 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | TamoGel |
| Other names | 4-Hydroxytamoxifen; 4-OHT; 4-HT; OHTAM; TamoGel |
| Routes of administration | Topical (gel) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.163.120 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
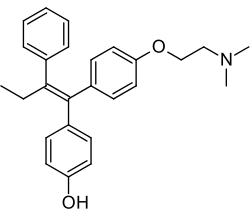
| Formula | C26H29NO2 |
| Molar mass | 387.523 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Afimoxifene, also known as 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT) and by its tentative brand name TamoGel, is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group and an active metabolite of tamoxifen.[1][2][3] The drug is under development under the tentative brand name TamoGel as a topical gel for the treatment of hyperplasia of the breast.[1][4] It has completed a phase II clinical trial for cyclical mastalgia,[5] but further studies are required before afimoxifene can be approved for this indication and marketed.[4]
Afimoxifene is a SERM and hence acts as a tissue-selective agonist–antagonist of the estrogen receptors ERα and ERβ with mixed estrogenic and antiestrogenic activity depending on the tissue. It is also an agonist of the G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER) with relatively low affinity (100–1,000 nM, relative to 3–6 nM for estradiol).[6] In addition to its estrogenic and antiestrogenic activity, afimoxifene has been found to act as an antagonist of the estrogen-related receptors (ERRs) ERRβ and ERRγ.[7][8][9]
See also
References
- 1 2 "Afimoxifene - BHR Pharma". AdisInsight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
- ↑ Desta Z, Ward BA, Soukhova NV, Flockhart DA (September 2004). "Comprehensive evaluation of tamoxifen sequential biotransformation by the human cytochrome P450 system in vitro: prominent roles for CYP3A and CYP2D6". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 310 (3): 1062–1075. doi:10.1124/jpet.104.065607. PMID 15159443. S2CID 21413981.
- ↑ "Statement on a nonproprietary name adopted by the USAN council: Afimoxifene" (PDF). American Medical Association. Retrieved 2008-03-26.
- 1 2 Goyal A, Mansel RE (16 November 2016). "Mastalgia". In Jatoi I, Rody A (eds.). Management of Breast Diseases. Springer. pp. 77–. ISBN 978-3-319-46356-8.
- ↑ Mansel R, Goyal A, Nestour EL, Masini-Etévé V, O'Connell K (December 2007). "A phase II trial of Afimoxifene (4-hydroxytamoxifen gel) for cyclical mastalgia in premenopausal women". Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 106 (3): 389–397. doi:10.1007/s10549-007-9507-x. PMID 17351746. S2CID 22382077.
- ↑ Prossnitz ER, Arterburn JB (July 2015). "International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. XCVII. G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor and Its Pharmacologic Modulators". Pharmacological Reviews. 67 (3): 505–540. doi:10.1124/pr.114.009712. PMC 4485017. PMID 26023144.
- ↑ Levine AC (3 October 2011). Hormones and Cancer: Breast and Prostate, An Issue of Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 271–. ISBN 978-1-4557-1239-7.
- ↑ Khetan SK (23 May 2014). "Anti-Androgenic Chemicals". Endocrine Disruptors in the Environment. Wiley. pp. 104–. ISBN 978-1-118-89115-5.
- ↑ Ariazi EA, Jordan VC (2006). "Estrogen-related receptors as emerging targets in cancer and metabolic disorders". Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry. 6 (3): 203–215. doi:10.2174/1568026610606030203. PMID 16515477.
External links
- 4-hydroxytamoxifen at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Afimoxifene - AdisInsight