| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 County Results
Obama 60-70% 70-80%
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elections in Hawaii |
|---|
 |
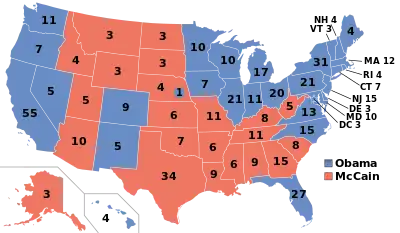
The 2008 United States presidential election in Hawaii took place on November 4, 2008, and was part of the 2008 United States presidential election. Voters chose 4 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.
Hawaii, Barack Obama's birth state, gave him 71.9% of the vote with a 45.3% margin of victory in 2008. Prior to the election, all 17 news organizations considered this a state Obama would win, or otherwise considered as a safe blue state. Hawaii has voted Democratic in every presidential election since 1988. Obama's margin of victory in this state is only surpassed by that of the District of Columbia and is the only actual state that gave either candidate more than 70% of the vote. Turnout here was much higher than previous elections.
This remains the second-best performance by any party in a presidential election in Hawaii after Lyndon Johnson's landslide election in 1964.
Caucuses
Campaign
Predictions
There were 16 news organizations who made state-by-state predictions of the election. Listed below are their last predictions before election day:
| Source | Ranking |
|---|---|
| D.C. Political Report[1] | Likely D |
| Cook Political Report[2] | Solid D |
| The Takeaway[3] | Solid D |
| Electoral-vote.com[4] | Solid D |
| Washington Post[5] | Solid D |
| Politico[6] | Solid D |
| RealClearPolitics[7] | Solid D |
| FiveThirtyEight[5] | Solid D |
| CQ Politics[8] | Solid D |
| The New York Times[9] | Solid D |
| CNN[10] | Safe D |
| NPR[5] | Solid D |
| MSNBC[5] | Solid D |
| Fox News[11] | Likely D |
| Associated Press[12] | Likely D |
| Rasmussen Reports[13] | Safe D |
Polling
Just 3 pre-election polls were ever taken in the state, averaging Obama at 64% to McCain at 30%.[14]
Fundraising
Obama raised $3,098,395. McCain raised $424,368.[15]
Advertising and visits
Obama spent $113,838 while a conservative interest group spent $31.[16] Obama visited the state once.[17]
Analysis
One of the most reliably blue states in the nation, Hawaii has only voted for two Republican candidates since statehood, both in national 49-state Republican landslides--Richard Nixon in 1972 and Ronald Reagan in 1984. A large concentration of Asian Americans makes the state very favorable to the Democrats. Although moderate Republicans occasionally win at the state level—for instance, then-Governor Linda Lingle and Lieutenant Governor Duke Aiona were both Republicans—Hawaii has long been reckoned as a Democratic stronghold.
It came as something of a surprise in 2004 when John Kerry only carried Hawaii by 8.7 points, the worst performance for a Democrat since Ronald Reagan carried the state in 1984. However, the state reverted to form in dramatic fashion in 2008, with Barack Obama (who was born in Hawaii) winning the state in a landslide over Republican John McCain. Obama outperformed Kerry by 36.3%, making Hawaii Obama's biggest improvement from 2004. During the same election, Democrats picked up one seat in the Hawaii House of Representatives and two seats in the Hawaii Senate, giving them a super-majority in the Hawaii state legislature with 45 out of 51 seats in the Hawaii House and 23 out of 25 seats in the Hawaii Senate.
