| Une Formation | |
|---|---|
| Stratigraphic range: Albian-Cenomanian ~ | |
| Type | Geological formation |
| Unit of | Villeta Group |
| Underlies | Chipaque Formation |
| Overlies | Fómeque Fm., Tibasosa Fm. |
| Thickness | up to 1,100 m (3,600 ft) |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Sandstone |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | 4°27′07″N 74°03′20″W / 4.45194°N 74.05556°W |
| Region | Altiplano Cundiboyacense Eastern Ranges, Andes |
| Country | |
| Type section | |
| Named for | Une |
| Named by | Hubach |
| Location | Une |
| Year defined | 1957 |
| Coordinates | 4°27′07″N 74°03′20″W / 4.45194°N 74.05556°W |
| Region | Cundinamarca, Boyacá |
| Country | |
 Paleogeography of Northern South America 105 Ma, by Ron Blakey | |
The Une Formation (Spanish: Formación Une, Kiu) is a geological formation of the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The predominantly sandstone formation dates to the Middle Cretaceous period; Albian to Cenomanian epochs and has a maximum thickness of 1,100 metres (3,600 ft).
Etymology
The formation was defined in 1957 by Hubach after Une, Cundinamarca.[1]
Description
Lithologies
The Une Formation has a maximum thickness of 1,100 metres (3,600 ft) and is characterised by a sequence of sandstones.[2] Fossils of Heminautilus etheringtoni have been found in the Une Formation.[3]
Stratigraphy and depositional environment
The Une Formation, part of the Villeta Group, overlies the Fómeque Formation and is overlain by the Chipaque Formation. The age has been estimated to be Albian-Cenomanian. Stratigraphically, the formation is time equivalent with the Simijaca, Aguardiente, Caballos and Pacho Formations. The formation has been deposited in a near shore deltaic environment.[4]
Outcrops
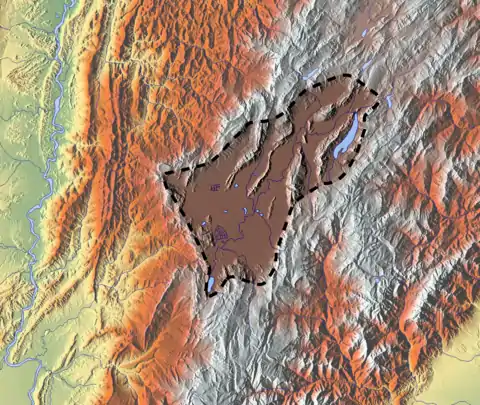
The Une Formation is apart from its type locality, found on the Sumapaz Páramo.[2]
Regional correlations
| Age | Paleomap | VMM | Guaduas-Vélez | W Emerald Belt | Villeta anticlinal | Chiquinquirá- Arcabuco | Tunja- Duitama | Altiplano Cundiboyacense | El Cocuy | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maastrichtian |  | Umir | Córdoba | Seca | eroded | Guaduas | Colón-Mito Juan | ||||||
| Umir | Guadalupe | ||||||||||||
| Campanian | Córdoba | ||||||||||||
| Oliní | |||||||||||||
| Santonian | La Luna | Cimarrona - La Tabla | La Luna | ||||||||||
| Coniacian | Oliní | Villeta | Conejo | Chipaque | |||||||||
| Güagüaquí | Loma Gorda | undefined | La Frontera | ||||||||||
| Turonian |  | Hondita | La Frontera | Otanche | |||||||||
| Cenomanian | Simití | hiatus | La Corona | Simijaca | Capacho | ||||||||
| Pacho Fm. | Hiló - Pacho | Churuvita | Une | Aguardiente | |||||||||
| Albian |  | Hiló | Chiquinquirá | Tibasosa | Une | ||||||||
| Tablazo | Tablazo | Capotes - La Palma - Simití | Simití | Tibú-Mercedes | |||||||||
| Aptian | Capotes | Socotá - El Peñón | Paja | Fómeque | |||||||||
