 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | BU-LAD, 6-butyl-6-nor-Lysergic acid diethylamide |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
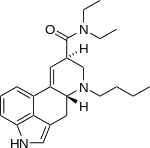
| Formula | C23H31N3O |
| Molar mass | 365.521 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
BU-LAD, also known as 6-butyl-6-nor-lysergic acid diethylamide, is an analogue of LSD first made by Alexander Shulgin and reported in the book TiHKAL. BU-LAD is a psychedelic drug similar to LSD, but is significantly less potent than LSD,[1] with a dose of 500 micrograms producing only mild effects.
References
- ↑ Hoffman AJ, Nichols DE (September 1985). "Synthesis and LSD-like discriminative stimulus properties in a series of N(6)-alkyl norlysergic acid N,N-diethylamide derivatives". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 28 (9): 1252–5. doi:10.1021/jm00147a022. PMID 4032428.
| Lysergic acid derivatives |
|
|---|---|
| Psychedelic lysergamides |
|
| Clavines | |
| Other ergolines | |
| Natural sources |
Morning glory: Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian Baby Woodrose), Ipomoea spp.(Morning Glory, Tlitliltzin, Badoh Negro), Rivea corymbosa (Coaxihuitl, Ololiúqui) |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.