生活方式医学
生活方式医学(Lifestyle medicine)是医学中的分支,著重在預防醫學及自我照顧,主要在處理生活方式造成的疾病以及可預防的死亡因子的預防、研究、教育及治療。可預防的死亡因子包括了營養不良、坐式生活型態、慢性壓力,以及使用煙類、物質濫用或酒精不當使用等自我毁灭行为[1]。生活方式医学的目的是透過生活方式醫學的六大支柱(營養、規律身體活動、充足睡眠、壓力管理、避免物質濫用以及正向社交連結)來改善個人健康以及福祉,並且預防心血管疾病、糖尿病、代謝症候群及肥胖等慢性病[1][2]。若透過這六個領域來改善健康,生活方式医学可以避免80%的慢性病以及非傳播疾病(NCD)[3]。
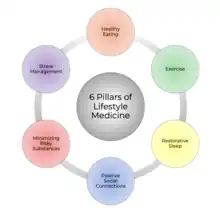 生活方式医学著重在圖中的六個方面 | |
| Focus | 營養、睡眠、運動、壓力管理、戒煙及戒酒、健康的人際關係 |
|---|---|
| 主要疾病 | |
| 專科醫生 | 生活方式医学医師 |
生活方式医学著重在健康教育,激勵患者用以下的方式提升生活质量:改變個人習慣以及行為,食用較健康,較少]] 超加工食品]]的飲食模式(較健康的飲食模式像是地中海飲食及植物性飲食)。不好的生活方式像是不好的飲食習慣、不運動、抽煙、酗酒或酒精依賴、藥物成瘾或依賴,也包括心理相關的因素,例如慢性壓力,缺乏社交及社群的支持,這些容易造成慢性疾病[1][4][5]。在臨床上,生活方式医学諮詢的阻力是醫生自覺準備不足,懷疑患者的接受程度[6]。但長遠來看,鼓勵患者作對健康較有幫助的選擇,可以對疾病有較好的管理,減緩,甚至可以避免一些疾病的發生。
參考資料
- Mechanick, Jeffrey I.; Kushner, Robert F. (编). . . Cham, Switzerland: Springer Nature. 2016: 9–15 [2023-06-17]. ISBN 978-3-319-24685-7. S2CID 29205050. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-24687-1. (原始内容存档于2023-03-31).
- . Wiley. doi:10.1002/(issn)2688-3740.
- Katz, David L.; Frates, Elizabeth P.; Bonnet, Jonathan P.; Gupta, Sanjay K.; Vartiainen, Erkki; Carmona, Richard H. . American Journal of Health Promotion. July 2018, 32 (6): 1452–1458 [2023-06-17]. ISSN 0890-1171. doi:10.1177/0890117117705949. (原始内容存档于2023-03-15) (英语).
- Kvaavik, Elisabeth. . JAMA Internal Medicine. April 2010, 170 (8): 711–8 [7 July 2015]. PMID 20421558. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2010.76
 . hdl:10536/DRO/DU:30131641
. hdl:10536/DRO/DU:30131641  . (原始内容存档于2023-03-31).
. (原始内容存档于2023-03-31). - Sagner, Michael. . International Journal of Clinical Practice. October 2014, 68 (11): 1289–1292. PMID 25348380. doi:10.1111/ijcp.12509
 .
. - Hivert, Marie-France; Arena, Ross; Forman, Daniel E.; Kris-Etherton, Penny M.; McBride, Patrick E.; Pate, Russell R.; Spring, Bonnie; Trilk, Jennifer; Horn, Linda V. Van; Kraus, William E.; Health, On behalf of the American Heart Association Physical Activity Committee of the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic; the Behavior Change Committee, a joint committee of the Council on Lifestyle and Cardiometabolic Health and the Council on Epidemiology and Prevention; the Exercise, Cardiac Rehabilitation; Nursing, and the Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke. . Circulation. 1 January 2016, 134 (15): e308–e327 [2018-01-30]. ISSN 0009-7322. PMID 27601568. S2CID 7847964. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000442
 . (原始内容存档于2023-07-08) (英语).
. (原始内容存档于2023-07-08) (英语).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.