.[45]
Further extensions from Tangier north across the Strait of Gibraltar to Algeciras in Spain have been discussed intermittently since the 1930s. In the summer of 2023, the Spanish government pledged €2.3 million for a design study in a joint commission with Morocco.[46]
Namibia
In 2020, the Namibian government undertook a detailed feasibility and design study for a line between the port in Walvis Bay through Windhoek to Gaborone, Botswana, and Pretoria, South Africa as part of the African Union's Agenda 2063. Construction was scheduled to begin in 2023.[47]
Sudan
A 250-kilometre-per-hour (160 mph) rail link from the Egyptian city of Aswan to Wadi Halfa in northern Sudan has been proposed,[26] and a $2.5 million feasibility study was agreed with Kuwaiti investors in April 2022.[48] A standard-gauge extension from Halfa to Khartoum has been proposed to connect travelers with Alexandria.[49]
Tunisia
The Tunisian government and Tunisian Railways (SNCFT) are planning high-speed rail in three parts; the first is a 180-kilometre (110 mi) line from Ras Jedir on the Libyan border to Gabès, built to 250 kilometres per hour (160 mph) for passenger trains and 120 kilometres per hour (75 mph) for freight at an estimated cost of TND 2.6 billion ($917 million). The second phase will continue from Gabès through Sfax, Sousse, Nabeul, and Tunis to Bizerte, a 480-kilometre (300 mi) segment which will involve new track and upgrading existing lines for an estimated TND 14 billion ($4.9 billion). The third phase will involve an upgrade of the line between Tunis and Tabarka on the Algerian border, a 180-kilometre (110 mi) segment with an estimated cost of TND 9.4 billion ($3.3 billion). The total cost of the 840-kilometre (520 mi) electrified standard-gauge line was estimated by the Tunisian government at TND 26 billion ($9.2 billion) in the fall of 2021.[50] No action seems to have been taken other than initiating discussion of a partnership by Tunisian president Kaïs Saïed and French president Emmanuel Macron on 22 June 2020.[51] In June 2021, Saïed attempted to secure a loan from the European Investment Bank to finance the project. It was refused, since the country had borrowed 7 billion TND ($2.3 billion) during the previous decade; the bank suggested upgrading existing rail infrastructure instead.[52]
South Africa
On 7 June 2010, Minister of Transport Sbusiso Ndebele said that plans were being considered for a high-speed line from Johannesburg to Durban. The line would reduce travel time from 12 hours to about three. The 721-kilometre (448 mi) line would involve engineering challenges, including traversing the Drakensberg mountains. A high-speed line from Johannesburg to Cape Town is also being studied.[53][54] The $30 billion plan was discussed with China Railway Group, which wanted South Africa to contribute 40 percent of the capital; South Africa was hoping that Chinese banks would provide a loan for the project.[55] In 2020, South Africa's Department of Transport announced plans to establish a high-speed rail network by 2025 between Pretoria, Johannesburg, and Durban.[56] The freight corridor was affirmed in Parliament in July 2021; the Chinese ambassador to South Africa confirmed in April 2022 that their country intended to collaborate in a passenger and freight rail link between Johannesburg and Durban, but funding would be uncertain.[57] In fall 2022, South African President Cyril Ramaphosa outlined a National Rail Act to finance feasibility studies.[58]
Americas
Argentina
A Buenos Aires–Rosario–Córdoba high-speed railway was planned,[59] operating at speeds of 320 km/h (200 mph). Construction was scheduled to begin in 2008 and was expected to be finished in 2012, but the project is currently on hold.[60] It would join Buenos Aires, Rosario, and Córdoba.[61] Other projected high-speed rail lines include:
- Buenos Aires-Mar del Plata (400 km [250 mi]): A line to the seaside beach-resort city and fishing port of Mar del Plata,[62] 400 km (250 mi) south of Buenos Aires
- Buenos Aires-Mendoza: 1,200 km (750 mi)[63]
Brazil
Rio-São Paulo High Speed Rail (Portuguese: Trem de Alta Velocidade Rio-São Paulo, abbreviated TAV RJ-SP) was proposed to connect Brazil's two largest metropolises (São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro) with an extension to Campinas, another municipality near São Paulo, and a 100-kilometre (62 mi) radius.[64][65] The proposed route, across some of Brazil's most mountainous and urbanized terrain, required about 40 percent of its tracks to be built through viaducts, bridges and tunnels. The proposed project was expected to cost US$16 billion.[66] Brazil proposed the following routes:
- Brasília – Goiânia – Rio Verde – Itumbiara – Uberlândia – Uberaba – Ribeirão Preto – Campinas – São Paulo – Rio de Janeiro: 1,200 kilometres (750 mi)
- Belo Horizonte – São Paulo: 594 kilometres (369 mi)
- Curitiba – São Paulo: 410 kilometres (250 mi)
- Santos – São Paulo: 80 kilometres (50 mi)
- Brasília – Goiânia: 200 kilometres (120 mi)
The country uses standard gauge, 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in). The proposed commercial speed was 350 kilometres per hour (220 mph). Stations included Rio de Janeiro Centre, Rio de Janeiro Intl Airport, Volta Redonda/Barra Mansa, São José dos Campos, São Paulo/Guarulhos Intl Airport, São Paulo Centre, São Paulo/Viracopos Intl Airport and Campinas Centre. The project was later cancelled for economic reasons.
Canada
Two routes have been frequently proposed as suitable for a high-speed rail corridor:
A possible international high-speed rail link between Montreal and Boston or New York City is often discussed by regional leaders, although little progress has been made.[67][68] Work is underway to improve the Amtrak Cascades service between Vancouver and Seattle, but the line will not reach speeds normally associated with high-speed rail. In Ontario, the Progressive Conservative government elected in 2018 postponed a decision on high-speed lines.
Chile
A high-speed 200-kilometre-per-hour (120 mph) rail connection between Santiago and Valparaíso was first proposed in 2018 by China Railway Group and the following year by Spanish-based Formento de Construccions y Contratas (FCC) and Talgo, via an alternate route through Limache and Tiltil. The project, initially planned to open in 2024, was suspended in 2021 because of the COVID-19 pandemic.[69] Either plan would cost $2 billion to $4 billion, which Empresa de low Ferrocarriles del Estado (EFE) head Pedro Pablo Errazuriz said was too expensive to prioritize in 2022.[70] In May 2022, however, President Gabriel Boric's administration reiterated that the project is a priority for the government and called for proposals by mid-year.[71]
Colombia
The Colombian National Agency of Infrastructure[72] (ANI) was interested in building a high-speed rail link as part of Colombia's 4G modernization. The transport minister had said that plans and studies for a bullet train would begin in 2015. However, Colombia has the smallest train ridership of any large Latin American nation. There have been many proposals since the 1990s, when Japanese firms wanted to build a bullet-train network from Bogota to nearby cities, but the project was cancelled.
Mexico
Mexico's Secretariat of Communications and Transport originally proposed a high-speed rail link[73][74] which would transport passengers from Mexico City to Guadalajara, Jalisco, with stops Querétaro, Guanajuato, Leon and Irapuato and a connected line from the port city of Manzanillo to Aguascalientes. The train, which would travel at 300 kilometres per hour (190 mph),[75] would enable passengers to travel from Mexico City to Guadalajara in two hours.[75] The network was planned to connect to Monterrey, Chilpancingo, Cuernavaca, Toluca, Puebla, Tijuana, Hermosillo, Cordoba, Veracruz, Oaxaca, Colima, Zacatecas, Torreon, Chihuahua, Puebla, San Luis Potosi, Mexicali Saltillo and Acapulco by 2015, but no progress had been made by 2020.[73] The project was projected to cost MXN$240, or about USD$25 billion.[73] In 2005, Mexican billionaire Carlos Helú expressed interest in investing in high-speed rail.[76] The Yucatan Peninsula has been studied for the development of high-speed rail, with the Transpeninsular Fast Train available for bidding in September 2011.[77]
By 2014, the route for the first phase of the Mexico City-Guadalajara HST had been selected. It would operate from the Buenavista station in Mexico City to Querétaro, a length of 212 kilometres (132 mi).[78] The HST would first extend to Guadalajara; after the first stage, it would extend to Celaya, Salamanca, Irapuato, and Leon. The first phase was expected to be completed by 2018.[79]
Latin America's first high-speed line had been announced in July 2014 with the opening of an international tender to build a passenger train linking Mexico City and Querétaro at up to 300 kilometres per hour (190 mph), moving 23,000 passengers a day. The line would extend over 210 kilometres (130 mi), with construction beginning that year, and operation beginning in the second half of 2017.[80]
On 6 November 2014, Mexico's president announced that the proposed bullet train was being postponed because there was only one bidder. Falling oil prices and the economic downturn delayed the project.[81] Mexican President Andrés Manuel López Obrador revived the project in July 2018,[82] and in 2020 the Mexican government secured a MXN$51.3 billion investment (US$2.3 billion) to fund it.[83] Eighty million pesos (US$3.93 million) had been allocated for initial feasibility studies by 2022, with the remaining funds planned through 2025.[84]
In 2021, Mexican rail officials began a US$2 million feasibility study for a rail connection between San Antonio, Texas, and Monterrey, Mexico; unlike previous US$20 billion proposals for a line to be built for 250-mph (400-km/h) operation, the US$7 billion proposal examines a 100-mph (160-km/h) route taking four hours.[85]
Panama
China approached the Panamanian government in 2019 with a feasibility plan for a 391-kilometer (243-mile) high-speed line from Panama City to David, on the Costa Rican border.[86] The line would have been partially financed under China's Belt and Road Initiative. The project was declined by Panamanian president Laurentino Cortizo in September of that year, who said that it would be a debt overload.[87]
United States

High-speed rail service in the United States, notably the Acela Express, is limited to the Northeast Corridor.[88] Amtrak uses the Acela Express as a high-speed service between Washington, D.C., and Boston via New York City and Philadelphia along the Northeast Corridor (NEC). Its tilting design allows the train to travel at higher speeds on the sharply-curved NEC without disturbing passengers. The Northeast Regional follows the same route, with more stops. All other high-speed rail services share part of the route.
