 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
potassium tetrafluoridoaluminate | |
| Other names
potassium tetrafluoroaluminate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.971 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
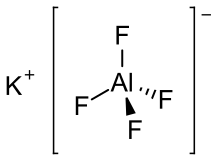
| KAlF4 | |
| Molar mass | 142 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 2.9 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | > 600 °C (1,112 °F; 873 K) |
| 2 g/L | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Danger | |
| H315, H319, H332, H335, H362, H372, H412 | |
| P201, P260, P261, P263, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P302+P352, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P312, P314, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Solvay MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Potassium aluminium fluoride (PAF, chemical formula KAlF4) is an inorganic compound.
This compound is used as flux in the smelting of secondary aluminium, to reduce or remove the magnesium content of the melt. The main environmental issue that arises from using PAF is the production of fluoride gases. Calcium hydroxide is widely used to suppress the fluorides produced but in most cases fails to remove it sufficiently.
PAF is also present in a wide range of products for the metals industry as a fluxing agent within additives to help its dispersion within a charge.
It is also used as an insecticide.[1]
A single natural occurrence has been reported at a burning coal bank at Forestville, Pennsylvania, as an unnamed mineral.[2]
References
- ↑ "potassium aluminium fluoride". AccessScience. Archived from the original on 2011-05-18.
- ↑ "Unnamed (K-Al Fluoride)". mindat.org.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.