 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
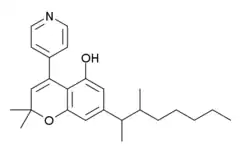
| Formula | C25H33NO2 |
| Molar mass | 379.544 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Nonabine (BRL-4664) is an experimental drug which is a synthetic THC analog.[1] It was studied in the 1980s for the prevention of nausea and vomiting associated with cancer chemotherapy but was never marketed.[1] It has strong antiemetic effects equivalent to those of chlorpromazine, and also produces some mild sedative effects, along with dry mouth and EEG changes typical of cannabinoid agonists, but with minimal changes in mood or perception, suggesting the abuse potential is likely to be low.[2][3]
References
- 1 2 Staquet M, Bron D, Rozencweig M, Kenis Y (1981). "Clinical studies with a THC analog (BRL-4664) in the prevention of cisplatin-induced vomiting". Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 21 (S1): 60S–63S. doi:10.1002/j.1552-4604.1981.tb02575.x. PMID 7197692. S2CID 30609591.
- ↑ Archer CB, Amlot PL, Trounce JR (January 1983). "Antiemetic effect of nonabine in cancer chemotherapy: a double blind study comparing nonabine and chlorpromazine". British Medical Journal. 286 (6362): 350–1. doi:10.1136/bmj.286.6362.350-a. PMC 1546960. PMID 6402096.
- ↑ McClelland GR, Sutton JA (1985). "Pilot investigation of the quantitative EEG and clinical effects of ketazolam and the novel antiemetic nonabine in normal subjects". Psychopharmacology. 85 (3): 306–8. doi:10.1007/BF00428192. PMID 2860687. S2CID 19560039.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.