There has been a resurgence of interest outside the Northeast Corridor in recent decades, with plans for high-speed rail across the country. The Texas High Speed Rail and Transportation Corporation (THSRTC), a grass-roots organization dedicated to bringing high-speed rail to Texas, was established in 2002.[89] In 2006, American Airlines and Continental Airlines joined THSRTC in an effort to bring high-speed rail to Texas as a passenger-collector system for the airlines. Lone Star High-Speed Rail was formed in 2009 to plan a railway between Dallas and Houston. The company changed its name to Texas Central Railway in 2013, and has been developing a system based on technology used on Japanese Shinkansen lines. The 240-mile (390 km) route traverses open farms and ranches, with one stop in the Brazos Valley. Regulatory approvals were received in September 2020,[90] and service is expected to begin in 2026.[91][92]
The California High-Speed Rail Authority was created in 1996 to implement a 800-mile (1,300 km) rail system which is estimated to cost about $40 billion. The system will not require operating subsidies, and is expected to generate $1 billion in annual profits. Construction was approved with the passage of Proposition 1A, authorizing a $9.95 billion general obligation bond. The system would provide high-speed service between major cities such as Sacramento, San Francisco, Los Angeles, and San Diego, and would allow travel between Los Angeles' Union Station and San Francisco Transbay Terminal in two-and-a-half hours. On 2 December 2010, the California High-Speed Rail Authority announced that the first section of the Californian high-speed rail network had been selected and construction was to start in 2012, but delays postponed it to 2015. The line will run from near Madera south to Bakersfield, with stations at Fresno and Hanford, for 105 kilometres (65 mi) through a rural portion of the San Joaquin Valley. It will connect with conventional Amtrak lines at each end.[93] In December 2010, its funding was doubled after the newly-elected governors of Ohio and Wisconsin decided to cancel right-of-way projects which had been allocated $1.2 billion by the federal government. Of that amount, $616 million was granted to California in addition to funding already promised; this, combined with a state bond issue to match the new funding, provided over $1.2 billion in additional funding. It will be used to add an additional 88 kilometres (55 mi) of track, bringing the line to the edge of Bakersfield.[94] Brightline West, a project of Fortress Investment Group, is a planned line between Los Angeles, and Las Vegas with speeds up to 200 miles per hour (320 km/h). Begun as an independent venture in 2005, the project changed hands several times before its acquisition by Brightline (who had recently begun its initial Florida route). Construction is expected to start in 2023, with service beginning in 2027.[95]
In September 2010, Amtrak announced proposals for 355 km/h (221 mph) trains to run between Washington, D.C., and Boston via Baltimore, Philadelphia, and New York. End-to-end travel time would be three hours. The proposals would cost $117 billion, and would take 30 years to complete. Amtrak estimates that extra capacity would be needed, since the Acela trains would be full by 2030. The proposal envisages completion by 2040.[96]
North American High Speed Rail Group is seeking to build a privately-financed high-speed rail line between Rochester and Minneapolis-St. Paul which is expected to cost $4.2 billion. The group's eventual goal is to extend high-speed rail service to Chicago.[97]
Asia
Bangladesh
Bangladesh considered building a high-speed rail link between Dhaka and Chittagong in 2005. The government short-listed France's SNCF and Japan Railways for the project,[98] which was ultimately abandoned. In 2014, Spain and China were interested in developing the Bangladesh Railway into a high-speed network.[99] Seven years later, Chinese ambassador Li Jiming said that China was interested in investing in the line's construction.[100] In March 2022, Russian-based RZD International approached Bangladesh Railway about financing the project after feasibility and design studies had been completed; the 225-kilometre (140 mi) route would cost an estimated $11.1 billion.[101] Chinese ambassador to Bangladesh Li Jiming wrote to Railways Minister Nurul Islam Sujan in June 2022 about signing a memorandum of understanding between China Railway Group and Bangladesh Railways under a government-to-government public–private partnership.[102]
Ninety percent of the country's trade passes through Chittagong and 80 percent of its exports are carried on the Dhaka-Chattogram highway, incentivizing the creation of a freight rail line. A 300-kilometre-per-hour (190 mph) passenger journey would take 55 minutes – 75 minutes with stops in Narayanganj, Cumilla, and Feni; the current travel time is six hours.[102] In February 2023, Whip Iqbalur Rahim promised a bullet train between Dinajpur and Dhaka by 2027 if the Awami League agreed.[103]
Cambodia
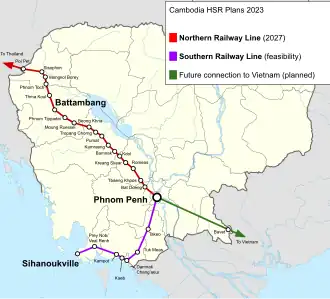
Cambodian Prime Minister Hun Sen confirmed in December 2021 that his government was interested in high-speed-rail, with a feasibility study for upgrading the 266-kilometre (165 mi) line from Phnom Penh to Sihanoukville and the 386-kilometre (240 mi) line to Poipet.[104] Sen indicated an intent to build new rail lines by continuing from Poipet through Siem Reap to Kampong Thom, and building a line from Phnom Penh to Bavet on the Vietnamese border.[105] The current railways can operate at only 20 to 30 kilometres per hour (12 to 19 mph), largely due to damage from the 1970s civil war. The line to Sihanoukville was rehabilitated in 2016; the line to Poipet was rehabilitated in 2018, and was reconnected with the Thai rail network across the border the following year.[106] Cambodia's prime minister has tasked the Minister of Public Works and Transport with finding an international development partner.[107] In early 2023, Sen traveled to China and signed a $44 million agreement (CN¥300 million) with Chinese President Xi Jinping and Chairman Li Zhanshu to upgrade the Phnom Penh-Poipet railway to 160-km/h operation after a China Road and Bridge Corporation (CRBC) feasibility study of the line; the project is estimated to cost a total of $4 billion.[108][109] In July 2023, Minister of Public Works and Transport Sun Chanthol announced the start of a feasibility study to convert the Phnom Penh-Sihanoukville railway to higher-speed rail.[110]
India
The Ministry of Railways of the Government of India has proposed to build 8,834.78 km (5,490 mi) of high-speed rail lines across fifteen corridors, with average operating speeds of up to 320 km/h (200 mph).[111] Formation of the National High Speed Rail Authority (NHSRA) was announced in the 2012–2013 rail budget, although no firm date was set for construction. The Central Japan Railway Company has promoted a Shinkansen for India,[112][113] and France has expressed interest in collaborating on long-term development of the Pune-Mumbai-Ahmedabad route.[114] Spain's Talgo has also expressed interest in the projects, and plans to open an office in India to promote its technology.[115]
In collaboration with Japan, India is building the Mumbai–Ahmedabad high-speed rail corridor (its first high-speed railway) on a 508 km-long (316 mi) route between Mumbai and the western city of Ahmedabad. On 12 December 2015, India and Japan signed a US$15 billion agreement to build a high-speed line between the cities in which Japan will provide a US$12 billion low-interest loan. The agreement was part of a memorandum of understanding involving the transfer of defense technology and civil nuclear cooperation.[116] Preparatory work began in the third quarter of 2017, and was expected to be completed in December 2023.[117] Due to slow land acquisition in Maharashtra and the COVID-19 pandemic, the expected date of completion for the portion from Surat to Bilimora in Gujarat has been postponed to 2026 and the entire corridor will be completed by October 2028.[118][119] The National High Speed Rail Corporation (NHSRC) plans to operate E5 Series Shinkansen trains at speeds up to 320 km/h (200 mph). It is expected to cost about ₹1.1 trillion (equivalent to ₹1.5 trillion or US$19 billion in 2023), of which 81 percent is financed by the Japan International Cooperation Agency.[120]
The Government of Kerala has proposed a high-speed rail corridor known as the Silver Line to carry freight and passengers from Kasargod in the north to Kerala's capital, Thiruvananthapuram, in the south. The 532 km (331 mi) project reduces the 12-hour travel time to less than four hours, with a maximum design speed of 220 km/h (140 mph); the current average speed is 45 kilometres per hour (28 mph).[121] The project, estimated to be completed by 2025, is expected to cost ₹0.66 trillion (equivalent to ₹740 billion or US$9.3 billion in 2023).[122] The Kerala government and the Union Ministry of Railways (as the Kerala Rail Development Corporation) plan intermediate stations in Kannur, Kozhikode, Tirur, Thrissur, Cochin Airport, Ernakulam, Kottayam, Chengannur, and Kollam. Of the 1,383 hectares (5.34 sq mi) required for the project, 1,198 hectares (4.63 sq mi) is private land; the project would displace 30,000 families.[121] Other issues affecting the project include the planned standard gauge in a system which uses Indian gauge, low ridership estimates, hydrological problems, and stations distant from city centers.[123] The project missed a mid-July 2022 deadline for completing its social-impact assessments (having consulted 45 out of 190 villages involved), leaving the project in legal limbo before the Kerala High Court.[124] Railway Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw expressed doubt about the Silver Line project's feasibility on 29 July 2022.[125]
A third high-speed rail project, between Delhi and Varanasi, is under construction and will cover 813 kilometres (505 mi) in less than four hours at a speed of 330 kilometres per hour (210 mph); the present travel time is 10 hours.[126] The project is planned to have service at 22-minute intervals and thirteen stations, including Delhi (Kale Khan), Noida, Jewar Airport,[127] Mathura, Agra, Etawah, South Kannauj, Lucknow, Ayodhya, Rae Bareli, Prayagraj, Bhadoi, Banaras and Varanasi, with a railway bridge over the Ganges River.[128]
A fourth high-speed rail project proposed by the Karnataka government would run 485 kilometres (301 mi) from Mysuru (Mysore) through Bengaluru (Bangalore) to Chennai, cutting the current nine-hour travel time to three hours (45 minutes between Mysuru and Bengaluru) at a cost of ₹1.15 trillion (equivalent to ₹1.2 trillion or US$15 billion in 2023).[129] By the summer of 2022, the state government had begun acquiring land for the right-of-way and is awaiting a memorandum of understanding with neighboring Tamil Nadu to facilitate land acquisition for the project.
| Corridor | Speed | Length | Status | Year | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Delhi-Varanasi | 320 km/h (200 mph) | 865 km (537 mi) | DPR under preparation | 2031 | [131] |
| Delhi–Amritsar | 320 km/h (200 mph) | 480 km (300 mi) | Approved | 2051 | [131] |
| Delhi–Ahmedabad | 320 km/h (200 mph) | 886 km (551 mi) | Approved | 2031 | [131] |
| Amritsar–Jammu | 320 km/h (200 mph) | 190 km (120 mi) | Proposed | 2051 | [130] |
| Varanasi–Howrah | 320 km/h (200 mph) | 711 km (442 mi) | DPR under preparation | 2031 | [132] |
| Patna–Guwahati | 320 km/h (200 mph) | 850 km (530 mi) | Proposed | 2051 | [130] |
| Mumbai–Ahmedabad | 320 km/h (200 mph) | 508.18 km (315.77 mi) | Under Construction | 2028 | [133] |
| Mumbai–Nagpur | 320 km/h (200 mph) | 736 km (457 mi) | DPR under preparation | 2051 | [130] |
| Mumbai–Hyderabad | 350 km/h (220 mph) | 711 km (442 mi) | DPR under preparation | 2051 | [134] |
| Pune–Nashik | 200 km/h (120 mph) | 235.15 km (146.12 mi) | Approved | 2027 | [135] |
| Ahmedabad–Rajkot | 220 km/h (140 mph) | 225 km (140 mi) | DPR Prepared | TBD | [136] |
| Nagpur-Varanasi | 320 km/h (200 mph) | 855 km (531 mi) | Proposed | 2041 | [130] |
| Chennai–Mysuru | 320 km/h (200 mph) | 435 km (270 mi) | DPR under preparation | 2031 | [130] |
| Hyderabad–Bengaluru | 320 km/h (200 mph) | 618 km (384 mi) | Proposed | 2041 | [130] |
| Thiruvananthapuram–Kasaragod | 200 km/h (120 mph) | 529.45 km (328.98 mi) | DPR Prepared | TBD | [137] |
Indonesia
Indonesian authorities have expressed an interest in high-speed rail for the densely-populated island of Java since 2006, probably linking the cities of Jakarta, Bandung, and Surabaya.[138] In 2008, the government, the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) and a Japanese transportation consultant conducted a pre-feasibility study. The planned 685-km (425-mi) Jakarta-Surabaya High-Speed Rail is expected to operate at 350 kilometres per hour (220 mph)and cost $20 billion.

In July 2015, the Indonesian government announced their plan to build high-speed rail in the country.[139] Japan and China competed for the project, since both have conducted comprehensive studies. In late September 2015, Indonesia awarded the project to China.[140][141] On 16 October 2015, Indonesia and China signed an agreement to build the Jakarta-Bandung High-Speed Rail as its first phase.[142] Ground was broken on 21 January 2016. The project is a 60-percent Indonesian consortium and 40 percent China Railway International.[143] The project was 90-percent completed by fall 2022, and was expected to begin operation at the end of that year.[144][145] The two governments resolved the Rp 16,800,000,000 (US $1174157) cost overrun for the first section.[146][147]
Completion of the project's next phases, to Cirebon, Semarang, and Surabaya is uncertain, since the capital's relocation and completion of the Trans-Java Toll Road might affect demand.[148] However, the Indonesian Transportation Ministry described the construction of high-speed rail to Semarang as a priority in spring 2022.[149] After successful phase-one testing in summer 2023, when a train reached 385 kilometres per hour (239 mph), Coordinating Minister for Maritime and Investments Affairs Luhut Binsar Pandjaitan announced a preliminary study of extending the line from Bandung to Surabaya.[147] In July of that year, the Indonesian Transportation Ministry announced plans to extend the line to Surabaya through Yogyakarta,[150] which were publicly supported by Chinese Premier Li Qiang in mid-September 2023.[151] The Jakarta-Bandung HSR began trial operation with passengers on 7 September 2023, and commercial operations on 2 October 2023.[152][153]
Iran
Iran has high-speed rail under construction to connect the three major cities of Tehran, Qom and Isfahan, with a station at Imam Khomeini International Airport. The route will be 422 km (262 mi) with an operating speed of 350 kilometres per hour (220 mph), reducing travel time from five hours to 90 minutes. The project, costing over €7 billion, is being built by China Railway Engineering Corporation.[154][155]
A 117-km (73-mi), 300-kilometre-per-hour (190 mph) double-track branch from Qom to Arak will be built at a cost of €1.2 billion (including the Arak station and six viaducts) with a contract the Islamic Republic of Iran Railways initially awarded to Italian-based Ferrovie dello stato in 2017.[156][157] The contract was re-awarded to Chinese corporations with the imposition of US-led sanctions the following year,[158] with other rail projects.[159]
High-speed rail was planned to link Tehran to Mashhad, Iran's second-largest city. The planned 2016 800 kilometres (500 mi), 400-kilometre-per-hour (250 mph) would have decreased travel time from eight to 3.5 hours.[160] A reduced $1.5 billion plan for electrification and upgrading of the existing 967-kilometre (601 mi) line, with speeds increasing from 160 to 200 kilometres per hour (99 to 124 mph), was signed by a consortium of the Iranian MAPNA Group and Chinese companies in July 2017; China backed out in January 2021.[161]
Israel
In 2020, Israel's National Infrastructure Committee approved high-speed rail links between the country's four metropolitan cities: Jerusalem, Tel Aviv, Haifa and Beersheba. The project is slated for completion by 2040, with a top speed of 250 km/h.[162] The high-speed electrified connection between Tel Aviv and Haifa, which will cost $3.8 billion and reduce travel time from one hour to 30 minutes, is due to be completed by 2030 but has no budget for rolling stock.[163] Further plans for completion by 2040 include an extension north of Haifa, a continuation from Tel Aviv through Ben Gurion Airport to Jerusalem, and a connection to Beersheva.[163]
Japan

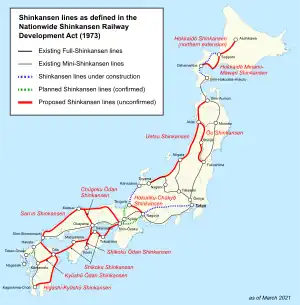
A maglev line between Tokyo and Osaka, the Chūō Shinkansen, is under construction by the Central Japan Railway Company (JR Central). The Nagoya-Tokyo section is planned to open in 2027, and the Nagoya-Osaka section is projected for completion in 2037.
