Portal maintenance status: (June 2018)
|
The Spain Portal (Bienvenido al portal español)
Spain (Spanish: España, [esˈpaɲa] ⓘ), or the Kingdom of Spain (Reino de España), is a country located in Southwestern Europe, with parts of its territory in the Atlantic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea and Africa. It is the largest country in Southern Europe and the fourth-most populous European Union member state. Spanning across the majority of the Iberian Peninsula, its territory also includes the Canary Islands in the Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands in the Mediterranean Sea, and the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla in Africa. Peninsular Spain is bordered to the north by France, Andorra, and the Bay of Biscay; to the east and south by the Mediterranean Sea and Gibraltar; and to the west by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. Spain's capital and largest city is Madrid; other major urban areas include Barcelona, Valencia, Zaragoza, Seville, Málaga, Murcia, Palma de Mallorca, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, and Bilbao.
In early antiquity, the Iberian Peninsula was inhabited by a mixture of Iberian and Celtic tribes, along with other local pre-Roman peoples. With the Roman conquest of the Iberian Peninsula, the province of Hispania was established. Following the Romanization and Christianization of Hispania, the fall of the Western Roman Empire ushered in the inward migration of tribes from Central Europe, including the Visigoths, who formed the Visigothic Kingdom centred on Toledo. In the early eighth century, most of the peninsula was conquered by the Umayyad Caliphate, and during early Islamic rule, Al-Andalus became a dominant peninsular power centred in Córdoba. Several Christian kingdoms emerged in Northern Iberia, chief among them Asturias, León, Castile, Aragon, Navarre, and Portugal; made an intermittent southward military expansion, known as the Reconquista, repelling Islamic rule in Iberia, which culminated with the Christian seizure of the Nasrid Kingdom of Granada in 1492. The dynastic union of the Crown of Castile and the Crown of Aragon in 1479 under the Catholic Monarchs is often considered the de facto unification of Spain as a nation-state. (Full article...)
 Featured article –
Featured article –
 Image 1
Image 1 Battle of Chiclana, 5 March 1811, Louis-François Lejeune
Battle of Chiclana, 5 March 1811, Louis-François Lejeune
The Battle of Barrosa (Chiclana, 5 March 1811, also known as the Battle of Chiclana or Battle of Cerro del Puerco) was part of an unsuccessful manoeuvre by an Anglo-Iberian force to break the French siege of Cádiz during the Peninsular War. During the battle, a single British division defeated two French divisions and captured a regimental eagle. (Full article...) Image 2
Image 2
The Mercenary War, also known as the Truceless War, was a mutiny by troops that were employed by Carthage at the end of the First Punic War (264–241 BC), supported by uprisings of African settlements revolting against Carthaginian control. It lasted from 241 to late 238 or early 237 BC and ended with Carthage suppressing both the mutiny and the revolt. (Full article...) Image 3
Image 3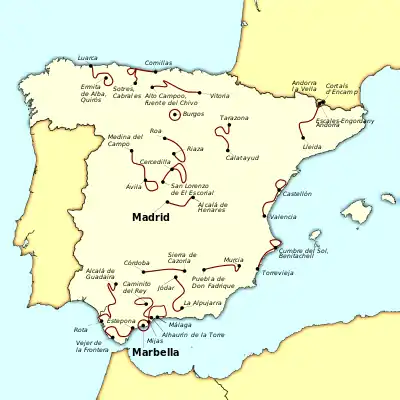 Map of the 2015 Vuelta a España route, from Marbella to Madrid.
Map of the 2015 Vuelta a España route, from Marbella to Madrid.
(stage courses in red)
The 2015 Vuelta a España was a three-week Grand Tour cycling race. The race was the 70th edition of the Vuelta a España and took place principally in Spain, although two stages took place partly or wholly in Andorra, and was the 22nd race in the 2015 UCI World Tour. The 3,358.1-kilometre (2,086.6 mi) race included 21 stages, beginning in Marbella on 22 August 2015 and finishing in Madrid on 13 September. It was won by Fabio Aru (Astana Pro Team), with Joaquim Rodríguez (Team Katusha) second and Rafał Majka (Tinkoff–Saxo) third. (Full article...) Image 4
Image 4
Joseph Anton Lopez SJ (born José Antonio López; October 4, 1779 – October 5, 1841) was a Mexican Catholic priest and Jesuit. Born in Michoacán, he studied canon law at the Colegio de San Nicolás and the Royal and Pontifical University of Mexico. He became acquainted with the future Empress consort Ana María Huarte and was made chaplain to the future imperial family. He was later put in charge of the education of all the princes in Mexico. Lopez was a close ally of Emperor Agustín de Iturbide, residing in Madrid for four years as his attorney and political informant, and accompanying him during his exile to Italy and England. (Full article...) Image 5Muhammad III (Arabic: محمد الثالث; 15 August 1257 – 21 January 1314) was the ruler of the Emirate of Granada in Al-Andalus on the Iberian Peninsula from 8 April 1302 until 14 March 1309, and a member of the Nasrid dynasty. He ascended the Granadan throne after the death of his father Muhammad II, which according to rumours, was caused by Muhammad III poisoning him. He had the reputation of being both cultured and cruel. Later in his life, he became visually impaired—which caused him to be absent from many government activities and to rely on high officials, especially the powerful Vizier Ibn al-Hakim al-Rundi. (Full article...)
