 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | MLD-41; N1-Methyl-Lysergic Acid Diethylamide |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
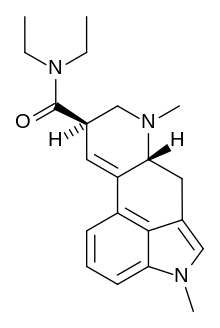
| Formula | C21H27N3O |
| Molar mass | 337.467 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
N1-Methyl-lysergic acid diethylamide (MLD-41) is a derivative of LSD that has about one-third the psychoactive effects. It has been studied in cross-tolerance of LSD.[1]
Metabolism of other 1-methylated-ergoloids to their secondary amine derivatives has been frequently noted in mammals.[2]
References
- ↑ Abramson HA, Rolo A, Sklarofsky B, Stache J (January 1960). "Production of cross-tolerance to psychosis-producing doses of lysergic acid diethylamide and psilocybin". The Journal of Psychology. 49 (1): 151–4. doi:10.1080/00223980.1960.9916396.
- ↑ Müller-Schweinitzer E, Tapparelli C (March 1986). "Methylergometrine, an active metabolite of methysergide". Cephalalgia: An International Journal of Headache. 6 (1): 35–41. doi:10.1046/j.1468-2982.1986.0601035.x. PMID 3698092. S2CID 5778173.
| Lysergic acid derivatives |
|
|---|---|
| Psychedelic lysergamides |
|
| Clavines | |
| Other ergolines | |
| Natural sources |
Morning glory: Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian Baby Woodrose), Ipomoea spp.(Morning Glory, Tlitliltzin, Badoh Negro), Rivea corymbosa (Coaxihuitl, Ololiúqui) |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.