The route is to be privately financed through bond sales by JR Central, and the intermediate stations will be financed by local governments. JR Central expects that it will need at least eight years between the completion of the Tokyo section and the beginning of construction of the Osaka section to rebuild its financial position. The federal government is exploring options to accelerate the project.[164]
Research on high-speed rail systems based on magnetic levitation, led by JR Central, has been ongoing since the 1970s. The trains and guideways are technologically ready, and over 100,000 passengers have ridden them. Pre-Series L0 crewed trains on the Yamanashi test line have reached speeds of 603 kilometres per hour (375 mph), making them the fastest trains in the world.[165] The Yamanashi test track is to be incorporated into the under-construction Tokyo–Osaka maglev route.
Extensions to the current network expansions, notably from Hakodate to Sapporo, have been approved for construction.[166] The route of the final extension of the Hokuriku Shinkansen has not been finalised. It will ultimately provide a northern route to Osaka.
Conventional routes planned in 1973 are on hold, to be built after the current lines open. A Hokkaido Shinkansen extension was proposed during the 1970s to the Russian border via tunnel. A tunnel to South Korea has also been proposed.
| Line | Speed | Length | Construction start | Expected start of revenue service |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hokkaido Shinkansen extension (Sapporo–Asahikawa) | 320+ km/h | 130 km | on hold | 2045 |
| Sapporo–Oshamambe | 200+ km/h | 180 km | on hold | 2045 |
| Uetsu Shinkansen (Toyama–Aomori via Niigata) | 200+ km/h | 560 km | on hold | 2030+ |
| Ōu Shinkansen (Fukushima–Akita via Yamagata) | 200+ km/h | 270 km | on hold | 2030+ |
| Hokuriku Shinkansen (Tokyo–Osaka via Kanazawa) | 200+ km/h | 50 km | Tokyo to Kanazawa in operation, Kanazawa to Tsuruga under construction, Tsuruga to Osaka planned | 2045 |
| Trans-Chūgoku Shinkansen (Okayama–Matsue) | 260 km/h | 150 km | on hold | 2030+ |
| San'in Shinkansen (Osaka–Shimonoseki via Tottori & Matsue) | 260 km/h | 550 km | on hold | 2030+ |
| Shikoku Shinkansen (Osaka–Oita via Matsuyama) | 260 km/h | 440 km | on hold | 2045 |
| Trans-Shikoku Shinkansen (Okayama–Kōchi) | 260 km/h | 150 km | on hold | 2045 |
| East Kyūshū Shinkansen (Hakata–Kagoshima-Chūō via Ōita) | 260 km/h | 390 km | on hold | 2045 |
| Trans-Kyūshū Shinkansen (Ōita–Kumamoto) | 260 km/h | 120 km | on hold | 2045 |
Kazakhstan
Qazaqstan Temir Zholy, Kazakhstan's national rail company, has awarded a contract to oversee the design and construction of a high-speed line from Astana (the country's capital) to Almaty (its largest city).[167][168] The line, expected to be 1,011 km (628 mi) long, will run via Karaganda and Balkhash.[167][168] A 10-kilometre (6.2 mi) viaduct across Lake Balkhash is planned near Sayaq.[167][168] The trains are expected by be built by Tulpar-Talgo (a joint venture established in 2011 between Qazaqstan Temir Zholy and the Spanish company Talgo),[169] will have a maximum speed of 250 km/h (155 mph) and make the trip in five-and-a-half hours.[167][168] The system will use Russian gauge, like Kazakhstan's existing conventional lines.[167][168] In 2021, Kazakh Prime Minister Asqar Mamin announced plans for high-speed rail line to Tashkent, Uzbekistan, via Shymkent and Turkistan in Kazakhstan.[170][171]
North Korea
Attempts were made during the 1970s to speed up North Korea's network, when one electric trainset (using bullet-train design) was built. The trainset never entered regular service due to the economic crisis which followed the dissolution of the Soviet Union. The Chinese government proposed a high-speed railway for the country during the 2000s, but the proposal is still far from the planning stage. Changes in foreign policy in during 2017 and 2018 encouraged both Koreas to begin international railway projects, and the chair of the State Affairs Commission has shown an interest in high-speed rail technology.[172]
Malaysia
A high-speed rail running at 300 km/h (186 mph) to link Kuala Lumpur and Singapore was proposed in 2006 by YTL Corporation, operator of the KLIA Express in Malaysia; the company also proposed a similar system during the late 1990s. Plans for the project were put on hold in April 2008 due to the high cost to the government, estimated at RM8 billion.[173] The project has been opposed by rail-operator rivals such as Keretapi Tanah Melayu, and the liberalisation of the Kuala Lumpur-Singapore air route also dampened its prospects for the proposal.
In 2007, Siemens expressed interest in providing technology for the proposed rail link.[174] By the middle of 2009, YTL revived talk about the project and expressed hope that the Malaysian government would reexamine the proposal[175] since delays in the project have increased development costs.[176]
In 2010, Malaysia made a proposal to revive the project.[177] In the new proposal, the route will be in two phases: the first from Kuala Lumpur to Singapore, and the second from Kuala Lumpur to Penang.
On 19 February 2013, Singapore and Malaysia announced an agreement to build a high-speed rail link between Kuala Lumpur and Singapore by 2020.[178] The KL–Singapore section, planned to be about 380 km long, would have an estimated travel time of 90 minutes.[179] The high-speed railway terminus for Singapore would be in Jurong East, at the Jurong Country Club site, and the terminus for Malaysia would be at the former RMAF Kuala Lumpur Air Base.
After the landslide defeat of Prime Minister Najib Razak in May 2018, his successor Mahathir Mohamad told the Financial Times that the project would be delayed in favor of cheaper alternatives such as spending RM 20 billion to upgrade the Keretapi Tanah Melayu (KTM) line to 200 km/h and extending it to Jurong East.[180] On 5 September 2018, an agreement to postpone the project until 31 May 2020 was signed between Singapore and Malaysia. Completion was pushed back to 1 January 2031 from 31 December 2026 after initial plans to scrap it.[181] Malaysia also paid Singapore S$15 million on 31 January 2019 as compensation for suspending the project.[182]
On 31 May 2020, Singapore agreed to Malaysia's request to delay the project to discuss and clarify proposed changes by 31 December of that year.[183] Since no agreement was reached by that date, the HSR project was terminated on 1 January 2021. As a result, Malaysia paid about S$102.8 million to Singapore on 29 March 2021.[184][185] In March 2022, talks were scheduled again between the Malaysian and Singaporean governments to revive the high-speed rail project with new terms.[186]
On 26 February 2022, Thailand and Malaysia agreed to conduct a feasibility study of a line between Kuala Lumpur and Bangkok.[186] On 17 May of that year, the countries established a joint committee to coordinate the planning of a Bangkok-Kuala Lumpur HSR project.[187] The project was still under discussion by May 2023, with no concrete plans.[188]
Myanmar
Plans have been announced to build a high-speed railway between Yangon and Kunming in China, a distance of 1920 km. Construction was planned to begin after agreements with China were signed in 2011.[11] The project, put on hold in 2014 due to financial feasibility and national-security concerns, was revived in 2019.[189][190]
Oman
Oman has planned a 2,144-km high-speed rail network connecting the seaports of Salalah, Duqm, and Sohar, and linking with the Gulf Railway at Hafeet on its border with the United Arab Emirates.[191] The project was put on hold in 2014 due to falling oil prices, and the link to the Gulf Railway was suspended in 2016.[192] The planned network would be double-tracked, non-electrified, with a speed of 220 km/h passenger traffic with a planned increase to 350 km/h, and international connections with Yemen through Mazyounah and to the United Arab Emirates through Al-Buraimi.[193]
Pakistan
Pakistan's railway minister said in 2016 that when the ministry asked about high-speed rail in Pakistan as part of the CPEC Project, the Chinese recommended a 160-km/h semi-high-speed service instead. The minister added that there was no market for such a project, and the country could not afford it.[194] In 2021, Haier Pakistan suggested a 1,872-km passenger line between Peshawar and Karachi along the motorway which could run at 350 km/h and reduce travel time to five hours and 30 minutes.[195]
Persian Gulf countries
The countries of the Gulf Cooperation Council (UAE, Oman, Qatar, Bahrain, Kuwait and Saudi Arabia) plan a 2,200-kilometre rail network,[196] Etihad Railway, which may include high-speed rail from Dubai to Abu Dhabi.[197] A freight line currently exists.
In 2010, the government of Qatar announced that it planned to have high-speed rail links to Bahrain and Saudi Arabia built in time for the 2022 FIFA World Cup.[198] The project was sidetracked by the Qatar crisis, but in early 2022 the Qatari and Saudi ministers of transport resumed talks about the proposed high-speed rail link.[199]
In 2022, the Saudi Crown Prince proposed The Line: a 500-km/h rail line in Tabuk Province.[200] Saudi transportation authorities were studying a high-speed link in September 2022 between Riyadh and the Eastern Province, with a planned travel time of one hour and 15 minutes.[201] In May 2023, the Kuwaiti government proposed a $3.25 million feasibility study for a 111-km line from Nuwaiseeb Point to Al-Shaddadiyah (Kuwait City) which would link its network to Saudi Arabia's.[202]
Philippines
The San Miguel Corporation proposed building a bullet-train system connecting Laoag in northern Luzon island with Manila and the Bicol Region in southeastern Luzon. By 2010, the project had been put on hold.[203][204]
In April 2013, the National Economic and Development Authority (NEDA) announced plans by Metro Pacific Investments to fund a Clark-Metro Manila high-speed train project as part of a build–operate–transfer scheme. The project, Express Airport Trains, will have at least three stops in Metro Manila and will be built between lanes of the North Luzon Expressway (NLEx). The trains are planned to stop in Quezon City, Manila, and Makati.[205] It would be higher-speed rail, similar to the Tel Aviv–Jerusalem railway (which was also marketed during its planning stage as a high-speed line). The PNR South Main Line reconstruction project, South Long Haul, will have express trains with the same maximum speed.[206]
Projects such as PNR South Long Haul are being designed for an eventual upgrade to high-speed rail.[207] There are also plans for a high-speed rail network in Mindanao as part of future upgrades to the upcoming Mindanao Railway network, with a top speed of 250 km/h (160 mph).[208]
Singapore
See Malaysia, above.
Thailand
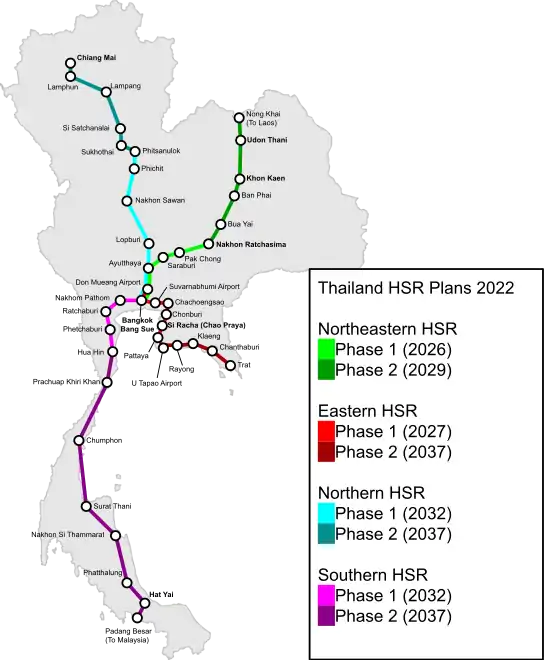
The State Railway of Thailand and the Thai Ministry of Transport have plans for several high-speed rail lines. An HSR line to the eastern seaboard was first proposed in 1996, but there was no progress for over a decade. In 2009, the government asked the Office of Transport and Traffic Policy and Planning (OTP) to create a plan for a new HSR network which included an eastern line to Rayong. In October 2009, it was reported that funding was being sought for four lines linking Bangkok to Chiang Mai (711 km), Nong Khai (600 km), Chanthaburi (330 km), and Padang Besar (983 km).[209] The Thai cabinet reportedly approved the plan the following month, with the shorter eastern route to Chanthaburi intended for construction first.[210] The total cost of all routes is ฿800 billion (US$25 billion). In October 2010, the Thai parliament approved initial proposals for a high-speed rail network to be built with Chinese industrial partners; five lines capable of 250 km/h would radiate from Bangkok, with the line to Ubon Ratchathani later dropped.[211] The routes were finalized before the 2011 election, with a promise to begin construction the following year if the government was re-elected; they lost the election.