| Paja | Paja | El Peñón | Trincheras | Río Negro | |||||||||
| La Naveta | |||||||||||||
| Barremian |  | ||||||||||||
| Hauterivian | Muzo | Cáqueza | Las Juntas | ||||||||||
| Rosablanca | Ritoque | ||||||||||||
| Valanginian | Ritoque | Furatena | Útica - Murca | Rosablanca | hiatus | Macanal | |||||||
| Rosablanca | |||||||||||||
| Berriasian |  | Cumbre | Cumbre | Los Medios | Guavio | ||||||||
| Tambor | Arcabuco | Cumbre | |||||||||||
| Sources | |||||||||||||
| Ma | Age | Paleomap | Regional events | Catatumbo | Cordillera | proximal Llanos | distal Llanos | Putumayo | VSM | Environments | Maximum thickness | Petroleum geology | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | Holocene |  | Holocene volcanism Seismic activity | alluvium | Overburden | ||||||||
| 1 | Pleistocene |  | Pleistocene volcanism Andean orogeny 3 Glaciations | Guayabo | Soatá Sabana | Necesidad | Guayabo | Gigante Neiva | Alluvial to fluvial (Guayabo) | 550 m (1,800 ft) (Guayabo) | [5][6][7][8] | ||
| 2.6 | Pliocene |  | Pliocene volcanism Andean orogeny 3 GABI | Subachoque | |||||||||
| 5.3 | Messinian | Andean orogeny 3 Foreland | Marichuela | Caimán | Honda | [7][9] | |||||||
| 13.5 | Langhian | Regional flooding | León | hiatus | Caja | León | Lacustrine (León) | 400 m (1,300 ft) (León) | Seal | [8][10] | |||
| 16.2 | Burdigalian | Miocene inundations Andean orogeny 2 | C1 | Carbonera C1 | Ospina | Proximal fluvio-deltaic (C1) | 850 m (2,790 ft) (Carbonera) | Reservoir | [9][8] | ||||
| 17.3 | C2 | Carbonera C2 | Distal lacustrine-deltaic (C2) | Seal | |||||||||
| 19 | C3 | Carbonera C3 | Proximal fluvio-deltaic (C3) | Reservoir | |||||||||
| 21 | Early Miocene | Pebas wetlands | C4 | Carbonera C4 | Barzalosa | Distal fluvio-deltaic (C4) | Seal | ||||||
| 23 | Late Oligocene |  | Andean orogeny 1 Foredeep | C5 | Carbonera C5 | Orito | Proximal fluvio-deltaic (C5) | Reservoir | [6][9] | ||||
| 25 | C6 | Carbonera C6 | Distal fluvio-lacustrine (C6) | Seal | |||||||||
| 28 | Early Oligocene | C7 | C7 | Pepino | Gualanday | Proximal deltaic-marine (C7) | Reservoir | [6][9][11] | |||||
| 32 | Oligo-Eocene | C8 | Usme | C8 | onlap | Marine-deltaic (C8) | Seal Source | [11] | |||||
| 35 | Late Eocene |  | Mirador | Mirador | Coastal (Mirador) | 240 m (790 ft) (Mirador) | Reservoir | [8][12] | |||||
| 40 | Middle Eocene | Regadera | hiatus | ||||||||||
| 45 | |||||||||||||
| 50 | Early Eocene |  | Socha | Los Cuervos | Deltaic (Los Cuervos) | 260 m (850 ft) (Los Cuervos) | Seal Source | [8][12] | |||||
| 55 | Late Paleocene | PETM 2000 ppm CO2 | Los Cuervos | Bogotá | Gualanday | ||||||||
| 60 | Early Paleocene | SALMA | Barco | Guaduas | Barco | Rumiyaco | Fluvial (Barco) | 225 m (738 ft) (Barco) | Reservoir | [5][6][9][8][13] | |||
| 65 | Maastrichtian |  | KT extinction | Catatumbo | Guadalupe | Monserrate | Deltaic-fluvial (Guadalupe) | 750 m (2,460 ft) (Guadalupe) | Reservoir | [5][8] | |||