Image 5Muhammad III (Arabic: محمد الثالث; 15 August 1257 – 21 January 1314) was the ruler of the Emirate of Granada in Al-Andalus on the Iberian Peninsula from 8 April 1302 until 14 March 1309, and a member of the Nasrid dynasty. He ascended the Granadan throne after the death of his father Muhammad II, which according to rumours, was caused by Muhammad III poisoning him. He had the reputation of being both cultured and cruel. Later in his life, he became visually impaired—which caused him to be absent from many government activities and to rely on high officials, especially the powerful Vizier Ibn al-Hakim al-Rundi. (Full article...) Image 6The Nyon Conference was a diplomatic conference held in Nyon, Switzerland, in September 1937 to address attacks on international shipping in the Mediterranean Sea during the Spanish Civil War. The conference was convened in part because Italy had been carrying out unrestricted submarine warfare, although the final conference agreement did not accuse Italy directly; instead, the attacks were referred to as "piracy" by an unidentified body. Italy was not officially at war, nor did any submarine identify itself. The conference was designed to strengthen non-intervention in the Spanish Civil War. The United Kingdom and France led the conference, which was also attended by Bulgaria, Egypt, Greece, Romania, Turkey, the Soviet Union and Yugoslavia. (Full article...)
Image 6The Nyon Conference was a diplomatic conference held in Nyon, Switzerland, in September 1937 to address attacks on international shipping in the Mediterranean Sea during the Spanish Civil War. The conference was convened in part because Italy had been carrying out unrestricted submarine warfare, although the final conference agreement did not accuse Italy directly; instead, the attacks were referred to as "piracy" by an unidentified body. Italy was not officially at war, nor did any submarine identify itself. The conference was designed to strengthen non-intervention in the Spanish Civil War. The United Kingdom and France led the conference, which was also attended by Bulgaria, Egypt, Greece, Romania, Turkey, the Soviet Union and Yugoslavia. (Full article...) Image 7
Image 7.jpg.webp) Muhammad I (red tunic and shield) depicted leading his troops during the Mudéjar revolt of 1264–1266 in the Cantigas de Santa Maria
Muhammad I (red tunic and shield) depicted leading his troops during the Mudéjar revolt of 1264–1266 in the Cantigas de Santa Maria
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Yusuf ibn Nasr (Arabic: أبو عبد الله محمد بن يوسف بن نصر; 1195 – 22 January 1273), also known as Ibn al-Ahmar (Arabic: ابن الأحمر, "Son of the Red") and by his honorific al-Ghalib billah (Arabic: الغالب بالله, "The Victor by the Grace of God"), was the first ruler of the Emirate of Granada, the last independent Muslim state on the Iberian Peninsula, and the founder of its ruling Nasrid dynasty. He lived during a time when Iberia's Christian kingdoms—especially Portugal, Castile and Aragon—were expanding at the expense of the Islamic territory in Iberia, called Al-Andalus. Muhammad ibn Yusuf took power in his native Arjona in 1232 when he rebelled against the de facto leader of Al-Andalus, Ibn Hud. During this rebellion, he was able to take control of Córdoba and Seville briefly, before he lost both cities to Ibn Hud. Forced to acknowledge Ibn Hud's suzerainty, Muhammad was able to retain Arjona and Jaén. In 1236, he betrayed Ibn Hud by helping Ferdinand III of Castile take Córdoba. In the years that followed, Muhammad was able to gain control over southern cities, including Granada (1237), Almería (1238), and Málaga (1239). In 1244, he lost Arjona to Castile. Two years later, in 1246, he agreed to surrender Jaén and accept Ferdinand's overlordship in exchange for a 20-year truce. (Full article...) Image 8
Image 8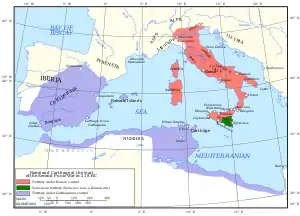 The western Mediterranean in 218 BC
The western Mediterranean in 218 BC
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Italy and Iberia, but also on the islands of Sicily and Sardinia and, towards the end of the war, in North Africa. After immense materiel and human losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were once again defeated. Macedonia, Syracuse and several Numidian kingdoms were drawn into the fighting, and Iberian and Gallic forces fought on both sides. There were three main military theatres during the war: Italy, where Hannibal defeated the Roman legions repeatedly, with occasional subsidiary campaigns in Sicily, Sardinia and Greece; Iberia, where Hasdrubal, a younger brother of Hannibal, defended the Carthaginian colonial cities with mixed success before moving into Italy; and Africa, where Rome finally won the war. (Full article...) Image 9
Image 9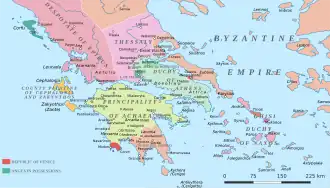 Map of the Greek and Latin states in southern Greece c. 1278
Map of the Greek and Latin states in southern Greece c. 1278
The Battle of Halmyros, known by earlier scholars as the Battle of the Cephissus or Battle of Orchomenos, was fought on 15 March 1311, between the forces of the Frankish Duchy of Athens and its vassals under Walter of Brienne against the mercenaries of the Catalan Company, resulting in a decisive victory for the mercenaries. (Full article...) Image 10Abu'l-Walid Ismail I ibn Faraj (Arabic: أبو الوليد إسماعيل الأول بن فرج, 3 March 1279 – 8 July 1325) was the fifth Nasrid ruler of the Emirate of Granada on the Iberian Peninsula from 1314 to 1325. A grandson of Muhammad II on the side of his mother Fatima, he was the first of the lineage of sultans now known as the al-dawla al-isma'iliyya al-nasriyya (the Nasrid dynasty of Ismail). Historians characterise him as an effective ruler who improved the emirate's position with military victories during his reign. (Full article...)