After the 2011 election of opposition leader Yingluck Shinawatra, the new government reviewed all HSR plans. It divided them into phases, prioritizing service between Bangkok and Pattaya, Hua Hin, and Nakhon Ratchasima, and expected to tender the lines in 2014.[212]
There were further delays while the military government reviewed all HSR lines after the May 2014 coup, and it initially deferred all projects. Transport Minister Prajin Juntong and his Japanese counterpart, Akihiro Ota, signed an agreement on 27 May 2015 to conduct a feasibility study of the northern HSR.[213] The NCPO agreed in early 2016 to proceed with the eastern HSR route and suggested that it could be extended to Don Mueang International Airport beyond the terminus at Bang Sue Grand Station, providing direct links between Bangkok's three major airports (including Suvarnabhumi Airport and U-Tapao International Airport).[214] In 2017, the Office of Traffic Policy and Planning, the Ministry of Transport and the State Railway of Thailand agreed to the revised plan. In October of that year, the Eastern Economic Corridor Office finalized plans to build a 10-station Eastern HSR line linking Don Mueang Airport, Bang Sue, Makkasan, Suvarnabhumi Airport, Chonburi, Si Racha, Pattaya, U-Tapao Airport, and Rayong. The section to Rayong was excluded in early 2018 due to environmental and safety concerns, and it was decided that the line would end at U-Tapao Airport.[215] In October 2019, after months of delay, the Thai government signed a $7.4 billion agreement with a Charoen Pokphand-China Railway Construction consortium to build eastern HSR from Bangkok to Pattaya in a public-private partnership, with assets reverting to the state after 50 years.[216]
The Japan International Cooperation Agency conducted a feasibility study of northern HSR to Chiang Mai, and reported in 2018 that passenger projections were too low for economic viability.[217] The 670-kilometer line was estimated to cost ฿400 billion, and private investors and the Japanese government declined the project.[218] The Ministry of Transport denied that Japan cancelled the project.[219] On 14 December 2022, the Department of Railways and MLIT-JICA discussed speeding up feasibility studies for the Bangkok-Chiang Mai HSR to March 2023, and requested a study on the economic impact of the station-area development.[220]
The Southern HSR to Hua Hin would be 211 km, with an estimated cost of ฿152 billion, and an extension to the Malaysian border was discussed in September 2021.[221] Malaysia and Thailand agreed in 2022 to set up a joint committee to coordinate a Bangkok-Kuala Lumpur high-speed rail project, beginning a feasibility study in February.[222]
In summer 2022, Thailand was committed to build a $12 billion northeastern HSR line to the Laotian border by 2028 at 250 km/h double-tracked standard gauge.[223] In March 2023, Japan and Thailand continued to discuss beginning construction between Bangkok and Chiang Mai.[224] Thailand agreed to a technology-transfer deal with China in May, with Chinese rail standards.[225]
Turkey
The Turkish government has invested in high-speed rail. The Ankara-Konya high-speed railway opened in 2011, and an extension to Karaman opened in winter 2022; the Ankara–Istanbul high-speed railway opened in 2014. Continuation of the line from Karaman to Ulukışla was under construction in 2022; a planned link with Aksaray, Ulukışla, and Mersin have an anticipated opening in 2024, but has not yet been tendered.[226] The Turkish government intends to connect 52 provinces with high-speed rail networks by 2053, and will develop further lines as current construction is completed.
The Ankara–Sivas high-speed railway, originally planned to open in late 2021, was delayed initially to 2022 and will reduce travel time from 12 hours to under two hours.[227][228][226] The 405-km line was planned to open in April 2023, with stations at Elmadağ, Kırıkkale, Yerköy, Yozgat, Sorgun, Akdağmadeni, Yıldızeli, and Sivas. It has 49 km of tunnels and 49 km of viaducts designed for 250-km/h operation.[229][230] A 247-km extension from Sivas to Kars is concretely planned as an electrified, double-track line with a design speed of 250 km/h, and a five-station design study between Sivas and Erzincan was completed in July 2021.[231]
A spur from Yerköy to Kayseri has not yet been tendered but is planned to be completed by 2025, reducing travel time between Ankara and Kayseri from seven hours to two hours. The 142-km spur to Kayseri would be double-track electrified rail designed for 250-km/h operation, with nine tunnels totaling 12.9 km.[232] Construction on the spur began in July 2022,[233] and will include stations at Şefaatli, Yenifakılı, and Himmetdede.[234]
The Ankara-Izmir high-speed railway is a planned 588-km double-track, electrified railway built for 250-km/h operation whose initial section to Afyonkarahisar was scheduled to open in 2022,[235] but construction was interrupted in 2018 and resumed in 2022. The extension to Izmir will contain 49 tunnels totaling 41 km, 56 viaducts totaling 23 km and six new stations, reducing the current nine-hour trip to three-and-a-half hours.[236]
A 106-km spur off the Istanbul-Ankara line from Osmaneli to Bursa is planned to open by 2023, after construction delays due to earthquake risk and expropriation lawsuits; a further extension to Bandirma was tendered in 2020. The full 201-km line will be built for 200-km/h operation and will cost ₺9.5 billion (US$650 million), reducing travel time between Ankara and Bursa to two hours and ten minutes.[237]
A 229-km high-speed rail line on the European side of the Bosporus will link the Halkalı railway station in Istanbul with the Kapıkule railway station in Edirne, with an anticipated opening of 2023, and will decrease travel time from four hours to one hour and 20 minutes. The double-track, electrified railway will be built for 200-km/h operation and cost ₺10.5 billion ($716 million), of which over half is a European Union grant.[238][239]
Turkmenistan
President Gurbanguli Berdimuhamedov announced that Turkmenistan would build a high-speed train between Turkmenbashi and Turkmenabat in 2012.[240]
Uzbekistan
In addition to the high-speed network from Tashkent through Samarkand to Bukhara, in December 2021 the Asian Development Bank approved a $162 million loan for electrification between Bukhara and Khiva which was 60 percent of the anticipated cost.[241] The 452-km line has a design speed of 250 km/h, and needs electrification for high-speed rail service. A contract was awarded in July 2022 to DB E&C for electrification; construction was scheduled to begin in fall 2022, with stops at Navbokhar, Parvoz, Kiyikli, Zhaikhun, Turon, Khazarasp, and Urgench.[242] High-speed rail service to Khiva is planned to begin in 2024, reducing travel time between Bukhara and Khiva from eight to three hours; in November 2022, President Shavkat Mirziyoyev announced an electrification extension from Khiva to Nukus.[243]
Vietnam
Vietnam's national railway company, Vietnam Railways, has proposed a 1,630-kilometre (1,013 mi) high-speed rail link between Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City capable of running at 250 to 300 km/h (155 to 186 mph).[244] Funding of the $56 billion line would be primarily by the Vietnamese government, with Japanese aid. Technology used on the Japanese Shinkansen has been suggested for the new railway.[245]
Current technology allows trains travelling on the current, single-track Hanoi to Ho Chi Minh City line to complete the journey in about thirty hours.[246] The high-speed rail line would have two standard gauge tracks with no direct road crossings, and would allow trains to complete the Hanoi–Ho Chi Minh City journey in about six hours. The existing line uses narrow-gauge tracks, common in Southeast Asia.[247]
Vietnamese Prime Minister Nguyễn Tấn Dũng had planned to complete the line by 2013, three years sooner than the previously-announced nine-year construction time.[248] Later reports suggested that Japanese development aid would only be available in stages, with completion of the line not expected until the mid-2030s and aid contingent on the use of Shinkansen technology.[244][245] On 19 June 2010, after a month of deliberation, Vietnam's National Assembly rejected the high-speed rail proposal due to its cost. The project's future was in doubt, with National Assembly deputies reportedly asking for further study.[249][250]
In January 2011, Vietnamese Minister of Transport Hồ Nghĩa Dũng suggested that the line might be completed by 2030. The line was 1,555 km long, with trains running at 300 km/h. After the original plan was rejected by the National Assembly, Dũng asked for a new feasibility plan by the end of 2011; the Japanese development agency suggested an interim solution in which the line could be built in separate north and south sections.[251] In 2021, the Vientamese Ministry of Transport announced plans to begin a 250-km segment from Hanoi to Vinh and a 450-km segment between Ho Chi Minh City and Nha Trang in 2028, with a total cost of $5 billion and a design speed of 320 km/h.[252] In July 2022, Prime Minister Phạm Minh Chính requested $10 billion in aid from the Japan Bank for International Cooperation for the project.[253] The Communist Party reaffirmed the strategic importance in March 2023 that the north-south high-speed rail project begin construction by 2030 and finish by 2045, focusing on the Hanoi-Vinh and Ho Chi Minh-Nha Trang sections; the project is estimated to cover 1,559 km, with a speed over 320 km/h and a cost of over $58 billion.[254]
Europe
Belarus
In 2017, Belarusian authorities agreed to offer land to CRCC Asia for construction of a high-speed corridor between the European Union (EU) and Russia. Chinese engineering companies are also interested in building highways and Russian high-speed railways in connection with this route, with a possible interchange with the Moscow–Kazan high-speed rail corridor.[255]
Belgium
The 25N line (opened between 2012 and 2018) is designed for speeds up to 220 km/h, but is limited to 160 km/h. To reduce traffic and travel time, an existing line from Mechelen to Antwerp has been upgraded. Construction began in June 2013 and was completed in November 2021, and it was opened on 14 December of that year.[256]
Czech Republic
In 2017, the government of the Czech Republic approved a high-speed rail development program predicted to cost 645 billion Kč (over €25 billion).[257] The network will cover about 660 kilometers, and will include the construction of new lines and upgrading existing lines to 200 km/h.
- RS1 – Prague–Brno–Ostrava, with a possible extension to Katowice in Poland
- RS2 – Brno–Breclav, with possible extensions to Vienna in Austria and Bratislava in Slovakia
- RS3 – Prague–Plzen, with a possible extension to Munich in Germany
- RS4 – Prague–Ústí nad Labem, with a possible extension to Dresden in Germany
- RS5 – Prague–Liberec or Hradec Králové, with a possible extension to Wrocław in Poland
In 2018, Správa železnic (the Czech railway infrastructure manager) began work on three pilot projects to increase speed on existing lines.[258] These include the sections between Prague and Poříčany (30 km), Brno and Vranovice (25 km), and Přerov and Ostrava (60 km).
In 2020, Deutsche Bahn and the Czech government began feasibility studies of a high-speed rail link (RS4) between Prague and Dresden. The project, projected to cost €5.4 billion, and will include a 25-km tunnel beneath the Ore Mountains. Travel time on the current route is two hours and 15 minutes, with the new link predicted to reduce travel time between Prague and Dresden to 60 minutes. The first section (between Prague and Lovosice) is predicted to be completed by 2035, with the remainder completed by 2050.[259]
Denmark
A high-speed rail line was built as a double track on the Copenhagen–Ringsted Line, which opened in 2019. It initially allowed 180 km/h, increasing to 200 km/h in 2023 when signalling was upgraded. The rail infrastructure is being prepared for 250 km/h. An upgrade of the Ringsted–Odense line to 200 km/h is planned. The Ringsted–Rødbyhavn line is being upgraded to 200 km/h in preparation for the completion of the Fehmarn tunnel, allowing a fast connection between Copenhagen and Hamburg.
Construction began on the Vestfyn Line, a 250-km/h line connecting Odense on the island of Funen to the bridge to Jutland in 2021, allowing alignment to a future bridge for high-speed crossing. A 250-km/h railway from Fredericia–Aarhus is planned. The Hobro-Aalborg line is planned to be upgraded to 200 km/h with new signalling. The projects are planned to reduce travel time between Copenhagen and Aalborg to three hours, compared to four hours and 20 minutes in 2018.
