
Wind power is a renewable energy source that is generally used to generate electricity via wind turbines. With a total installed wind capacity of around 9,100 megawatts (MW),[1] wind power constitutes 5% of Australia's total primary energy supply and 35% of its renewable energy supply.[2] Abundant wind resources are located close to residential areas in the southern parts of the country and on the slopes of the Great Dividing Range in the east, with approximately half of Australia's wind farms located around the coast.[3]
In December 2022, the government formally declared the Bass Strait off Gippsland as the country's first offshore wind zone.[4]
Wind resources
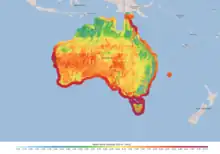
The abundant wind resources in Australia provide a major opportunity for the country to grow its renewable energy sector. The southern coastline lies in the roaring forties. Many sites have average wind speeds above 8–9 m/s at turbine hub height.
During the 1980s and 1990s, several states carried out a systematic monitoring of wind speed, which results are available to the public. Most tested sites are close to Australia's main population centres, making wind power a convenient resource for electricity generation.
Australian wind farms produce an average capacity factor range of 30–35%, making wind a viable option. South Australia's large share (along with nearby Victoria) means most of Australia's wind power occurs around the same time. The correlation between South Australia and New South Wales is 0.34, while the correlation between South Australia and Tasmania is 0.10.
Wind farms
As of October 2022, there were 94 operational wind farms in Australia, totaling 9,234 MW in capacity.[1]
The largest wind farm is Coopers Gap Wind Farm in Queensland, which began generating to the grid in June 2019, with a capacity of 453 MW.[2] As of December 2019, 50 Coopers Gap Wind Farm's turbines out of the initial 123 were operational.[3]
By generating capacity, the ten largest wind farms in Australia are:
| No. | Project | State | Capacity (MW) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M’intyre Wind Farm Project | Queensland | 2026 |
| 2 | Coopers Gap Wind Farm | Queensland | 453 |
| 3 | Macarthur Wind Farm | Victoria | 420 |
| 4 | Snowtown Wind Farm | South Australia | 369 |
| 5 | Hallett Wind Farm | South Australia | 351 |
| 6 | Hornsdale Wind Farm | South Australia | 315 |
| 7 | Lake Bonney Wind Farm | South Australia | 278 |
| 7 | Sapphire Wind Farm[5] | New South Wales | 270 |
| 8 | Ararat Wind Farm[6] | Victoria | 240 |
| 9 | Murra Warra Wind Farm | Victoria | 226 |
| 10 | Collgar Wind Farm | Western Australia | 222 |
Australia's first commercial wind farm, Salmon Beach Wind Farm, near Esperanza in Western Australia, operated for 15 years from 1987 but was decommissioned due to urban encroachment. It has since been replaced by Ten Mile Lagoon Wind Farm and Nine Mile Beach Wind Farm.[7]
Wind power by state

A full listing of all the wind farms in Australia can be found in the List of wind farms in Australia. Relevant state articles are:
- New South Wales wind power
- Queensland wind farms
- South Australia wind power
- Tasmania wind farms
- Victoria wind farms
- Western Australia wind farms
- Installed capacity by state
The following figures are based on capacity and generation as of the end of 2020.[8] Proposed figures are updated to December 2020.[9][10][11]
Note that figures may not agree with aggregate figures previously stated, due to different data sources and reporting dates contained within them.
| # | State /
Territory |
Wind Power Capacity | Proposed | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Installed capacity | Under construction or committed | ||||||
| Projects | Turbines | Total MW | Penetration (%)[12][13] | Projects | Total MW | ||
| 1 | Victoria | 31 | 1,004 | 2,610 | 13.3 | 10 | 1,537 |
| 2 | South Australia | 24 | 820 | 2,053 | 41.5 | 1 | 86 |
| 3 | New South Wales | 20 | 698 | 1,902 | 6.8 | 4 | 729 |
| 4 | Western Australia | 16 | ? | 638 | 12.9 | 4 | 746 |
| 5 | Tasmania | 5 | 194 | 563 | 14.2 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | Queensland | 2 | 73 | 193 | 2.1 | 4 | 826 |
| Australia | 98 | 2,789+ | 7,959 | 9.9 | 23 | 3,924 | |
South Australia provided 29.2% of Australia's wind power in 2019, accounting for 41% of the state electricity needs in 2019. By the end of 2011, wind power in South Australia reached 26% of the state electricity generation, edging out coal-fired power for the first time. At that stage, South Australia, with only 7.2% of Australia's population, had 54% of Australia's installed wind capacity.