Results
| 2008 United States presidential election in Hawaii | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Running mate | Votes | Percentage | Electoral votes | |
| Democratic | Barack Obama | Joe Biden | 325,871 | 71.85% | 4 | |
| Republican | John McCain | Sarah Palin | 120,566 | 26.58% | 0 | |
| Independent | Ralph Nader | Matt Gonzalez | 3,825 | 0.84% | 0 | |
| Libertarian | Bob Barr | Wayne Allyn Root | 1,314 | 0.29% | 0 | |
| Constitution | Chuck Baldwin (write-in) | Darrell Castle | 1,013 | 0.22% | 0 | |
| Green | Cynthia McKinney | Rosa Clemente | 979 | 0.22% | 0 | |
| Totals | 453,568 | 100.00% | 4 | |||
| Voter turnout (Voting age population) | 46.4% | |||||
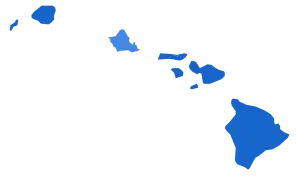
By county
| County | Barack Obama Democratic |
John McCain Republican |
Various candidates Other parties |
Margin | Total votes cast | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | % | # | % | # | % | # | % | ||
| Hawaii | 50,819 | 75.94% | 14,866 | 22.22% | 1,231 | 1.84% | 35,953 | 53.72% | 66,916 |
| Honolulu | 214,239 | 69.83% | 88,164 | 28.74% | 4,410 | 1.44% | 126,075 | 41.09% | 306,813 |
| Kalawao | 24 | 77.42% | 6 | 19.35% | 1 | 3.23% | 18 | 58.07% | 31 |
| Kauai | 20,416 | 74.99% | 6,245 | 22.94% | 563 | 2.07% | 14,171 | 52.05% | 27,224 |
| Maui | 39,727 | 76.71% | 11,154 | 21.54% | 908 | 1.75% | 28,573 | 55.17% | 51,789 |
| Totals | 325,871 | 71.85% | 120,566 | 26.58% | 7,131 | 1.57% | 205,305 | 45.27% | 453,568 |
By congressional district
Barack Obama swept both of Hawaii’s two congressional districts easily.
| District | McCain | Obama | Representative |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 28.14% | 70.43% | Neil Abercrombie |
| 2nd | 25.15% | 73.14% | Mazie Hirono |
Electors
Technically the voters of Hawaii cast their ballots for electors: representatives to the Electoral College. Hawaii is allocated 4 electors because it has 2 congressional districts and 2 senators. All candidates who appear on the ballot or qualify to receive write-in votes must submit a list of 4 electors, who pledge to vote for their candidate and his or her running mate. Whoever wins the majority of votes in the state is awarded all 4 electoral votes. Their chosen electors then vote for president and vice president. Although electors are pledged to their candidate and running mate, they are not obligated to vote for them.[18] An elector who votes for someone other than his or her candidate is known as a faithless elector.
The electors of each state and the District of Columbia met on December 15, 2008, to cast their votes for president and vice president. The Electoral College itself never meets as one body. Instead the electors from each state and the District of Columbia met in their respective capitols.
The following were the members of the Electoral College from the state. All 4 were pledged to Barack Obama and Joe Biden:[19]
- Joy Kobashigawa
- Marie Dolores
- Amefil Agbayani
- Frances K. Kagawa
References
- ↑ "D.C.'s Political Report: The complete source for campaign summaries". January 1, 2009. Archived from the original on January 1, 2009. Retrieved August 23, 2021.
- ↑ "Presidential". May 5, 2015. Archived from the original on May 5, 2015. Retrieved August 23, 2021.
- ↑ "Vote 2008 - The Takeaway - Track the Electoral College vote predictions". April 22, 2009. Archived from the original on April 22, 2009. Retrieved August 23, 2021.
- ↑ "Electoral-vote.com: President, Senate, House Updated Daily". electoral-vote.com. Retrieved August 23, 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 Based on Takeaway
- ↑ "POLITICO's 2008 Swing State Map - POLITICO.com". www.politico.com. Retrieved September 22, 2016.
- ↑ "RealClearPolitics - Electoral Map". Archived from the original on June 5, 2008.
- ↑ "CQ Presidential Election Maps, 2008". CQ Politics. Archived from the original on June 14, 2009. Retrieved December 20, 2009.
- ↑ Nagourney, Adam; Zeleny, Jeff; Carter, Shan (November 4, 2008). "The Electoral Map: Key States". The New York Times. Retrieved May 26, 2010.
- ↑ "October – 2008 – CNN Political Ticker - CNN.com Blogs". CNN. October 31, 2008. Archived from the original on June 19, 2010. Retrieved May 26, 2010.
- ↑ "Winning The Electoral College". Fox News. April 27, 2010.
- ↑ "roadto270". hosted.ap.org. Retrieved September 22, 2016.
- ↑ "Election 2008: Electoral College Update - Rasmussen Reports™". www.rasmussenreports.com. Retrieved September 22, 2016.
- ↑ Election 2008 Polls - Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections
- ↑ "Presidential Campaign Finance". Archived from the original on March 24, 2009. Retrieved August 20, 2009.
- ↑ "Map: Campaign Ad Spending - Election Center 2008 from CNN.com". CNN. Retrieved May 26, 2010.
- ↑ "Map: Campaign Candidate Visits - Election Center 2008 from CNN.com". CNN. Retrieved May 26, 2010.
- ↑ "Electoral College". California Secretary of State. Archived from the original on October 30, 2008. Retrieved November 1, 2008.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on November 6, 2008. Retrieved November 8, 2008.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)