Estonia
An undersea Helsinki–Tallinn Tunnel is a proposed high-speed rail connection between Helsinki and Tallinn with planned maximum speed of 250 km/h (160 mph). This high speed connection would cut the travel time from about 3 hours to half an hour.
Finland
The Helsinki–Turku high-speed railway is a proposed link between Helsinki and Turku with planned maximum speed of 300 km/h (190 mph). A high-speed connection between Helsinki and Tampere with a travel time of one hour through the planned Lentorata tunnel from Helsinki to Kerava via Helsinki Airport station is planned, with an upgrade of the Riihimäki–Tampere railway to high speed or construction of a parallel line. Itärata, an eastern high-speed line between Helsinki and Kouvola via the airport and Porvoo, is also planned.
Hungary
On 28 January 2020, a call for tenders was issued for a detailed feasibility study of the proposed line between Budapest and Cluj-Napoca in Romania. The Hungarian section is expected to allow speeds of 250 to 350 kilometres per hour (160 to 220 mph), and the Romanian section will have a speed of 160 km/h.[260]
Iceland
The Lava Express, an airport rail link passing southeastern Iceland's lava fields, is planned. The line will be 49 km long, of which 14 km will be underground near Reykjavík. Average speed will be 180 km/h, with a maximum speed of 250 km/h. Construction was postponed by 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Ireland
The Irish government said in 2020 that it would begin a study of a 500-km high-speed railway from Belfast via Dublin to Cork and Limerick,[261] which could cost about €15 billion.[262]
Netherlands
The proposed HSL-Oost line was cancelled in 2009. The section of that line between Amsterdam and Utrecht is four-tracked. Two of the four tracks can accommodate 200 km/h, but the voltage is insufficient and the line is planned to be re-electrified to 25 kV AC. Like much of the Netherlands, also, the ground is not stable enough for higher speeds due to peat deposits.[263]
Norway
The Norwegian government has studied five long-distance high-speed lines radiating from Oslo to Bergen, Kristiansand/Stavanger, Trondheim, Gothenburg, and Stockholm. A sixth line would run along the coast, connecting Bergen, Haugesund and Stavanger. Cost and benefit studies were published in 2007 and 2012.[264]
Poland
The Central Rail Line was designed for speeds up to 250 km/h. Although 200 km/h is used for commercial service, higher speeds are planned.
Portugal
Portuguese prime minister António Costa announced in September 2022 a $4.7 billion passenger rail line running about 300 km (185 miles) from Lisbon-Oriente to Porto-Campanhã, cutting travel time by over 50 percent to 75 minutes non-stop and 105 minutes with stops in Leiria, Coimbra and Aveiro.[265] A second phase will include another 150-km (100 miles) line to Porto Airport, Braga, Valença, and a connection to Vigo in Spain. A Lisbon–Porto high-speed rail line was proposed in 2020.[266] The Spanish company Renfe has confirmed that the desire to extend the Madrid-Extremadura high-speed rail line under construction across the border to Evora.[267]
Romania
The European Commission approved €3.9 billion for rail in Romania's National Recovery and Resilience Plan in 2021, which will modernize railways, rolling stock, and signaling systems. A €120 million feasibility study of a high-speed line between Constanta through Bucharest to the Hungarian border was begun in 2022, and is expected to be completed by 2026. Options include a high-speed 590-km route through Sibiu, Cluj, and Oradea, which could cost €17 billion euros; another possibility is a hybrid line with some sections at 200 km/h, and others at 160 km/h.[268]
Russia
Since the 1980s, several high-speed rail networks have been proposed. Vladimir Putin announced plans at a 2013 St. Petersburg economic forum to build a 770-km high-speed line which would connect Kazan and Moscow. Russia's first high-speed line, trains would operate at up to 350 km/h and travel time would be reduced from 13 hours to 3.5. Trains on the Moscow–St. Petersburg line run at up to 250 km/h.[269]
In September 2023, President Putin announced a 1.7 trillion ruble (US$18 billion) new project to build two new tracks between Moscow and St. Petersburg, increasing train speeds to 400km/h over the 650km journey, with financing by VEB.RF and Gazprombank for a proposed operation date of 2028.[270] The long-stalled plans for a line between Moscow and Kazan have been resumed, with Chinese CRRC contracted to build part of the track and supply the trainsets at a Russian-owned Ural Locomotives plant, with the full project expected to be completed by 2024.[270] The final proposed line is between Moscow and Rostov-on-Don, by the Ukrainian border.[270]
Spain
In the summer of 2023, the Spanish government pledged €2.3 million for a design study of a high-speed rail tunnel across the Strait of Gibraltar to connect to Moroccan high-speed rail in Tangier.[46]
Sweden

Many new railway lines in Sweden, including Botniabanan, Grödingebanan, Mälarbanan, Svealandsbanan, Västkustbanan, Vänernbanan (Gothenburg–Trollhättan), can accommodate speeds up to 250 km/h.[271] The country's signaling system (ATC), however, does not allow speeds over 200 km/h. It is being replaced by the European Rail Traffic Management System (ERTMS), allowing speeds up to 250 km/h.[272] ERTMS level 2 has been installed and is being tested on Botniabanan, which allows 250 km/h although passenger trains operate at 200. The Bombardier Regina X55 has been delivered to the SJ rail corporation with a maximum speed of 200 km/h and an option to upgrade the EMU to 250 km/h.[273]
Four major high-speed projects have been proposed in Sweden with speeds between 250 and 350 km/h:
- Norrbotniabanan (Umeå–Luleå) will be built for 250 km/h with mixed passenger and freight traffic in northern Sweden to relieve the congested, outdated single-track Main Line Through Upper Norrland, increase freight traffic, and speed up passenger traffic along the coast.[274]
- Umeå–Dåva (15 km): Under construction since 2018, it is expected to be ready in 2024 initially for firewood freight to the main heating plant in Umeå.
- Dåva–Skellefteå: Construction is planned to begin by 2030.
- Ostlänken (Järna–Linköping) would relieve the congested, slow main lines on the Järna-Linköping section of the Southern Main Line.[275][276] Construction is planned to begin around 2025.
- Götalandsbanan (Gothenburg–Jönköping–Linköping to Stockholm via Ostlänken) would reduce travel time from Gothenburg to Stockholm from three hours and five minutes to two hours.[277]
- Europabanan (Jönköping–Lund), with a speed of 320 km/h[278]
The first three have been studied in detail by the Swedish Transport Administration, and some alignments have been decided. There is political interest in building all four. The Moderate Party government decided in 2012 to build Ostlänken with a maximum speed of 250 km/h after putting all projects on hold in the 2011 budget.[279]
Ukraine
During the early 2000s, Ukraine planned to build 2,593 km of high-speed rail tracks between 2005 and 2015.[280] Rolling stock was purchased in 2010. The maximum operating speed in Ukraine is still 160 km/h, however, and lack of maintenance has caused a number of derailments.
A Moscow-Kyiv high-speed line was proposed in 2011, but Ukraine canceled the project after the 2014 annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation. Russia, which had purchased rolling stock for the planned rail line to Kyiv, used the trains on its Moscow-Nizhny Novgorod line. In January 2023, Ukraine Railways signed an agreement with the Polish government to develop a standard-gauge high-speed rail line from Warsaw through Lviv to Kyiv with a 250-km/h operating speed.[281]
United Kingdom
High Speed 2 (HS2) is a planned high-speed rail line from London to Birmingham, which will connect to the existing British railway network. Its first phase, which will connect London and Birmingham, is expected to be completed between 2029 and 2033.[282] The second phase, which was planned to connect Birmingham to Manchester, was cancelled in 2023. A proposed East Midlands Hub station to serve Nottingham and Derby as part of HS2 was also cancelled in 2021.[283]
The first phase is currently under construction. Northern Powerhouse Rail is a proposed east–west line connecting Liverpool, Manchester and Leeds.
Greengauge 21 released its "Beyond HS2" report in May 2018, which examined how the rail network could develop by 2050. It proposed a number of projects:[284]
- A new high-speed line from Colchester and Cambridge (via Stansted) to Stratford, possibly extending to Canary Wharf
- A new higher-speed line from Perth and Dundee to the Shotts Line
- A new high-speed line bypassing Motherwell
- A new connection between the HS2 eastern leg and Kingsbury, serving Bristol, Cardiff and Plymouth via Cheltenham Spa
- A new link between the West Coast Main Line and Crossrail
- A new link between Langley and Heathrow
- A new link between Richmond and Waterloo to Heathrow Terminal 2
- A new link between Heathrow and Staines
- Northern Powerhouse Rail
- A new line between Darlington and Newcastle
Oceania
Australia
There have been several proposals to develop an HSR line between Sydney and Canberra (via Sydney Airport and Canberra Airport) to link the cities and provide an effective second airport for Sydney. The line is proposed to continue to Melbourne, possibly via Melbourne Airport. The SYD-MEL air-traffic corridor is one of the world's busiest, and HSR would provide faster city-center-to-city-center travel times than flights. In September 2010, Infrastructure Partnership Australia (IPA) and AECOM proposed an east-coast very-fast-train corridor from the Sunshine Coast and Brisbane to Sydney, Canberra and Melbourne.[285] The proposed 71-km Geelong Line (Melbourne-Geelong) would have a maximum speed of 300 km/h and enter service during the 2020s.[286]
In May 2022, a leaked government document contained a draft for a 250 km/h Sydney-Wollongong-Newcastle rail network. Travel time between Parramatta and Newcastle would be reduced from 2.5 hours to one hour, and a Parramatta-Gosford trip would take 25 minutes; Parramatta to Canberra would take 90 minutes.[287]
New Zealand
As part of studies to increase the speed of Te Huia service from Auckland to Hamilton, a new standard gauge line was proposed at a cost of NZ$14.425 billion. Trains would travel at 250 km/h, and travel time between the cities would be 69 minutes.[288][289]
References
- ↑ General definitions of highspeed. Archived 10 December 2006 at the Wayback Machine uic.asso.fr/ 28 November 2006. Retrieved 3 January 2007.
- ↑ "Flagship Projects of Agenda 2063". African Union. Retrieved 28 May 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Towards the African Integrated High Speed Railway Network (AIHSRN) Development" (PDF). African Union. Retrieved 28 May 2022.
- ↑ Zuma, Nkosazana Dlamini (2 April 2016). "Talking points to the 4th General Assembly of the African Forum of Former Heads of State and Government" (PDF). African Union. Retrieved 28 May 2022.
- ↑ "Second Continental Report: On the Implementation of Agenda 2063" (PDF). African Union. February 2022. Retrieved 28 May 2022.
- 1 2 "Detailed Scoping Study (DSS) of Vision 2063 Africa Integrated High Speed Railway Network and Master Plan". Virtual PIDA Information Centre. 1 February 2020. Retrieved 28 May 2022.
- ↑ Kaulbeck, George (12 February 2020). "Detailed Scoping Study (DSS) – of Vision 2063 Africa Integrated High Speed Railway Network and Master Plan". Program for Infrastructure Development in Africa. Retrieved 28 May 2022.
- 1 2 "Tlemcen: Le LGV se rapproche de Maghnia à petite vitesse". ITA (in French). Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ↑ "Tlemcen: La "LGV" vers Oued Tlelat sur de bons rails". Djazairess. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ↑ "» Tlemcen – Akkid Abbas HSR Project, Algeria". Archived from the original on 4 November 2021. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ↑ "Développement du rail à l'ouest : Des projets et des attentes | El Watan". www.elwatan.com. Archived from the original on 4 November 2021. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ↑ "Egypt plans railway project to link Mediterranean with Red Sea – Egypt Independent". Egypt Independent. 13 March 2018. Retrieved 11 April 2018.
- ↑ "Egypt to Construct High-Speed Railway To Link Between Mediterranean and Red Sea: Minister | Egyptian Streets". egyptianstreets.com. 14 March 2018. Retrieved 11 April 2018.
- ↑ "Chinese-led consortium to build $9bn high-speed railway in Egypt, report says". Global Construction Review. 16 September 2020. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- ↑ "Egypt's high-speed electric train route to include 15 stations". Egypt Independent. 7 October 2020. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- ↑ "Egypt agrees deal for $23 billion high-speed rail link". Arab News. 15 January 2021. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- ↑ "Siemens Mobility to commission first high-speed rail network in Egypt". Global Railway Review. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- 1 2 "Egypt takes step toward $23bn high-speed rail network – News – GCR". Global Construction Review. 18 January 2021. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- ↑ "Egypt agrees with Siemens to implement express train 2nd, 3rd phases". EgyptToday. 24 February 2022. Retrieved 16 March 2022.