| 72 | Campanian | End of rifting | Colón-Mito Juan | [8][14] | |||||||||
| 83 | Santonian | Villeta/Güagüaquí | |||||||||||
| 86 | Coniacian | ||||||||||||
| 89 | Turonian | Cenomanian-Turonian anoxic event | La Luna | Chipaque | Gachetá | hiatus | Restricted marine (all) | 500 m (1,600 ft) (Gachetá) | Source | [5][8][15] | |||
| 93 | Cenomanian |  | Rift 2 | ||||||||||
| 100 | Albian | Une | Une | Caballos | Deltaic (Une) | 500 m (1,600 ft) (Une) | Reservoir | [9][15] | |||||
| 113 | Aptian |  | Capacho | Fómeque | Motema | Yaví | Open marine (Fómeque) | 800 m (2,600 ft) (Fómeque) | Source (Fóm) | [6][8][16] | |||
| 125 | Barremian | High biodiversity | Aguardiente | Paja | Shallow to open marine (Paja) | 940 m (3,080 ft) (Paja) | Reservoir | [5] | |||||
| 129 | Hauterivian |  | Rift 1 | Tibú- Mercedes | Las Juntas | hiatus | Deltaic (Las Juntas) | 910 m (2,990 ft) (Las Juntas) | Reservoir (LJun) | [5] | |||
| 133 | Valanginian | Río Negro | Cáqueza Macanal Rosablanca | Restricted marine (Macanal) | 2,935 m (9,629 ft) (Macanal) | Source (Mac) | [6][17] | ||||||
| 140 | Berriasian | Girón | |||||||||||
| 145 | Tithonian | Break-up of Pangea | Jordán | Arcabuco | Buenavista Batá | Saldaña | Alluvial, fluvial (Buenavista) | 110 m (360 ft) (Buenavista) | "Jurassic" | [9][18] | |||
| 150 | Early-Mid Jurassic |  | Passive margin 2 | La Quinta | Montebel Noreán | hiatus | Coastal tuff (La Quinta) | 100 m (330 ft) (La Quinta) | [19] | ||||
| 201 | Late Triassic |  | Mucuchachi | Payandé | [9] | ||||||||
| 235 | Early Triassic |  | Pangea | hiatus | "Paleozoic" | ||||||||
| 250 | Permian |  | |||||||||||
| 300 | Late Carboniferous |  | Famatinian orogeny | Cerro Neiva () | [20] | ||||||||
| 340 | Early Carboniferous | Fossil fish Romer's gap | Cuche (355-385) | Farallones () | Deltaic, estuarine (Cuche) | 900 m (3,000 ft) (Cuche) | |||||||
| 360 | Late Devonian |  | Passive margin 1 | Río Cachirí (360-419) | Ambicá () | Alluvial-fluvial-reef (Farallones) | 2,400 m (7,900 ft) (Farallones) | [17][21][22][23][24] | |||||
| 390 | Early Devonian |  | High biodiversity | Floresta (387-400) El Tíbet | Shallow marine (Floresta) | 600 m (2,000 ft) (Floresta) | |||||||
| 410 | Late Silurian | Silurian mystery | |||||||||||
| 425 | Early Silurian | hiatus | |||||||||||
| 440 | Late Ordovician |  | Rich fauna in Bolivia | San Pedro (450-490) | Duda () | ||||||||
| 470 | Early Ordovician | First fossils | Busbanzá (>470±22) Chuscales Otengá | Guape () | Río Nevado () | Hígado () | [25][26][27] | ||||||
| 488 | Late Cambrian |  | Regional intrusions | Chicamocha (490-515) | Quetame () | Ariarí () | SJ del Guaviare (490-590) | San Isidro () | [28][29] | ||||
| 515 | Early Cambrian | Cambrian explosion | [27][30] | ||||||||||
| 542 | Ediacaran |  | Break-up of Rodinia | pre-Quetame | post-Parguaza | El Barro () | Yellow: allochthonous basement (Chibcha Terrane) Green: autochthonous basement (Río Negro-Juruena Province) | Basement | [31][32] | ||||