Image 10Abu'l-Walid Ismail I ibn Faraj (Arabic: أبو الوليد إسماعيل الأول بن فرج, 3 March 1279 – 8 July 1325) was the fifth Nasrid ruler of the Emirate of Granada on the Iberian Peninsula from 1314 to 1325. A grandson of Muhammad II on the side of his mother Fatima, he was the first of the lineage of sultans now known as the al-dawla al-isma'iliyya al-nasriyya (the Nasrid dynasty of Ismail). Historians characterise him as an effective ruler who improved the emirate's position with military victories during his reign. (Full article...) Image 11
Image 11 Plate 3: Lo mismo (The same). A Spanish man about to kill by cutting off the head of a French soldier with an axe.
Plate 3: Lo mismo (The same). A Spanish man about to kill by cutting off the head of a French soldier with an axe.
The Disasters of War (Spanish: Los desastres de la guerra) is a series of 82 prints created between 1810 and 1820 by the Spanish painter and printmaker Francisco Goya (1746–1828). Although Goya did not make known his intention when creating the plates, art historians view them as a visual protest against the violence of the 1808 Dos de Mayo Uprising, the subsequent Peninsular War of 1808–1814 and the setbacks to the liberal cause following the restoration of the Bourbon monarchy in 1814. During the conflicts between Napoleon's French Empire and Spain, Goya retained his position as first court painter to the Spanish crown and continued to produce portraits of the Spanish and French rulers. Although deeply affected by the war, he kept private his thoughts on the art he produced in response to the conflict and its aftermath. (Full article...)![Image 12Portrait of a Man (presumed self-portrait of El Greco, c. 1595–1600) in Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York CityDomḗnikos Theotokópoulos (Greek: Δομήνικος Θεοτοκόπουλος, IPA: [ðoˈminikos θeotoˈkopulos]; 1 October 1541 – 7 April 1614), most widely known as El Greco (Spanish pronunciation: [el ˈɣɾeko]; "The Greek"), was a Greek painter, sculptor and architect of the Spanish Renaissance. El Greco was a nickname, and the artist normally signed his paintings with his full birth name in Greek letters, often adding the word Κρής (Krḗs), which means "Cretan". (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 12
Image 12 Portrait of a Man (presumed self-portrait of El Greco, c. 1595–1600) in Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York City
Portrait of a Man (presumed self-portrait of El Greco, c. 1595–1600) in Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York City
Domḗnikos Theotokópoulos (Greek: Δομήνικος Θεοτοκόπουλος, IPA: [ðoˈminikos θeotoˈkopulos]; 1 October 1541 – 7 April 1614), most widely known as El Greco (Spanish pronunciation: [el ˈɣɾeko]; "The Greek"), was a Greek painter, sculptor and architect of the Spanish Renaissance. El Greco was a nickname, and the artist normally signed his paintings with his full birth name in Greek letters, often adding the word Κρής (Krḗs), which means "Cretan". (Full article...)![Image 13Las Meninas (Spanish for 'The Ladies-in-waiting' pronounced [las meˈninas]) is a 1656 painting in the Museo del Prado in Madrid, by Diego Velázquez, the leading artist of the Spanish Baroque. It has become one of the most widely analyzed works in Western painting for the way its complex and enigmatic composition raises questions about reality and illusion, and for the uncertain relationship it creates between the viewer and the figures depicted. (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 13Las Meninas (Spanish for 'The Ladies-in-waiting' pronounced [las meˈninas]) is a 1656 painting in the Museo del Prado in Madrid, by Diego Velázquez, the leading artist of the Spanish Baroque. It has become one of the most widely analyzed works in Western painting for the way its complex and enigmatic composition raises questions about reality and illusion, and for the uncertain relationship it creates between the viewer and the figures depicted. (Full article...)
Image 13Las Meninas (Spanish for 'The Ladies-in-waiting' pronounced [las meˈninas]) is a 1656 painting in the Museo del Prado in Madrid, by Diego Velázquez, the leading artist of the Spanish Baroque. It has become one of the most widely analyzed works in Western painting for the way its complex and enigmatic composition raises questions about reality and illusion, and for the uncertain relationship it creates between the viewer and the figures depicted. (Full article...)
 Image 14Muhammad II (Arabic: محمد الثاني) (also known by the epithet al-Faqih, "the canon-lawyer", c. 1235 – 8 April 1302; reigned from 1273 until his death) was the second Nasrid ruler of the Emirate of Granada in Al-Andalus on the Iberian Peninsula, succeeding his father, Muhammad I. Already experienced in matters of state when he ascended the throne, he continued his father's policy of maintaining independence in the face of Granada's larger neighbours, the Christian kingdom of Castile and the Muslim Marinid state of Morocco, as well as an internal rebellion by his family's former allies, the Banu Ashqilula. (Full article...)