- ↑ Zand, Bernhard (13 September 2021). "Egypt Picks Europe Over China: High-Speed Rail To Connect Red Sea and Mediterranean". Der Spiegel. ISSN 2195-1349. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ↑ "Siemens to finalise more contracts for Egypt's $4.45bn high-speed rail system by year-end". The National. 13 October 2021. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ↑ Dharma, RanjithKumar (24 February 2023). "NGE wins high-speed rail contract in Egypt". Railway Technology. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- 1 2 "Egypt, Siemens to ink contract for 2 lines of high-speed electric rail in May". Zawya. 16 May 2022. Retrieved 24 May 2022.
- 1 2 "Egypt's Transport Ministry starts construction of 2nd express train line". Egypt Independent. 14 March 2022. Retrieved 1 May 2022.
- ↑ "Egypt's High-Speed Electric Train to be extended to Toshki in Western Desert". EgyptToday. 16 May 2022. Retrieved 24 May 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 "Egypt Expands Railway Network to Include Sudan, Libya". Asharq AL-awsat. Retrieved 1 May 2022.
- ↑ "Kuwait to fund studies for Egypt-Sudan line". International Railway Journal. 12 April 2022. Retrieved 24 May 2022.
- ↑ "Egypt, Sudan connecting Khartoum with Cairo-Cape Town rail line". Arab News. 12 June 2021. Retrieved 25 May 2022.
- ↑ "Egypt extends route of Giza-Aswan high-speed electric train to Abu Simbel". Egypt Independent. 23 January 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ↑ "Siemens to implement 2nd, 3rd lines of Egypt's first high speed train: Ministry". EgyptToday. 12 April 2022. Retrieved 24 May 2022.
- ↑ "Siemens finalises contract for entire Egyptian high-speed rail system". RailTech.com. 31 May 2022. Retrieved 21 June 2022.
- ↑ Zaptia, Sami (20 January 2021). "Egypt and Libya contemplating extending Egypt's rail line to Benghazi". Libya Herald. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ↑ "Egypt plans to extend high-speed rail lines to Sudan, Libya: Transport minister". EgyptToday. 8 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ↑ Ngueyap, Romuald (21 January 2021). "L'Egypte envisage d'étendre son futur TGV jusqu'à Benghazi en Libye (French)". Agence Ecofin. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ↑ "First 14 km of Libyan rail network in place". Railway Gazette International. Retrieved 1 May 2022.
- ↑ "Libya to approve final part of coastal high-speed railway". MEED. 30 November 2010. Retrieved 1 May 2022.
- ↑ Oryx. "This Was Gaddafi's Personal Italian High-Speed Train". Oryx. Retrieved 1 May 2022.
- ↑ "Russian-Libyan Rail Project may be Resumed | Libya Business News". 21 April 2015. Retrieved 1 May 2022.
- ↑ "Talks to Resume Construction of Sirte-Benghazi Railway | Libya Business News". 2 October 2018. Retrieved 1 May 2022.
- ↑ "Egypt may extend high-speed electric train to Libya". EgyptToday. 18 January 2021. Retrieved 1 May 2022.
- ↑ "Train from Tunis to Casablanca, New High Speed Link Between Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia – Tunisia Live". 27 April 2015. Archived from the original on 16 August 2016. Retrieved 5 August 2016.
- ↑ "Morocco : 100 bln MAD for Kénitra-Marrakech-Agadir high-speed rail". en.yabiladi.com. Retrieved 28 April 2021.
- ↑ tarik (2 June 2021). "Un groupe chinois se positionne sur le projet du TGV Marrakech-Agadir". Infomédiaire (in French). Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ↑ "Morocco seeks to more than double its railway network by 2040, reaching 4,400 km". Ecofin Agency. Retrieved 1 May 2022.
- ↑ "Morocco to Launch Rabat-Fez High-Speed Train". Morocco World News. 16 July 2022. Retrieved 22 July 2022.
- 1 2 Johnson, Thomas (20 June 2023). "Europe to Africa high speed rail tunnel boosted by feasibility funding". New Civil Engineer. Retrieved 22 June 2023.
- ↑ "Namibia to pilot SADC high-speed railway project | Confidente". 9 April 2020. Retrieved 28 May 2022.
- ↑ "Egypt, Kuwait Fund sign $2.5m grant deal for railway project". Arab News. 9 April 2022. Retrieved 1 May 2022.
- ↑ "Egypt and Sudan in talks to build new 900km-long railway line". Railway Technology. 9 April 2021. Retrieved 25 May 2022.
- ↑ Republic of Tunisia. "LGV (Ras Jedir – Gabès – Tunis) et (Tunis Tabarka)". Instance générale des partenariats public-privé. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ↑ Sarra, Abdou (3 July 2020). "La Tunisie aura-t-elle son TGV ?". Webmanagercenter. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ↑ "Le TGV de Kais Saied n'est pas une priorité". Espace Manager (in French). Retrieved 16 March 2022.
- ↑ "Ambitious plans will still need funding". Railway Gazette International. 7 June 2010. Archived from the original on 8 September 2012.
- ↑ "The rise of Chinese railway diplomacy". 24 September 2010.
- ↑ "Chinese Company in Talks on South Africa Rail Project". The New York Times. 25 August 2010. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ Onyango, Seth (13 September 2021). "African economies place bet on bullet trains for growth". The Star. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ↑ de Wet, Phillip (20 April 2022). "China is keen to help build a Johannesburg to Durban high-speed train". Business Insider: South Africa. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ "Plans for new high-speed trains in South Africa". Businesstech. 19 October 2022. Retrieved 24 October 2022.
- ↑ Argentina confirms high speed rail consortium Railway Gazette International 17 January 2008.
- ↑ "2009-02-01". Retrieved 22 October 2010.
- ↑ 'Cobra' offers high speed future Archived 15 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine Railway Gazette International August 2007.
- ↑ "El Tren bala hacia Mar del Plata". Clarín (in Spanish). 2008. Archived from the original on 22 February 2008. Retrieved 21 February 2008.
- ↑ New prospects for very high speed rail travel 28 April 2008
- ↑ In Tokyo Rio governor assures high speed rail Archived 12 October 2010 at the Wayback Machine Rio 2016. Retrieved 21 June 2009.
- ↑ Brazil to build high-speed rail linking Rio and Sao Paulo Pravda. 28 May 2007. Retrieved 21 June 2009.
- ↑ Brazil eyes 2-phase high speed train tender in Feb Reuters. Retrieved 21 June 2009.
- ↑ Vermont Agency of Transportation (VTRANS) Archived 24 April 2011 at the Wayback Machine, State of Vermont, Boston to Montreal High-Speed Rail (BMHSR) Planning and Feasibility Study
- ↑ "U.S. Department of Transportation: Barack Obama 2009 HSR proposal". Archived from the original on 24 May 2009.
- ↑ Cooperativa.cl. "Proyecto de tren rápido Santiago-Valparaíso se congeló producto de la pandemia". Cooperativa.cl (in Spanish). Retrieved 17 March 2022.
- ↑ "BNamericas – Santiago-Valparaíso high-speed rail link not..." BNamericas.com. Retrieved 17 March 2022.
- ↑ "BNamericas – Plans for Santiago-Valparaíso high-speed tra..." BNamericas.com. Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ↑ "Portal ANI". Portal ANI.
- 1 2 3 http://www.azcentral.com/arizonarepublic/business/articles/0106mextrain06.html
- ↑ "Bullet Train to Mexico City Looks to be Back on Track ? | Guadalajara Reporter". Archived from the original on 30 April 2011. Retrieved 30 October 2010.
- 1 2 "Systra : Project for a Mexico City – Guadalajara High Speed Line. Rail transport engineering, public transport engineering". Archived from the original on 1 May 2011. Retrieved 30 October 2010.
- ↑ "Slim to invest in Santa Cruz". The America's Intelligence Wire. 21 January 2005.
- ↑ "Mexico to build cross-peninsular high-speed railway line" 16 June 2011; see http://www.globalmasstransit.net/archive.php?id=6819 Archived 27 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Route selected for Mexico City – Querétaro high speed line". Railway Gazette International. Retrieved 11 May 2023.
- ↑ "Tips to Improve the Style of Your College Essay Significantly | theguadalajarareporter.com". Retrieved 11 May 2023.
- ↑ "Mexico tenders for high-speed train linking capital and Queretaro". Reuters. 27 July 2014. Retrieved 11 May 2023.
- ↑ "Mexico Suddenly Canceled Its Multi-Billion-Dollar Deal for a Bullet Train". Business Insider. Retrieved 6 August 2016.
- ↑ "Mexico-Queretaro train back on drawing board in new transport plan". Mexico News Daily. 10 July 2018. Retrieved 17 March 2022.
- ↑ "BNamericas – Mexico green lights US$2.3bn high-speed trai..." BNamericas.com. Retrieved 17 March 2022.
- ↑ "TM Sourcing Announces The Start Of "El Bajío" Train". Mexico Business. Retrieved 17 March 2022.
- ↑ Diamond, Randy (1 September 2021). "Can new interest in S.A.-to-Monterrey train make it reality?". mySA. Retrieved 17 March 2022.
- ↑ "China gives Panama its plan for a $4bn high-speed rail line to Costa Rica". Global Construction Review. 21 March 2019. Retrieved 11 June 2020.
- ↑ "Tren chino, fuera de las prioridades de Cortizo". La Estrella de Panamá (in Spanish). Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ↑ Goldberg, Bruce (June 2006). "Metroliner's Amazing Rave". Trains: 53.
- ↑ "History of THSRTC". Texas High Speed Rail and Transportation Corporation. Retrieved 2 September 2023.
- ↑ "FRA approvals pave way for Texas high speed line construction". Railway Gazette. 23 September 2020. Retrieved 26 September 2020.
- ↑ "Texas central selects Renfe as operating partner". www.rtands.com. 11 October 2018.
- ↑ "High speed rail moves ahead: Texas Central proceeds with addition of Italian engineering, construction group". Corsicana Daily Sun. 9 October 2018. Retrieved 16 October 2018.
- ↑ "California picks first high speed section". Railway Gazette International.
- ↑ "Grant reallocations double California's high speed pilot section". Railway Gazette International.
- ↑ "High-speed train connecting LA and Las Vegas expected to open in 2027". Spectrum News 1. Retrieved 24 April 2023.
- ↑ "Amtrak proposes Northeast Corridor high speed line". Railway Gazette International.
- ↑ Heather J. Carlson (27 July 2016). "Not so fast: high-speed rail plan advancing slower than expected". Retrieved 6 August 2016.
- ↑ "Yahoo News – Latest News & Headlines".
- ↑ "Spain keen to invest in rail sector". Archived from the original on 16 September 2014. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- ↑ "China wants to invest in Dhaka-Ctg high-speed train". New Age | The Most Popular Outspoken English Daily in Bangladesh. Retrieved 8 April 2022.
- ↑ Adhikary, Tuhin Shubhra (3 March 2022). "Russia keen on funding three rail projects". The Daily Star. Retrieved 16 March 2022.
- 1 2 Adhikary, Tuhin Shubhra (8 June 2022). "High-speed rail network: China seeks MoU ASAP". The Daily Star. Retrieved 21 June 2022.
- ↑ "JS whip: Bullet train on Dinajpur-Dhaka route by 2027". www.dhakatribune.com. 4 February 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ↑ "Cambodia to examine possibility of developing and expanding existing railways into high-speed railways – Khmer Times". 17 December 2021. Retrieved 8 April 2022.
- ↑ "PM Mulls High Speed Rail Plan ⋆ Cambodia News English". Cambodia News English. 16 December 2021. Retrieved 8 April 2022.
- ↑ Pisei, Hin. "Cambodia-Thailand rail reconnected after 45 years". www.phnompenhpost.com. Retrieved 8 April 2022.
- ↑ "Cambodia considers high-speed rail development – Khmer Times". 4 April 2022. Retrieved 8 April 2022.
- ↑ "PM on his way back to Cambodia after successful China trip – Khmer Times". 11 February 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ↑ Smith, Kevin (13 February 2023). "China pledges funding for Cambodian railway upgrade". International Railway Journal. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ↑ Kunmakara, May (4 July 2023). "Study underway for Phnom Penh-S'ville high-speed rail". The Phnom Penh Post. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- ↑ "Railways likely to propose creation of four new bullet train corridors taking total to 12 – The New Indian Express". www.newindianexpress.com. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ↑ "Japan hopes to sell bullet trains to India | Local | House of Japan – Japan News Technology Autos Culture Life Style". Archived from the original on 15 November 2011. Retrieved 27 February 2012.
- ↑ "India to get shinkansen sales blitz | the Japan Times Online". Archived from the original on 23 April 2012. Retrieved 27 February 2012.
- ↑ "France to help India realise high-speed train dream | mydigitalfc.com". Archived from the original on 1 January 2013. Retrieved 27 February 2012.
- ↑ "Spains Talgo eyes high-speed train biz, plans office in India". 6 October 2011.