| 600 | Neoproterozoic | Cariri Velhos orogeny | Bucaramanga (600-1400) | pre-Guaviare | [28] | ||||||||
| 800 |  | Snowball Earth | [33] | ||||||||||
| 1000 | Mesoproterozoic |  | Sunsás orogeny | Ariarí (1000) | La Urraca (1030-1100) | [34][35][36][37] | |||||||
| 1300 | Rondônia-Juruá orogeny | pre-Ariarí | Parguaza (1300-1400) | Garzón (1180-1550) | [38] | ||||||||
| 1400 | 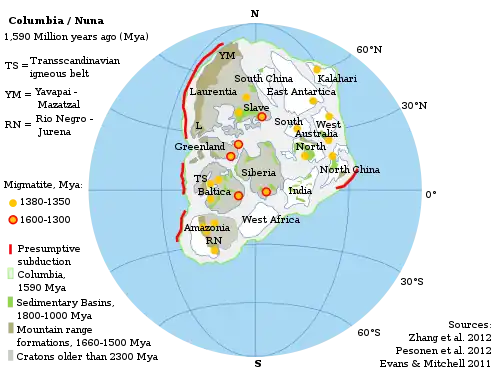 | pre-Bucaramanga | [39] | ||||||||||
| 1600 | Paleoproterozoic | Maimachi (1500-1700) | pre-Garzón | [40] | |||||||||
| 1800 | Tapajós orogeny | Mitú (1800) | [38][40] | ||||||||||
| 1950 | Transamazonic orogeny | pre-Mitú | [38] | ||||||||||
| 2200 | Columbia | ||||||||||||
| 2530 | Archean |  | Carajas-Imataca orogeny | [38] | |||||||||
| 3100 | Kenorland | ||||||||||||
| Sources | |||||||||||||
- Legend
- group
- important formation
- fossiliferous formation
- minor formation
- (age in Ma)
- proximal Llanos (Medina)[note 1]
- distal Llanos (Saltarin 1A well)[note 2]
See also
Notes
References
- ↑ Acosta & Ulloa, 2002, p.53
- 1 2 Acosta & Ulloa, 2002, p.54
- ↑ Badouin et al., 2016, p.87
- ↑ Acosta & Ulloa, 2002, p.46
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 García González et al., 2009, p.27
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 García González et al., 2009, p.50
- 1 2 García González et al., 2009, p.85
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Barrero et al., 2007, p.60
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Barrero et al., 2007, p.58
- ↑ Plancha 111, 2001, p.29
- 1 2 Plancha 177, 2015, p.39
- 1 2 Plancha 111, 2001, p.26
- ↑ Plancha 111, 2001, p.24
- ↑ Plancha 111, 2001, p.23
- 1 2 Pulido & Gómez, 2001, p.32
- ↑ Pulido & Gómez, 2001, p.30
- 1 2 Pulido & Gómez, 2001, pp.21-26
- ↑ Pulido & Gómez, 2001, p.28
- ↑ Correa Martínez et al., 2019, p.49
- ↑ Plancha 303, 2002, p.27
- ↑ Terraza et al., 2008, p.22
- ↑ Plancha 229, 2015, pp.46-55
- ↑ Plancha 303, 2002, p.26
- ↑ Moreno Sánchez et al., 2009, p.53
- ↑ Mantilla Figueroa et al., 2015, p.43
- ↑ Manosalva Sánchez et al., 2017, p.84
- 1 2 Plancha 303, 2002, p.24
- 1 2 Mantilla Figueroa et al., 2015, p.42
- ↑ Arango Mejía et al., 2012, p.25
- ↑ Plancha 350, 2011, p.49
- ↑ Pulido & Gómez, 2001, pp.17-21
- ↑ Plancha 111, 2001, p.13
- ↑ Plancha 303, 2002, p.23
- ↑ Plancha 348, 2015, p.38
- ↑ Planchas 367-414, 2003, p.35
- ↑ Toro Toro et al., 2014, p.22
- ↑ Plancha 303, 2002, p.21
- 1 2 3 4 Bonilla et al., 2016, p.19
- ↑ Gómez Tapias et al., 2015, p.209
- 1 2 Bonilla et al., 2016, p.22
- 1 2 Duarte et al., 2019
- ↑ García González et al., 2009
- ↑ Pulido & Gómez, 2001
- ↑ García González et al., 2009, p.60
Bibliography
- Acosta Garay, Jorge E., and Carlos E. Ulloa Melo. 2002. Mapa Geológico del Departamento de Cundinamarca - 1:250,000 - Memoria explicativa, 1–108. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-04-26.