Image 14Muhammad II (Arabic: محمد الثاني) (also known by the epithet al-Faqih, "the canon-lawyer", c. 1235 – 8 April 1302; reigned from 1273 until his death) was the second Nasrid ruler of the Emirate of Granada in Al-Andalus on the Iberian Peninsula, succeeding his father, Muhammad I. Already experienced in matters of state when he ascended the throne, he continued his father's policy of maintaining independence in the face of Granada's larger neighbours, the Christian kingdom of Castile and the Muslim Marinid state of Morocco, as well as an internal rebellion by his family's former allies, the Banu Ashqilula. (Full article...) Image 15
Image 15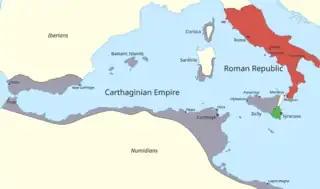 The Western Mediterranean just before the start of the war in 264 BC: Rome is shown in red, Carthage in grey, and Syracuse in green
The Western Mediterranean just before the start of the war in 264 BC: Rome is shown in red, Carthage in grey, and Syracuse in green
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and greatest naval war of antiquity, the two powers struggled for supremacy. The war was fought primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. After immense losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were defeated. (Full article...) Image 16
Image 16
The black stork (Ciconia nigra) is a large bird in the stork family Ciconiidae. It was first described by Carl Linnaeus in the 10th edition of his Systema Naturae. Measuring on average 95 to 100 cm (37 to 39 in) from beak tip to end of tail with a 145-to-155 cm (57-to-61 in) wingspan, the adult black stork has mainly black plumage, with white underparts, long red legs and a long pointed red beak. A widespread but uncommon species, it breeds in scattered locations across Europe (predominantly in Portugal and Spain, and central and eastern parts), and east across the Palearctic to the Pacific Ocean. It is a long-distance migrant, with European populations wintering in tropical Sub-Saharan Africa, and Asian populations in the Indian subcontinent. When migrating between Europe and Africa, it avoids crossing broad expanses of the Mediterranean Sea and detours via the Levant in the east, the Strait of Sicily in the center, or the Strait of Gibraltar in the west. An isolated, non-migratory, population occurs in Southern Africa. (Full article...) Image 17
Image 17.jpg.webp) Witches' Sabbath, 1821–1823. Oil on plaster wall, transferred to canvas; 140.5 × 435.7 cm (56 × 172 in). Museo del Prado, Madrid
Witches' Sabbath, 1821–1823. Oil on plaster wall, transferred to canvas; 140.5 × 435.7 cm (56 × 172 in). Museo del Prado, Madrid
Witches' Sabbath or The Great He-Goat (Spanish: Aquelarre or El gran cabrón) are names given to an oil mural by the Spanish artist Francisco Goya, completed sometime between 1821 and 1823. It explores themes of violence, intimidation, aging and death. Satan hulks, in the form of a goat, in moonlit silhouette over a coven of terrified witches. Goya was then around 75 years old, living alone and suffering from acute mental and physical distress. (Full article...) Image 18
Image 18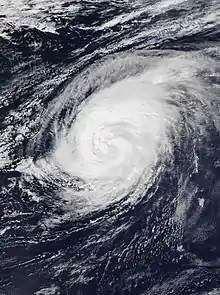 Hurricane Leslie near peak intensity southwest of the Azores on 11 October
Hurricane Leslie near peak intensity southwest of the Azores on 11 October
Hurricane Leslie (known as Storm Leslie or Cyclone Leslie while extratropical) was the strongest cyclone of tropical origin to strike the Iberian Peninsula since 1842. A large, long-lived, and very erratic tropical cyclone, Leslie was the twelfth named storm and sixth hurricane of the 2018 Atlantic hurricane season.[1] The storm had a non-tropical origin, developing from an extratropical cyclone that was situated over the northern Atlantic on 22 September. The low quickly acquired subtropical characteristics and was classified as Subtropical Storm Leslie on the following day. The cyclone meandered over the northern Atlantic and gradually weakened, before merging with a frontal system on 25 September, which later intensified into a powerful hurricane-force extratropical low over the northern Atlantic. (Full article...) Image 19
Image 19 A Wehrmacht Panzerkampfwagen I Ausf. A light tank on display at the Deutsches Panzermuseum Munster in Munster, Germany.
A Wehrmacht Panzerkampfwagen I Ausf. A light tank on display at the Deutsches Panzermuseum Munster in Munster, Germany.