- ↑ "Japan and India agree bullet train, nuclear deals". news.yahoo.com. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ↑ "First glimpse of Mumbai-Ahmedabad bullet train – Mumbai-Ahmedabad bullet train". The Economic Times. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ↑ "India's First-ever Bullet Train Set to Roll by 2026, says Railway Minister". News18. 8 December 2021. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ↑ "India's bullet train faces 5-year delay: High costs, Japan firms not so keen". The Indian Express. 6 September 2020. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ↑ "Confident Of Running First Bullet Train In 2026: Ashwini Vaishnaw". odishabytes. 6 June 2022. Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- 1 2 "Kerala's SilverLine: why it has been planned, why it is facing protests". The Indian Express. 22 December 2021. Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- ↑ "Project at a glance". Archived from the original on 25 November 2021. Retrieved 25 November 2021.
- ↑ "SilverLine debate: Has K-Rail fallen for the trap set by Japan?". OnManorama. Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- ↑ "Deadline for social impact study over, SilverLine loses steam". The New Indian Express. Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- ↑ "SilverLine a burden on Kerala, Indian Railways: Ashwini Vaishnaw". The New Indian Express. Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- ↑ "Delhi-Varanasi Bullet Train to Cover 800km distance in less than 4 hours". TimesNow. 28 July 2022. Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- ↑ Sikarwar, Ayushi (28 July 2022). "Delhi-Varanasi Bullet Train: 10 hours long journey confined for 3, Railway's mega plan on floor". NewsroomPost. Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- ↑ Tekwani, Muskaan. "Aerial inspection of New Delhi-Lucknow-Varanasi bullet train's elevated tracks underway". Knocksense. Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- ↑ "Mysuru-Chennai High-Speed Rail: Govt. To Acquire Land". Star of Mysore. 30 July 2022. Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Railway Budget 2021: Indian Railways to focus on new bullet train networks in coming years?". The Times of India. 23 January 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2023.
- 1 2 3 Agarwal, Anshu (31 January 2021). "Delhi likely to get 2 stations under 3 proposed Bullet train projects". Business Standard India. Retrieved 1 December 2023.
- ↑ "Growever Wins Varanasi – Howrah design". Metrorail. 9 April 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2023.
- ↑
- ↑ "High speed rail corridor: Travel time from Mumbai to Hyderabad and Nagpur to reduce by 50 percent". Mumbai Mirror. 31 January 2020. Retrieved 11 June 2020.
- ↑ "Big boost for city as Pune-Nashik high-speed rail project gets Centre's in-principle approval". Hindustan Times. 5 February 2023. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ↑ "Ahmedabad-Rajkot new rail link approved; to help Saurashtra region avail Bullet Train services". The Financial Express. 19 December 2020. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ↑ Shah, Narendra (23 December 2022). "A Silverline Project to connect entire Kerala". Metro Rail News. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ↑ "Indonesia to Build Railway for High-Speed Trains". RedOrbit, 7 February 2006.
- ↑ "Indonesia Plans 'Beauty Contest' Between China and Japan for High-Speed Train". Jakarta Globe. 14 July 2015. Retrieved 1 October 2015.
- ↑ "Indonesia to award fast train contract to China – Japanese embassy official". Reuters. 29 September 2015. Retrieved 1 October 2015.
- ↑ "Indonesia awards multi-billion-dollar railway project to China over Japan". ABC. 30 September 2015. Retrieved 1 October 2015.
- ↑ "Proyek Kereta Super Cepat Jakarta-Surabaya Pakai Dana Utang 40 Tahun". 21 February 2012.
- ↑ "Groundbreaking of High Speed Rail Project Jakarta – Bandung". WIKA. 21 January 2016.
- ↑ Bestari, Fardi (13 April 2021). "Progres Pembangunan Proyek Kereta Cepat Jakarta – Bandung" [Jakarta – Bandung High Speed Rail Project Development Progress]. Tempo.co (in Indonesian). Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ↑ Dita Alangkara (14 October 2022). "Indonesia Gears Up to Start its First High-Speed Rail Line". The Diplomat. Retrieved 24 October 2022.
- ↑ "Indonesia in Talks with China on High-Speed Rail Cost Overrun". D-Insights. 2 August 2022. Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- 1 2 Siregar, Kiki (22 June 2023). "Indonesia to conduct study on Bandung-Surabaya high-speed rail link: Coordinating Minister". Channel News Asia. Retrieved 22 June 2023.
- ↑ Fahky, Adimas (11 February 2022). "Govt urged to review Jakarta-Semarang high-speed train project". Antara News. Retrieved 16 March 2022.
- ↑ Adimas Raditya, F P (9 February 2022). "Transportation Ministry outlines prioritised railway projects in 2022". Antara News. Retrieved 16 March 2022.
- ↑ Juwita, Ruth Dea (6 July 2023). "Government plans to extend high-speed rail to Surabaya vis Yogyakarta". The Jakarta Post. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- ↑ Sulaiman, Stefanno (6 September 2023). "China, Indonesia discuss extending Jakarta high-speed railway". Reuters. Retrieved 15 September 2023.
- ↑ "High-speed railway delayed again, but it's for the better, experts say". The Jakarta Post. 8 August 2023. Retrieved 6 October 2023.
- ↑ "Chinese Premier Li Qiang takes a test ride on Indonesia's new high-speed railway". AP News. 6 September 2023. Retrieved 9 September 2023.
- ↑ "تامین اعتبار ۲ میلیارد یورویی در مرحله اول توسعه راهآهن تهران-قم- اصفهان/ تکمیل آزادراه کنارگذر شرق اصفهان/ عقد قرارداد توسعه فرودگاه اصفهان با چهارمین شرکت عمرانی جهان" (in Persian). 24 August 2016. Retrieved 12 September 2016.
- ↑ "Pandemic Not Likely to Stop China From Building Influence in Iran". VOA. 31 March 2020. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ↑ "Iran, Italy Sign High-Speed Rail Deal". Financial Tribune. 11 July 2017. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ↑ "Italy's state train company to help Iran develop rail system". Reuters. 9 February 2016. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ↑ "Chinese firms to build Qom-Arak railway line". irandaily.ir. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ↑ "Iranian Railway Projects In Jeopardy Of Being Canned, Due To Trump's Sanctions". caspiannews.com. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ↑ "در صورت تامین مالی طرح قطار پرسرعت، مسیر تهران – مشهد تا پنج سال دیگر 3 ساعت و نیمه می شود". danakhabar.com. Retrieved 12 September 2016.
- ↑ "China quits Tehran-Mashhad railway electrification project". Mehr News Agency. 23 January 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ↑ Mirovsky, Arik (17 November 2020). "The goal: Tel Aviv to Beersheva by train in 35 minutes". Globes. Retrieved 20 November 2020.
- 1 2 "Israel Plans 30-Minute High-Speed Train From Haifa to Tel Aviv". The Algemeiner. Retrieved 16 March 2022.
- ↑ "Abe says gov't will bring forward Tokyo-Osaka maglev train service – the Mainichi". Archived from the original on 2 June 2016. Retrieved 13 June 2016.
- ↑ "Japanese maglev train breaks 600 kph record in last of test runs". International Business Times UK. 21 April 2015.
- ↑ "Shinkansen to get 3 new sections : National : DAILY YOMIURI ONLINE (The Daily Yomiuri)". Archived from the original on 7 July 2012. Retrieved 30 June 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Kazakhstan plans 1 000 km high speed line". Railway Gazette International. 13 March 2013. Archived from the original on 17 March 2013. Retrieved 16 March 2013.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Kazakhstan to build first high-speed line". International Railway Journal. 13 March 2013.
- ↑ "President Opens Train Manufacturing Plant "Tulpar-Talgo"". 9 December 2011.
- ↑ Hashimova, Umida. "What a New High-Speed Railway Tells Us About Kazakhstan-Uzbekistan Relations". thediplomat.com. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ "Ташкент и Туркестан свяжет высокоскоростная ж/д магистраль". Газета.uz (in Russian). 28 January 2021. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ "Ким Чен Ын прокатится на поезде ВСМ". www.rzd-partner.ru.
- ↑ "KL-Singapore bullet train derailed by high cost". 23 April 2008. Archived from the original on 23 April 2008.
- ↑ "Siemens keen on Kuala Lumpur-Singapore high-speed train deal". 7 April 2007. Archived from the original on 17 July 2010.
- ↑ "BERNAMA – YTL Hopes for Bullet Train Project to Materialise". Archived from the original on 4 June 2011. Retrieved 17 December 2009.
- ↑ "Fast track the Sípore bullet train project". 4 July 2009. Archived from the original on 4 July 2009.
- ↑ http://www.sun2surf.com/article.cfm?id=47759%5B%5D
- ↑ "KL-Singapore high-speed link to kick off". Investvine.com. 20 February 2013. Archived from the original on 5 March 2013. Retrieved 27 February 2013.
- ↑ Senator Datuk Abdul Rahim Rahman (25 June 2011). "High-speed rail will spur growth in hub cities". The Star.
- ↑ "Report: KL-Singapore rail link could be RM50b cheaper | Malay Mail". www.malaymail.com. Archived from the original on 19 June 2018. Retrieved 19 June 2018.
- ↑ Yong, Charissa (5 September 2018). "Malaysia, Singapore ink agreement to defer high-speed rail project for 2 years; KL to pay S$15m for suspending work". The Straits Times. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- ↑ Lim, Adrian (31 January 2019). "Deferred High-Speed Rail deal: Malaysia informs Singapore of $15m remittance". The Straits Times. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- ↑ Yusof, Amir (31 May 2020). "Malaysia, Singapore agree to defer HSR project until Dec 31: Khaw Boon Wan". CNA. Archived from the original on 11 June 2020. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- ↑ Tham, Yuen-C (1 January 2021). "KL-Singapore High Speed Rail terminated after both countries fail to reach agreement on M'sia's proposed changes to project". The Straits Times. Retrieved 1 January 2021.
- ↑ Baharudin, Hariz (29 March 2021). "Malaysia pays S'pore $102.8 million for costs incurred in terminated HSR project". The Straits Times. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- 1 2 Azman, Nur Hanani (16 March 2022). "KL-Bangkok HSR may not be economically viable". The Malaysian Reserve. Retrieved 16 March 2022.
- ↑ Jaafar, Fayyadh (19 July 2022). "Govt to continue high-speed rail projects". The Malaysian Reserve. Retrieved 23 July 2022.
- ↑ Shadique, Jassmine (11 May 2023). "Malaysia and Singapore keen to revive KL-Singapore HSR project". New Straits Times. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ↑ "Full steam ahead for China-Myanmar high-speed railway". Asia Times Online. 21 February 2019. Retrieved 31 August 2019.
- ↑ "China-Myanmar high-speed railway quietly back on track". The Myanmar Times. 6 July 2018. Archived from the original on 27 January 2022. Retrieved 31 August 2019.
- ↑ Prabhu, Conrad; Observer, Oman Daily. "Nod for GCC Railway Authority spurs hopes for revival of Omani rail project". www.zawya.com. Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ↑ "Oman halts work on trans-Gulf rail link". Global Construction Review. 4 May 2016. Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ↑ "Oman Rail". 12 February 2017. Archived from the original on 12 February 2017. Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ↑ "Pakistan can't afford to have bullet trains: Railway minister". The Times of India. 30 November 2016. ISSN 0971-8257. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ↑ "Javed Afridi hints at introducing bullet train from Peshawar to Karachi". Global Village Space. 15 January 2021. Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ↑ "2010-10-01". Retrieved 12 October 2010.
- ↑ "High speed Dubai to Abu Dhabi rail plan revealed". arabiansupplychain.com. Archived from the original on 6 October 2011. Retrieved 12 October 2010.
- ↑ International2010-12-09T11:18:00, Railway Gazette. "Urban rail network to underpin Qatar World Cup". Railway Gazette International.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ↑ "Saudi-Qatar reconciliation, from a divisive canal to a railroad connection". Doha News | Qatar. 11 January 2022. Retrieved 14 January 2022.
- ↑ "Saudi Arabia's The Line is what happens when tech bro culture meets Middle Eastern autocracy". New Statesman. 1 August 2022. Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- ↑ "Ministry studies project linking Riyadh and Eastern Province with a fast train". Saudigazette. 5 September 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ↑ Staff Writer; Times, Arab. "Systra tasked with studying railway link between Saudi Arabia & Kuwait". www.zawya.com. Retrieved 9 May 2023.
- ↑ "San Miguel mulls bullet train project". Philstar.com (The Philippine Star Online). 26 March 2010. Archived from the original on 6 September 2012.
- ↑ "Philippine San Mig eyes airport, bullet train deals for infrastructure". The Malaysian Insider. 11 April 2010. Archived from the original on 28 March 2010.
- ↑ "NEDA says MRT-7 and bullet train projects under BOT". Manila Bulletin. 17 April 2013.