- Badouin, Cyril; Gérard Delanoy; Josep Antón Moreno Bedmar; Antoine Pictet; Jean Vermeulen; Gabriel Conte; Roland Gonnet; Patrick Boselli, and Marc Bonelli. 2016. Revision of the Early Cretaceous genera Heminautilus SPATH, 1927, and Josanautilus MARTÍNEZ & GRAUGES, 2006 (Nautilida, Cenoceratidae). Carnets Geologicás 16. 61-212. Accessed 2017-01-20.
- García González, Mario; Ricardo Mier Umaña; Luis Enrique Cruz Guevara, and Mauricio Vásquez. 2009. Informe Ejecutivo - evaluación del potencial hidrocarburífero de las cuencas colombianas, 1-219. Universidad Industrial de Santander.
- Villamil, Tomas. 2012. Chronology Relative Sea Level History and a New Sequence Stratigraphic Model for Basinal Cretaceous Facies of Colombia, 161–216. Society for Sedimentary Geology (SEPM).
Maps
- Renzoni, Giancarlo, and Humberto Rosas. 2009. Plancha 171 - Duitama - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Ulloa, Carlos E.; Álvaro Guerra, and Ricardo Escovar. 1998. Plancha 172 - Paz de Río - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Renzoni, Giancarlo; Humberto Rosas, and Fernando Etayo Serna. 1998. Plancha 191 - Tunja - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Ulloa, Carlos E.; Erasmo Rodríguez, and Ricardo Escovar. 1998. Plancha 192 - Laguna de Tota - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Renzoni, Giancarlo. 1992. Plancha 193 - Yopal - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Montoya, Diana María, and Germán Reyes. 2009. Plancha 209 - Zipaquirá - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Terraza, Roberto; Giovanni Moreno; José A. Buitrago; Adrián Pérez, and Diana María Montoya. 2010. Plancha 210 - Guateque - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Ulloa, Carlos, and Erasmo Rodríguez. 2009. Plancha 211 - Tauramena - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Buitrago, José Alberto; Roberto Terraza M., and Fernando Etayo. 1998. Plancha 228 - Santafé de Bogotá Noreste - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Acosta, Jorge E., and Carlos E. Ulloa. 1998. Plancha 246 - Fusagasugá - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Acosta, Jorge; Juan Carlos Calcedo, and Carlos Ulloa. 1999. Plancha 265 - Icononzo - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Pulido, Orlando; Luz Stella Gómez, and Pedro Marín. 1998. Plancha 266 - Villavicencio - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS. Accessed 2017-06-06.
- Acosta, Jorge; Pablo Caro; Jaime Fuquen, and José Osorno. 2002. Plancha 303 - Colombia - 1:100,000, 1. INGEOMINAS.
External links
- Gómez, J.; N.E. Montes; Á. Nivia, and H. Diederix. 2015. Plancha 5-09 del Atlas Geológico de Colombia 2015 – escala 1:500,000, 1. Servicio Geológico Colombiano. Accessed 2017-03-16.