 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
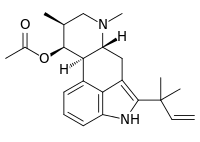
| IUPAC name
[(6aR,9S,10S)-7,9-Dimethyl-5-(2-methylbut-3-en-2-yl)-6,6a,8,9,10,10a-hexahydro-4H-indolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-10-yl] acetate | |
| Other names
SM-1; (8β,9β)-2-(1,1-Dimethyl-2-propenyl)-6,8-dimethylergolin-9-ol acetate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H30N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 366.505 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Fumigaclavine C is an ergoline alkaloid produced by Aspergillus fumigatus.[1]
Both 8α and 8β diastereomers (epimers) were named fumigaclavine C in scientific literature.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Ma, HY; Song, YC; Mao, YY; Jiang, JH; Tan, RX; Luo, L (2006). "Endophytic fungal metabolite fumigaclavine C causes relaxation of isolated rat aortic rings". Planta Medica. 72 (5): 387–92. doi:10.1055/s-2005-916235. PMID 16557450.
- ↑ Wallwey, Christiane; Li, Shu-Ming (2011-03-01). "Ergot alkaloids: structure diversity, biosynthetic gene clusters and functional proof of biosynthetic genes". Natural Product Reports. 28 (3): 496–510. doi:10.1039/C0NP00060D. ISSN 1460-4752. PMID 21186384.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.