The Panzer I was a light tank produced by Nazi Germany in the 1930s. Its name is short for Panzerkampfwagen I (German for "armored fighting vehicle mark I"), abbreviated as PzKpfw I. The tank's official German ordnance inventory designation was Sd.Kfz. 101 ("special purpose vehicle 101"). (Full article...) Image 20
Image 20 The siege of Nice by a Franco-Ottoman fleet in 1543 (drawing by Toselli, after an engraving by Aeneas Vico)
The siege of Nice by a Franco-Ottoman fleet in 1543 (drawing by Toselli, after an engraving by Aeneas Vico)
The Italian War of 1542–1546 was a conflict late in the Italian Wars, pitting Francis I of France and Suleiman I of the Ottoman Empire against the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V and Henry VIII of England. The course of the war saw extensive fighting in Italy, France, and the Low Countries, as well as attempted invasions of Spain and England. The conflict was inconclusive and ruinously expensive for the major participants. (Full article...) Image 21
Image 21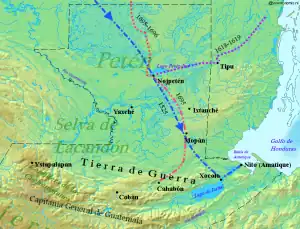 Spanish entry routes to Petén during the 17th century, overlaid with the route that Hernán Cortés took in 1525
Spanish entry routes to Petén during the 17th century, overlaid with the route that Hernán Cortés took in 1525
The Spanish conquest of Petén was the last stage of the conquest of Guatemala, a prolonged conflict during the Spanish colonisation of the Americas. A wide lowland plain covered with dense rainforest, Petén contains a central drainage basin with a series of lakes and areas of savannah. It is crossed by several ranges of low karstic hills and rises to the south as it nears the Guatemalan Highlands. The conquest of Petén, a region now incorporated into the modern republic of Guatemala, climaxed in 1697 with the capture of Nojpetén, the island capital of the Itza kingdom, by Martín de Ursúa y Arizmendi. With the defeat of the Itza, the last independent and unconquered native kingdom in the Americas fell to European colonisers. (Full article...) Image 22
Image 22 An AMX-30E on display at the Museum of Armored Vehicles of El Goloso, in Spain
An AMX-30E on display at the Museum of Armored Vehicles of El Goloso, in Spain
The AMX-30E (E stands for España, Spanish for Spain) is a Spanish main battle tank based on France's AMX-30. Although originally the Spanish government sought to procure the German Leopard 1, the AMX-30 was ultimately awarded the contract due to its lower price and the ability to manufacture it in Spain. 280 units were manufactured by Santa Bárbara Sistemas for the Spanish Army, between 1974 and 1983. (Full article...) Image 23
Image 23 North View of Gibraltar from Spanish Lines by John Mace (1782)
North View of Gibraltar from Spanish Lines by John Mace (1782)
The history of Gibraltar, a small peninsula on the southern Iberian coast near the entrance of the Mediterranean Sea, spans over 2,900 years. The peninsula has evolved from a place of reverence in ancient times into "one of the most densely fortified and fought-over places in Europe", as one historian has put it. Gibraltar's location has given it an outsized significance in the history of Europe and its fortified town, established in the Middle Ages, has hosted garrisons that sustained numerous sieges and battles over the centuries. (Full article...) Image 24
Image 24 An M48 Patton tank of the Spanish Army on display at the El Goloso Museum of Armored Vehicles in October 2007.
An M48 Patton tank of the Spanish Army on display at the El Goloso Museum of Armored Vehicles in October 2007.
Tanks in the Spanish Army have over 90 years of history, from the French Renault FTs first delivered in 1919 to the Leopard 2 and B1 Centauro models of the early 21st century. The Spanish FTs took part in combat during the Rif War and participated in the first amphibious landing with tanks in history, at Alhucemas. In 1925, the Spanish Army began to undertake a program to develop and produce a Spanish tank, an upgraded version of the Renault FT, called the Trubia A4. Although the prototype performed well during testing, the tank was never put into mass production. Spain also experimented with the Italian Fiat 3000, acquiring one tank in 1925, and with another indigenous tank program called the Landesa. However, none of these evolved into a major armor program, and as a result the FT remained the most important tank, in numbers, in the Spanish Army until the beginning of the Spanish Civil War. (Full article...) Image 25
Image 25 View of Badajoz, across the Guadiana river from the foothills of the San Cristóbal heights, by Eugène-Ferdinand Buttura
View of Badajoz, across the Guadiana river from the foothills of the San Cristóbal heights, by Eugène-Ferdinand Buttura
The Battle of the Gebora was a battle of the Peninsular War between Spanish and French armies. It took place on 19 February 1811, northwest of Badajoz, Spain, where an outnumbered French force routed and nearly destroyed the Spanish Army of Extremadura. (Full article...)
Selected biography

Pedro Almodóvar Caballero (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈpeð̞ɾo almoˈð̞oβ̞aɾ kaβ̞aˈʝeɾo]) (born September 24, 1949 in Calzada de Calatrava, Spain) is a Spanish film director, screenwriter and producer. Almodóvar is the most successful and internationally known Spanish filmmaker of his generation. His films, marked by complex narratives, employ the codes of melodrama and use elements of pop culture, popular songs, irreverent humor, strong colors and glossy décor. He never judges his character's actions, whatever they do, but he presents them as they are in all their complexity. Desire, passion, family and identity are the director's favorite themes. Almodóvar’s films enjoy a worldwide following and he has become a major figure on the stage of world cinema.
Pedro Almodóvar Caballero was born on September 24, 1949 in Calzada de Calatrava, a rural small town of Ciudad Real, a province of Castile-La Mancha in the administrative district of Almagro. La Mancha is the windswept region of flat lands made famous by Don Quijote. He was born as one of four children (two boys, two girls) in a large and impoverished family of peasant stock. His father, Antonio Almodóvar, who could barely read or write worked most of his life hauling barrels of wine by mule. Almodóvar's mother, Francisca Caballero, turned her son into a part time teacher of literacy in the village and also a letter reader and transcriber for the neighbors. When Pedro was eight years old, the family sent him to study at a religious boarding school in the city of Cáceres, Extremadura, in the west of the country, with the hope that he might someday become a priest.