Victoria also has a substantial system, which provided 27.8% of Australia's wind power in 2019. In August 2015, the Victorian government announced financial backing for new wind farms as part of a push to encourage renewable energy in the state. This was supposed to bring forward the building of a modest 100 MW of new wind energy in the state, worth $200 million in investment. The government estimated that 2400 MW worth of Victorian projects had been approved but were yet to be built.
Installed capacity (nameplate) is the theoretical maximum capacity of the engineered design in perfect operating conditions. The accepted AEMO rating is the capacity factor rating that adds up to 30 to 35 per cent of installed/nameplate capacity. And then, depending on the wind turbine location, there is a loss of energy in the feeder transmission line (depending on length) leading to the main electricity grid.
Economics

Wind developments typically involve significant upfront capital costs, while operating costs are relatively low. However, maintenance costs can add up over time due to the need for periodic replacement of components subject to wear.
By contrast, conventional energy sources such as gas and coal require large capital investments and ongoing operating costs. Gas and coal power stations also typically have much longer working lives when compared to wind turbines. When properly maintained, coal and gas plants can continue operating for up to three times longer than wind turbines.
These differing cost profiles make it challenging to directly compare the costs of alternative energy sources. Wind power may be a more attractive option for some due to its low operating costs, but the high upfront capital costs may be prohibitive for others. Similarly, while coal and gas-fired power stations require significant ongoing investment, their longer working lives may make them a more cost-effective option over the long term.
Despite these complexities, existing data indicate that wind energy is one of the most cost-efficient renewable energy sources but approximately two times the cost of coal-generated power in 2006.[1] When the costs associated with pollution were factored in, it was competitive with coal- and gas-fired power stations even then. By 2014, wind had the lowest levelised cost of energy (LCOE) of any power source in Australia.[failed verification]
A 2012 study by SKM on the economic benefits of wind farms in Australia[14] found that, for every 50 MW in capacity, a wind farm delivered the following benefits:
- direct employment of up to 48 construction workers, with each worker spending approximately $25,000 in the local area in shops, restaurants, hotels and other services – a total of up to $1.2 million
- direct employment of around five staff – a total annual input of $125,000 spent in the local economy
- indirect employment during the construction phase of approximately 160 people locally, 504 state jobs and 795 nationwide jobs
- up to $250,000 per year for farmers in land rental income and $80,000 on community projects yearly.
Environmental impact

Australia is the fifth highest per capita emitter of greenhouse gases with 25.8 tonne CO2-e per person annually, ranking first of the industrialized countries, and ranks sixteenth of all countries in total country emissions with 495 Mt CO2-e per annum.[15] It is one of the major exporters of coal, the burning of which releases CO2 into the atmosphere. It is also one of the countries most at risk from climate change according to the Stern report. This is partially because of the size of its agriculture sector and long coastline.
A wind farm, when installed on agricultural land, has one of the lowest environmental impacts of all energy sources:[16]
- It occupies less land area per kilowatt-hour (kWh) of electricity generated than any other energy conversion system, apart from rooftop solar energy, and is compatible with grazing and crops.
- It generates the energy used in its construction in just 3 months of operation, yet its operational lifetime is 20–25 years.
- Greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution produced by its construction are small and declining. There is very little emission or pollution produced by its operation.
- In substituting for base-load (mostly coal power) in mainland Australia, wind power produces a net decrease in greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution.
- Modern wind turbines are almost silent and rotate so slowly (in terms of revolutions per minute) that they are rarely a hazard to birds.[16]
Landscape and heritage issues can be a significant issue for certain wind farms. However, these are minimal when compared with the environmental effects of coal. However, when appropriate planning procedures are followed, the heritage and landscape risks should be minimal. People may still object to wind farms, perhaps on the grounds of aesthetics, but their concerns should be weighed against the need to address the threats posed by climate change and the opinions of the broader community.[17]
Overseas experience has shown that community consultation and direct involvement of the general public in wind farm projects have helped to increase community approval.[18] Some wind farms become tourist attractions.[19]
The Garnaut Climate Change Review, the Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme and the Mandatory Renewable Energy Target announced by the Australian Government involve a reduction in Australian greenhouse gas emissions. Australia is the highest emitter of greenhouse gases per capita in the developed world[20][21] and wind power is well placed to grow and deliver greenhouse gas emission cuts on a cost-competitive basis. A typical 50-megawatt (MW) wind farm in Australia can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by between 65,000 and 115,000 tonnes a year.[22]
Based on the 2010 figures for electricity production of 5 TWh nationally, it is estimated that wind power saved Australia 5,100,000 tonnes of CO2 emissions in that year. In relative terms, that is calculated to be the equivalent of removing 1,133,000 cars from the nation's roads.[23]
Politics
From 2001 to early 2006, the main driving force for the establishment of wind farms in Australia was the Government's Mandatory Renewable Energy Target (MRET).[24][25] However, by mid-2006, sufficient renewable energy had been installed or was under construction to meet the small MRET target for 2010. Also, in 2006, several Federal Government Ministers spoke out against several wind farm proposals.[25]
Mark Diesendorf has suggested that the Australian Government has tried to stop the development of wind power, the lowest-cost, new, renewable electricity source until coal-fired power stations with CO2 capture and sequestration and possibly nuclear power stations were available. However, "clean coal" technologies may not be commercially available for at least 20 years. Furthermore, to bring down the high cost of nuclear power to a level where it could compete with wind power would require a new generation of nuclear power stations that is still on the drawing board, which could take at least 15 years.[25]
In November 2007, when the Rudd (Labor) government was elected in Australia, it ratified Australia's commitment to the Kyoto Protocol, promised a target of 20% renewable power by 2020 and to do more to reduce Australia's greenhouse gas emissions. As a result, several new wind power projects were proposed in anticipation of an expanded MRET.
