 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H34O3 |
| Molar mass | 358.522 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
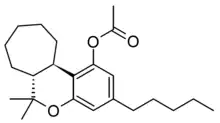
abeo-HHC acetate is a is a semi-synthetic derivative of tetrahydrocannabinol, first described in the 1980s. It is synthesised from the acetate ester of Delta-11-Tetrahydrocannabinol, which can be made to undergo a ring expansion reaction via a hydrazone intermediate to form abeo-HHC acetate.[1][2] It is structurally similar to HHC-acetate except it's substituted with a cycloheptyl ring instead of a cyclohexyl ring.
See also
References
- ↑ Srebnik M, Mechoulam R (1984). "Reactions of cannabinoid tosylhydrazones: Stereochemical aspects". Tetrahedron. 40 (19): 3839–3843. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)88815-3.
- ↑ Ujváry I (June 2023). "Hexahydrocannabinol and closely related semi-synthetic cannabinoids: A comprehensive review". Drug Testing and Analysis. doi:10.1002/dta.3519. PMID 37269160. S2CID 259046522.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.