Selected picture
_jeannaea.jpg.webp) Image 1Photograph: Benny TrappThe Spanish painted frog (Discoglossus jeanneae) is a species of frog in the family Alytidae. Endemic to Spain, it mostly lives in open areas, pine groves and shrublands. It feeds mostly on insects and worms.
Image 1Photograph: Benny TrappThe Spanish painted frog (Discoglossus jeanneae) is a species of frog in the family Alytidae. Endemic to Spain, it mostly lives in open areas, pine groves and shrublands. It feeds mostly on insects and worms. Image 2Coin design credit: Duchy of ParmaThe doubloon was a Spanish gold coin worth two escudos or 32 reales weighing 6.867 grams (0.221 troy ounces), introduced in 1537. It became the model for several other gold coins issued in Europe, including this 1626 two-doppie gold coin issued in Piacenza in northern Italy by the Duchy of Parma, depicting Odoardo Farnese, Duke of Parma, on the obverse. The coin is part of the National Numismatic Collection at the National Museum of American History.
Image 2Coin design credit: Duchy of ParmaThe doubloon was a Spanish gold coin worth two escudos or 32 reales weighing 6.867 grams (0.221 troy ounces), introduced in 1537. It became the model for several other gold coins issued in Europe, including this 1626 two-doppie gold coin issued in Piacenza in northern Italy by the Duchy of Parma, depicting Odoardo Farnese, Duke of Parma, on the obverse. The coin is part of the National Numismatic Collection at the National Museum of American History. Image 3Painting: Francisco GoyaThe Third of May 1808 is a painting completed in 1814 by the Spanish master Francisco Goya, now in the Museo del Prado, Madrid. Along with its companion piece of the same size, The Second of May 1808 (or The Charge of the Mamelukes), it was commissioned by the provisional government of Spain at Goya's suggestion. Goya sought to commemorate Spanish resistance to Napoleon's armies during the Peninsular War.
Image 3Painting: Francisco GoyaThe Third of May 1808 is a painting completed in 1814 by the Spanish master Francisco Goya, now in the Museo del Prado, Madrid. Along with its companion piece of the same size, The Second of May 1808 (or The Charge of the Mamelukes), it was commissioned by the provisional government of Spain at Goya's suggestion. Goya sought to commemorate Spanish resistance to Napoleon's armies during the Peninsular War. Image 4
Image 4 Pablo PicassoCredit: TyreniusPablo Picasso (October 25, 1881 — April 8, 1973) was an artist and sculptor. Picasso was born in Málaga, Spain. This image was taken of him in 1962, eleven years before his death.
Pablo PicassoCredit: TyreniusPablo Picasso (October 25, 1881 — April 8, 1973) was an artist and sculptor. Picasso was born in Málaga, Spain. This image was taken of him in 1962, eleven years before his death. Image 5
Image 5 An exterior view of the Museo del Prado.The Museo del Prado is a museum and art gallery located in Madrid; the capital of Spain. It features one of the world's finest collections of European art, from the 12th century through the early 19th century, based on the former Spanish Royal Collection.
An exterior view of the Museo del Prado.The Museo del Prado is a museum and art gallery located in Madrid; the capital of Spain. It features one of the world's finest collections of European art, from the 12th century through the early 19th century, based on the former Spanish Royal Collection..jpg.webp) Image 6Photograph credit: Biblioteca Nacional de EspañaAna Santos Aramburo (born 1957) has been the director of the National Library of Spain since February 2013. Having received a degree in geography and history from the University of Zaragoza in Spain, she has spent much of her career working at the Complutense University of Madrid, first at the library of the Faculty of Economics and Business Sciences, and later serving as deputy director of the university library. Later she served as Director of the Historical Library Marquis of Valdecilla, General Director of Libraries and Archives of the City of Madrid, and Director of Cultural Action at the National Library. This photograph of Santos shows her at the headquarters of the National Library of Spain in Madrid.
Image 6Photograph credit: Biblioteca Nacional de EspañaAna Santos Aramburo (born 1957) has been the director of the National Library of Spain since February 2013. Having received a degree in geography and history from the University of Zaragoza in Spain, she has spent much of her career working at the Complutense University of Madrid, first at the library of the Faculty of Economics and Business Sciences, and later serving as deputy director of the university library. Later she served as Director of the Historical Library Marquis of Valdecilla, General Director of Libraries and Archives of the City of Madrid, and Director of Cultural Action at the National Library. This photograph of Santos shows her at the headquarters of the National Library of Spain in Madrid. Image 7Photograph: J.Ligero & I.BarriosA three-month old Spanish ibex (Capra pyrenaica) in Sierra de Gredos, Spain. These ibexes are strong mountain animals characterized by their large and flexible hooves and short legs.
Image 7Photograph: J.Ligero & I.BarriosA three-month old Spanish ibex (Capra pyrenaica) in Sierra de Gredos, Spain. These ibexes are strong mountain animals characterized by their large and flexible hooves and short legs.
The two sexes of adults form separate social groups; juveniles stay with the female groups from birth until the following birth season, when they leave. Yearling males then join male groups, while females eventually return to their mothers' groups and stay several years. Image 8Photo credit: DiliffThe Torre Agbar is a landmark skyscraper and the third tallest building in Barcelona, Spain. It was designed by French architect Jean Nouvel, who stated that the shape of the Torre Agbar was inspired by the mountains of Montserrat that surround Barcelona, and by the shape of a geyser of water rising into the air. Its design combines a number of different architectural concepts, resulting in a striking structure built with reinforced concrete, covered with a facade of glass, and over 4,500 window openings cut out of the structural concrete.