- ↑ "Towards Improving Connectivity Between the Bicol and Calabarzon Regions". nro5.neda.gov.ph. National Economic and Development Authority. Archived from the original on 14 November 2019. Retrieved 8 February 2020.
- ↑ Agence France-Presse. "FACT CHECK: No, this is not a map of the Philippines' high-speed rail system". ABS-CBN News. Retrieved 8 February 2019.
- ↑ Sarmiento, Bong (27 November 2019). "Dream train for Mindanao still in the doldrums". MindaNews. Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- ↑ "SRT to seek funds for infrastructure". The Nation. 29 October 2009. Archived from the original on 8 October 2012.
- ↑ "SCabinet approves Bt100 billion hi-speed rail construction plan". MCOT English News. 11 November 2009. Archived from the original on 19 November 2009.
- ↑ "Thailand to negotiate with China on high-speed proposal – International Railway Journal". 30 October 2010. Archived from the original on 1 November 2010. Retrieved 30 October 2010.
- ↑ Marukatat, Saritdet (13 May 2013). "Rayong added to high-speed rail link". Bangkok Post. Retrieved 23 July 2022.
- ↑ "Japan sets high-speed railway survey". Bangkok Post. 29 July 2015.
- ↑ Mahitthirook, Amornrat (25 January 2016). "Military government set to link 3 airports". Bangkok Post. Retrieved 23 July 2022.
- ↑ Theparat, Chatrudee; Chantanusornsiri, Wichit (14 February 2018). "EEC high-speed railway to steer clear of Rayong on safety fears". Bangkok Post. Retrieved 23 July 2022.
- ↑ "Thailand signs agreement to build Bangkok-Pattaya rail link". South China Morning Post. 24 October 2019. Retrieved 23 July 2022.
- ↑ Hongtong, Thodsapol (25 July 2018). "Losses predicted for high-speed railway". Bangkok Post. Retrieved 23 July 2022.
- ↑ Hongtong, Thodsapol (27 September 2019). "Govt mulls end of fast train plan". Bangkok Post. Retrieved 23 July 2022.
- ↑ "ก.คมนาคม ยันญี่ปุ่นไม่ยกเลิกลงทุนรถไฟความเร็วสูง". thaipbs.or.th (in Thai). 27 October 2018.
- ↑ ""กรมราง" ถก "ญี่ปุ่น" เร่งศึกษาลงทุนรถไฟความเร็วสูง "กรุงเทพฯ-เชียงใหม่" จบใน มี.ค. 66". 14 December 2022.
- ↑ "Muhyiddin floats idea of KL-Bangkok high-speed rail in Parliament | Coconuts". coconuts.co/. Retrieved 23 July 2022.
- ↑ Bernama (17 May 2022). "Malaysia, Thailand agree to set up special committee on HSR project". Free Malaysia Today. Retrieved 23 July 2022.
- ↑ "Thailand Sets 2028 Target to Finish High-Speed Rail Link with China". VOA. 17 July 2022. Retrieved 23 July 2022.
- ↑ "Bangkok-Chiang Mai rail project gears up". Bangkok Post. 8 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ↑ Chen, Stephen (15 May 2023). "China will transfer high-speed railway tech to Thailand, engineers say". South China Morning Post. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- 1 2 "Ankara-Sivas YHT hattı yıl sonunda hizmete alınacak". www.trthaber.com (in Turkish). 14 April 2022. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ "Testing underway on Ankara – Sivas high speed line". Railway Gazette International. 9 March 2020. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ "Ankara Sivas High Speed Train Project Completion Date Announced". Raillynews. 1 January 2020. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ "Domestic Rail Used for the First Time on Ankara Sivas High Speed Train Line". 16 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ↑ "99,67 percent physical progress was achieved in Ankara-Sivas High Speed Line". 22 November 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ↑ "The design of the high-speed railroad Sivas-Erzincan in Turkey was completed | RailTarget". www.railtarget.eu. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ "Bakan Karaismailoğlu'ndan Kayseri'ye hızlı tren müjdesi – Son Dakika Haberler". 16 December 2021. Archived from the original on 16 December 2021. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ Preston, Robert (30 July 2022). "Work starts on Yerköy – Kayseri high-speed line in Turkey". International Railway Journal. Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- ↑ "Turkey breaks ground for new high-speed line". RailTech.com. 25 July 2022. Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- ↑ "Ankara İzmir YHT 2022 Yılı Sonunda Tamamlanıyor | RayHaber | RaillyNews". 29 June 2020. Archived from the original on 29 June 2020. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ "Ankara-İzmir Yüksek Hızlı Tren Hattı'nda çalışmalar hızlanıyor". www.trthaber.com (in Turkish). 22 March 2022. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ Ozarfat, Esra (1 April 2021). "Bursa'nın hızlı treni 2023'te raylarda". Dunya. Archived from the original on 1 April 2021. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ "Halkalı-Kapıkule 'hızlı' demir yolu hattının yapımı sürüyor". www.aa.com.tr. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ "Halkalı-Kapıkule Demir Yolu Projesi'nin Edirne'deki viyadük çalışmaları sürüyor". www.aa.com.tr. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ "Turkmenistan will build high-speed train line". Railly News. 5 January 2012. Retrieved 20 April 2022.
- ↑ Asian Development Bank (29 December 2021). "Loan Agreement (Ordinary Operations) for Loan 4170-UZB: Central Asia Regional Economic Coperation (sic) Corridor 2 (Bukhara-Miskin-Urgench-Khiva) Railway Electrification Project". Asian Development Bank. Retrieved 21 June 2022.
- ↑ Allan, Keri (2 August 2022). "DB Engineering and Consulting to Oversee Rail Electrification Project in Uzbekistan". Railway-News. Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- ↑ "High-speed trains to Nukus to be launched in Uzbekistan". m.akipress.com. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- 1 2 "The hare and the tortoise". Railway Gazette International. 21 September 2009.
- 1 2 "Vietnam to build high-speed rail with Japan aid". Reuters News. 20 July 2006. Retrieved 20 July 2006.
- ↑ "Vietnam Railways Website (English)". Vietnam Railways. Archived from the original on 10 May 2008. Retrieved 10 May 2008. Check the timetable from Ha Noi to Sai Gon (or vice versa) to see journey times.
- ↑ "Railway plans to build 880 km express line". Viet Nam News. 20 July 2006. Retrieved 20 July 2006.
- ↑ Bill Hayton (20 July 2006). "Vietnam plans new railway link". BBC News. Retrieved 20 July 2006.
- ↑ "National Assembly rejects express railway project". VietNamNet Bridge. 21 June 2010. Archived from the original on 28 June 2010. Retrieved 21 June 2010.
- ↑ "Vietnamese legislators reject $56B bullet train in rare move against Communist leaders". Metro News Vancouver. Associated Press. 21 June 2010. Retrieved 21 June 2010.
- ↑ "Cross-border upgrading advances".
- ↑ "Vietnam announces start date for 1,500km North–South railway". Global Construction Review. 2 November 2021. Retrieved 20 March 2022.
- ↑ Tuan, Viet (22 July 2022). "PM requests Japan's help for north-south high speed railway". VN Express. Retrieved 23 July 2022.
- ↑ VnExpress. "Trans-Vietnam high-speed railway work to start by 2030 – VnExpress International". VnExpress International – Latest news, business, travel and analysis from Vietnam. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ↑ "ЗА ЧАС ИЗ СМОЛЕНСКА ДО МИНСКА: КИТАЙЦЫ ПЛАНИРУЮТ ПОСТРОИТЬ В БЕЛАРУСИ СКОРОСТНУЮ ЖЕЛЕЗНУЮ ДОРОГУ (in Russian) An hour from Smolensk to Minsk: The Chinese plan to build a high-speed railway in Belarus". rus-bel.online. 22 May 2017. Archived from the original on 25 January 2022. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ↑ "Infrabel and SNCB to open Mechelen rail bypass". International Railway Journal. 9 December 2020. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ↑ "Vláda schválila více peněz pro vědu i školství a plán rozvoje vysokorychlostní železnice v ČR". www.vlada.cz (in Czech). Retrieved 26 January 2021.
- ↑ Sura, Jan (23 April 2018). "Polabí či Moravská Brána. SŽDC začala řešit "izolované" vysokorychlostní tratě". Retrieved 25 January 2021.
- ↑ Hayes, Mike (3 March 2020). "Dresden-Prague high-speed rail gets nod". khl.
- ↑ "Budapest – Cluj high-speed design tender gets underway". International Railway Journal. 3 February 2020. Retrieved 4 February 2020.
- ↑ "Study to investigate Belfast – Dublin – Cork high-speed line". International Railway Journal. 4 August 2020. Retrieved 26 September 2020.
- ↑ "Review of €15bn high-speed rail line linking Dublin, Belfast, Cork". Irish Times. 5 August 2020. Retrieved 26 September 2020.
- ↑ treinreiziger.nl (14 December 2021). "Spoorbodem zorgt voor problemen: snelheidsbeperkingen voor nieuwe treinen dreigen". Treinreiziger.nl (in Dutch). Retrieved 10 February 2022.
- ↑ Jernbaneverket: Oppsummering og hovedkonklusjoner for høyhastighetsutredningen (Norwegian)
- ↑ Russell, Edward; September 29th, Skift; EDT, 2022 at 6:48 AM. "Portugal Plans $4.7 Billion Lisbon-Porto High-Speed Rail Line". Skift. Retrieved 24 October 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ↑ Portugal, Rádio e Televisão de (22 October 2020). "Governo quer linha ferroviária de Alta Velocidade entre Lisboa e Porto". Governo quer linha ferroviária de Alta Velocidade entre Lisboa e Porto.
- ↑ "Is a new high-speed train route launching between Madrid and Lisbon?". euronews. 17 August 2023. Retrieved 15 September 2023.
- ↑ "Romania to study first high-speed railway and revamp rail infrastructure". RailTech.com. 28 April 2022. Retrieved 29 April 2022.
- ↑ "Potential Investors Get Preview of Moscow-Kazan High-Speed Rail Project". 4 March 2014. Retrieved 5 August 2016.
- 1 2 3 Briefing, Russia (27 August 2023). "Putin Signs Off US$18 Billion On Europe's Largest High-Speed Rail Project". Russia Briefing News. Retrieved 15 September 2023.
- ↑ "BanaVäg i Väst – BanaVäg i Väst". Archived from the original on 27 October 2010. Retrieved 17 September 2012.
- ↑ "The Swedish ERTMS Programme – Trafikverket". Archived from the original on 25 August 2010. Retrieved 17 September 2012.
- ↑ "Vagnguide – Motorvagn X55 | Järnväg.net – guiden till Sveriges tåg och järnvägar". Archived from the original on 18 August 2012. Retrieved 17 September 2012.
- ↑ "Norrbotniabanan – Trafikverket". Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 28 March 2015.
- ↑ "Ostlänken – Trafikverket". Archived from the original on 16 September 2012. Retrieved 17 September 2012.
- ↑ "Kapacitetssituationen 2009 Banverkets järnvägsnät" (PDF) (in Swedish). Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 9 September 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ↑ "Götalandsbanan – Trafikverket". Archived from the original on 25 May 2012. Retrieved 20 July 2010.
- ↑ "Europabanan". Archived from the original on 23 September 2009. Retrieved 11 November 2010.
- ↑ "Statens budget 2011" [State Budget 2011]. Government.se (in Swedish). Regeringskansliet. Archived from the original on 22 March 2011.
- ↑ "Скоростной железнодорожный транспорт в Украине | Харьковчане за электротранспорт". Archived from the original on 16 April 2019. Retrieved 11 February 2019.
- ↑ "Ukrainian Railways to study first high-speed rail line to Poland in European gauge". RailTech.com. 20 January 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ↑ "HS2 Phase One full business case". GOV.UK. Archived from the original on 19 April 2020. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- ↑ "Integrated Rail Plan for the North and Midlands" (PDF). Department for Transport. 18 November 2021. p. 81. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 November 2021. Retrieved 18 November 2021.
- ↑ Greengauge 21 (May 2018). Beyond HS2 (PDF) (Report).
{{cite report}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ↑ "East Coast High Capacity Infrastructure Corridors". Archived from the original on 10 July 2011. Retrieved 4 May 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link) - ↑ "Mapping Australia's high-speed rail routes". www.railway-technology.com. 6 November 2018.
- ↑ Rabe, Matt O'Sullivan, Tom (11 May 2022). "'Radically faster': Parramatta at centre of NSW's high-speed rail future". The Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 11 May 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ "Multibillion-dollar cost of Hamilton to Auckland Rapid Rail service revealed". Stuff (Fairfax). 25 August 2020.
- ↑ "Hamilton to Auckland Intercity Connectivity – Interim Indicative Business Case" (PDF). July 2020.