Major wind projects
In January 2022, construction began on the Goyder South development, which is expected to become one of Australia’s largest wind farms. Run by French firm Neoen, the project expects to be able to provide 209 MW of power generation by 2024, and a similar amount again when construction is complete.[26]
In south east Queensland, Australia’s first gigawattscale wind project is in development: the MacIntrye facility (923 MW), majority owned by Spanish energy firm Acciona, and the Karara Wind Farm (103 MW), owned and operated by CleanCo. [26]
As of April 2023, one of the most significant wind projects underway in Victoria is the 756 MW stage one of the Golden Plains development in Rokewood.[26]
See also
References
- ↑ "Wind energy". Australian Trade and Investment Commission. Retrieved 13 October 2023.
- ↑ Ritchie, Hannah; Roser, Max; Rosado, Pablo (27 October 2022). "Energy". Our World in Data.
- ↑ Harvey, Nick; Dew, Romana E. C.; Hender, Sarah (1 February 2017). "Rapid land use change by coastal wind farm development: Australian policies, politics and planning". Land Use Policy. 61: 368–378. doi:10.1016/j.landusepol.2016.11.031. ISSN 0264-8377.
- ↑ The Hon Chris Bowen MP (19 December 2022). "Joint media release: Unlocking the power of offshore wind in Gippsland". Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water Ministers. Retrieved 13 October 2023.
- ↑ "Sapphire – A New Future". sapphirewindfarm.com.au. Retrieved 9 February 2019.
- ↑ "Ararat Wind Farm Powering Ahead | Premier of Victoria".
- ↑ "Walking in the wind". Clean Energy Council. Retrieved 17 October 2023.
- ↑ "Clean Energy Australia Report 2021" (PDF). Clean Energy Council.
- ↑ "Clean Energy Projects Australia | Clean Energy Council". www.cleanenergycouncil.org.au. Retrieved 4 April 2019.
- ↑ "NEM Generation Information October 2021 | AEMO". www.aemo.com.au. Retrieved 8 November 2021.
- ↑ "Wind Map of Australia 2020 | EcoGeneration" (PDF). www.ecogeneration.com.au/. Retrieved 8 November 2021.
- ↑ "OpenNEM: An Open Platform for National Electricity Market Data". opennem.org.au. Retrieved 4 April 2019.
- ↑ "WEM Data Dashboard". aemo.com.au. Retrieved 4 April 2019.
- ↑ "Landmark report shows economic benefits of wind farms". www.sustainabilitymatters.net.au. Retrieved 17 October 2023.
- ↑ World Resources Institute
- 1 2 Why Australia needs wind power
- ↑ The Australia Institute (2006).Wind Farms The facts and the fallacies Discussion Paper Number 91, October, ISSN 1322-5421
- ↑ "The world's leader in Wind Power". scandinavica.com. Retrieved 17 April 2018.
- ↑ Ten Mile Lagoon Wind Farm
- ↑ "Global Warming: The Facts". cana.net.au. Retrieved 17 April 2018.
- ↑ "Australia tops greenhouse pollution index – Environment". The Sydney Morning Herald. 19 June 2004. Retrieved 17 April 2018.
- ↑ "National code for wind farms" (PDF). greenhouse.gov.au. Retrieved 17 April 2018.
- ↑ "Technologies: Wind: Wind Energy – how it works". cleanenergycouncil.org.au. 2011. Retrieved 12 June 2011.
- ↑ Lovegrove, Keith. Election 2004: The Government’s non policy on energy Australian Review of Public Affairs, 10 September 2004.
- 1 2 3 Diesendorf, Mark (2007). Greenhouse Solutions with Sustainable Energy, UNSW Press, p. 107.
- 1 2 3 Thornton, Kane (April 2023). "CLEAN ENERGY AUSTRALIA REPORT 2023" (PDF). Clean Energy Council. Retrieved 30 October 2023.