Image 8Photo credit: DiliffThe Torre Agbar is a landmark skyscraper and the third tallest building in Barcelona, Spain. It was designed by French architect Jean Nouvel, who stated that the shape of the Torre Agbar was inspired by the mountains of Montserrat that surround Barcelona, and by the shape of a geyser of water rising into the air. Its design combines a number of different architectural concepts, resulting in a striking structure built with reinforced concrete, covered with a facade of glass, and over 4,500 window openings cut out of the structural concrete. Image 9
Image 9 AlhambraCredit: Ra-smit
AlhambraCredit: Ra-smit
The Alhambra (Arabic: الحمراء = Al-Ħamrā; literally "the red") is a palace and fortress complex of the Moorish monarchs of Granada in southern Spain (known as Al-Andalus when the fortress was constructed), occupying a hilly terrace on the southeastern border of the city of Granada. Image 10Photo: David IliffThe Giralda is a 104.5 m (343 ft) tall bell tower for the Seville Cathedral in Seville, Andalusia, Spain. It was originally constructed as a minaret in 1198, when Seville was ruled by the Almohad Caliphate. After the city was taken by the Christians in the Reconquista, the city's mosque was converted to a church. The upper third of the structure was completed during the Spanish Renaissance.
Image 10Photo: David IliffThe Giralda is a 104.5 m (343 ft) tall bell tower for the Seville Cathedral in Seville, Andalusia, Spain. It was originally constructed as a minaret in 1198, when Seville was ruled by the Almohad Caliphate. After the city was taken by the Christians in the Reconquista, the city's mosque was converted to a church. The upper third of the structure was completed during the Spanish Renaissance. Image 11
Image 11 Alcántara bridgeCredit:
Alcántara bridgeCredit:
The Roman bridge of Alcántara, located in the province of Cáceres, Extremadura. Image 12
Image 12 Cala FigueraCredit: BuzzWoof
Cala FigueraCredit: BuzzWoof
The harbor entrance to Cala Figuera, a district of Mallorca in the Balearic Islands. The town is located approximately 60 kilometers north of Palma de Mallorca. The earliest records of the town date back to 1306, although houses were not built on the land until the early 19th century. Image 13Banknote: Bank of SpainThe Spanish peseta is a former currency of Spain and, alongside the French franc, a former de facto currency in Andorra. It was introduced in 1868, replacing the peso, at a time when Spain was considering joining the Latin Monetary Union. Spain joined the euro in 1999, and the peseta was replaced by euro notes and coins in 2002.
Image 13Banknote: Bank of SpainThe Spanish peseta is a former currency of Spain and, alongside the French franc, a former de facto currency in Andorra. It was introduced in 1868, replacing the peso, at a time when Spain was considering joining the Latin Monetary Union. Spain joined the euro in 1999, and the peseta was replaced by euro notes and coins in 2002.
This picture shows a 1000 peseta banknote from 1957. The obverse depicts the Catholic Monarchs while the reverse shows the coat of arms of Spain. Image 14Photo credit: David IliffThe Tagus River, seen here passing through the World Heritage listed city of Toledo, Spain. It is the longest river on the Iberian Peninsula at 1,038 kilometres (645 mi). It begins its journey in the Albarracín mountains in Spain, and follows a very constricted course for much of its length before reaching the Atlantic Ocean in Portugal.
Image 14Photo credit: David IliffThe Tagus River, seen here passing through the World Heritage listed city of Toledo, Spain. It is the longest river on the Iberian Peninsula at 1,038 kilometres (645 mi). It begins its journey in the Albarracín mountains in Spain, and follows a very constricted course for much of its length before reaching the Atlantic Ocean in Portugal. Image 15Photo credit: David IliffThe Queen Sofia Palace of the Arts (Valencian: Palau de les Arts Reina Sofía) is an opera house located in Valencia, Spain. The last to be completed of the City of Arts and Sciences complex, it was designed by architect Santiago Calatrava. The 14-story structure opened on 8 October 2005.
Image 15Photo credit: David IliffThe Queen Sofia Palace of the Arts (Valencian: Palau de les Arts Reina Sofía) is an opera house located in Valencia, Spain. The last to be completed of the City of Arts and Sciences complex, it was designed by architect Santiago Calatrava. The 14-story structure opened on 8 October 2005. Image 16
Image 16 The Battle of RavennaCredit: Ary Scheffer
The Battle of RavennaCredit: Ary Scheffer
An artists portrayal of the Battle of Ravenna (1512). This artwork also shows the death of Gaston de Foix, as well as the general scene during the time of battle. Image 17Photo: Mick StephensonThe peaks of the Central Massif overlook the village of Sotres in Cabrales, located in the Picos de Europa, a mountain range in northern Spain forming part of the Cantabrian Mountains. The name (literally: "Peaks of Europe") is believed to derive from being the first European landforms visible to mariners arriving from the Americas.
Image 17Photo: Mick StephensonThe peaks of the Central Massif overlook the village of Sotres in Cabrales, located in the Picos de Europa, a mountain range in northern Spain forming part of the Cantabrian Mountains. The name (literally: "Peaks of Europe") is believed to derive from being the first European landforms visible to mariners arriving from the Americas. Image 18Photograph: Diego DelsoMoros is a municipality in the province of Zaragoza, Spain. Located in the Sistema Ibérico mountain range, the village lies on a hill, with the church and former town hall at the top, the residences in the middle, and the sheep pens at the bottom. The population of Moros has been steadily decreasing in recent decades, and was 478 in 2006.
