 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
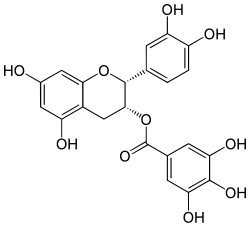
| IUPAC name
(2R,3R)-3′,4′,5,7-Tetrahydroxyflavan-3-yl 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,3R)-2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzopyran-3-yl 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.116.252 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H18O10 | |
| Molar mass | 442.37 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Epicatechin gallate (ECG) is a flavan-3-ol, a type of flavonoid, present in green tea.[1] It is also reported in buckwheat[2] and in grape.[3]
The tea component epicatechin gallate is being researched because in vitro experiments showed it can reverse methicillin resistance in bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus.[1] Nevertheless, the compound is significantly degraded by steeping in boiling water, unlike related catechins.[4]
Epicatechin, as well as many other flavonoids, has been found to act as a non-selective antagonist of the opioid receptors, albeit with somewhat low affinity.[5]
References
- 1 2 Shiota, S; Shimizu, M; Mizushima, T; Ito, H; Hatano, T; Yoshida, T; Tsuchiya, T (1999). "Marked reduction in the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of beta-lactams in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus produced by epicatechin gallate, an ingredient of green tea (Camellia sinensis)". Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 22 (12): 1388–90. doi:10.1248/bpb.22.1388. PMID 10746177.
- ↑ Danila, Ana-Maria; Kotani, Akira; Hakamata, Hideki; Kusu, Fumiyo (2007). "Determination of Rutin, Catechin, Epicatechin, and Epicatechin Gallate in BuckwheatFagopyrum esculentumMoench by Micro-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Electrochemical Detection". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 55 (4): 1139–43. doi:10.1021/jf062815i. PMID 17253718.
- ↑ Souquet, Jean-Marc; Cheynier, Véronique; Brossaud, Franck; Moutounet, Michel (1996). "Polymeric proanthocyanidins from grape skins". Phytochemistry. 43 (2): 509–512. doi:10.1016/0031-9422(96)00301-9.
- ↑ Saklar, Sena; Ertas, Erdal; Ozdemir, Ibrahim S.; Karadeniz, Bulent (October 2015). "Effects of different brewing conditions on catechin content and sensory acceptance in Turkish green tea infusions". Journal of Food Science and Technology. 52 (10): 6639–6646. doi:10.1007/s13197-015-1746-y. PMC 4573099. PMID 26396411.
- ↑ Katavic PL, Lamb K, Navarro H, Prisinzano TE (August 2007). "Flavonoids as opioid receptor ligands: identification and preliminary structure-activity relationships". J. Nat. Prod. 70 (8): 1278–82. doi:10.1021/np070194x. PMC 2265593. PMID 17685652.
See also
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.