Image 18Photograph: Diego DelsoMoros is a municipality in the province of Zaragoza, Spain. Located in the Sistema Ibérico mountain range, the village lies on a hill, with the church and former town hall at the top, the residences in the middle, and the sheep pens at the bottom. The population of Moros has been steadily decreasing in recent decades, and was 478 in 2006. Image 19Architecture credit: José Grases Riera; photographed by Carlos DelgadoThe Monument to Alfonso XII is located in Buen Retiro Park (El Retiro) in Madrid, Spain. Measuring 30 m (98 ft) high, 86 m (282 ft) long, and 58 m (190 ft) wide, it has at its center an equestrian statue of King Alfonso XII, cast in bronze by the Spanish sculptor Mariano Benlliure in 1904. The monument is situated on the eastern edge of an artificial lake near the center of the park and was inaugurated on 6 June 1922.
Image 19Architecture credit: José Grases Riera; photographed by Carlos DelgadoThe Monument to Alfonso XII is located in Buen Retiro Park (El Retiro) in Madrid, Spain. Measuring 30 m (98 ft) high, 86 m (282 ft) long, and 58 m (190 ft) wide, it has at its center an equestrian statue of King Alfonso XII, cast in bronze by the Spanish sculptor Mariano Benlliure in 1904. The monument is situated on the eastern edge of an artificial lake near the center of the park and was inaugurated on 6 June 1922. Image 20Painting credit: Francisco GoyaCharles IV of Spain and His Family is a portrait of the royal family of Spain painted by Francisco Goya in 1800 and 1801. King Charles IV, his wife Maria Luisa of Parma, and his children and relatives are dressed in the height of contemporary fashion, lavishly adorned with jewelry and the sashes of the order of Charles III. The artist does not attempt to flatter the family; instead the group portrait is unflinchingly realist, both in detail and tone. The artist, seated at his easel, is visible in the background. The painting is in the collection of the Museo del Prado in Madrid.
Image 20Painting credit: Francisco GoyaCharles IV of Spain and His Family is a portrait of the royal family of Spain painted by Francisco Goya in 1800 and 1801. King Charles IV, his wife Maria Luisa of Parma, and his children and relatives are dressed in the height of contemporary fashion, lavishly adorned with jewelry and the sashes of the order of Charles III. The artist does not attempt to flatter the family; instead the group portrait is unflinchingly realist, both in detail and tone. The artist, seated at his easel, is visible in the background. The painting is in the collection of the Museo del Prado in Madrid. Image 21
Image 21_02b.jpg.webp) A statue showing Christopher ColumbusA statue showing Christopher Columbus and Queen Isabella, the statue was made in 1885.
A statue showing Christopher ColumbusA statue showing Christopher Columbus and Queen Isabella, the statue was made in 1885. Image 22Photo credit: David IliffThe Casa Milà, a 1912 work by Catalán architect Antoni Gaudi, in the Eixample district of Barcelona, Spain. Gaudí's fascination with trencadís-influenced decoration and curves (predating biomorphism by almost 20 years) can be seen here.
Image 22Photo credit: David IliffThe Casa Milà, a 1912 work by Catalán architect Antoni Gaudi, in the Eixample district of Barcelona, Spain. Gaudí's fascination with trencadís-influenced decoration and curves (predating biomorphism by almost 20 years) can be seen here.
Did you know...
- ... that the Monument to the Victims of the Holocaust in Madrid was the first Holocaust memorial in Spain when it opened in 2007?
- ... that the Spanish Inquisition sentenced Diego Mateo Zapata to wear the sanbenito, receive 200 lashes, have his 600 books confiscated, and be exiled, despite being acquitted?
- ... that after Spanish footballer Elene Lete had to leave Spain's under-20 football team with an injury in 2022, she returned to join the senior World Cup squad in 2023?
- ... that in 2019, a rockfall on the Spanish Autovia C-13 caused skiing holidays to be cancelled?
- ... that Chief Rabbi of Madrid Yehuda Benasouli's first language was Castilian Spanish, but he also knew Hebrew, French, Arabic, Ladino, Haketia, and some English?
- ... that Spanish mystic Marina de Escobar founded a convent but never joined one?
 Good article –
Good article –
 Image 1The 1957 Latin Cup (Spanish: Copa Latina de 1957) was the eighth and final edition of the annual Latin Cup. It was contested by the domestic league champions the Southwest European nations of France, Italy, Portugal, and Spain. The clubs which competed in the tournament were AS Saint-Étienne, AC Milan, SL Benfica, and Real Madrid CF. (Full article...)
Image 1The 1957 Latin Cup (Spanish: Copa Latina de 1957) was the eighth and final edition of the annual Latin Cup. It was contested by the domestic league champions the Southwest European nations of France, Italy, Portugal, and Spain. The clubs which competed in the tournament were AS Saint-Étienne, AC Milan, SL Benfica, and Real Madrid CF. (Full article...) Image 2The 2015 Clásica de San Sebastián was a one-day cycling classic that took place in the Basque Country in Spain on 1 August 2015. It was the 35th edition of the Clásica de San Sebastián and was the nineteenth race of the 2015 UCI World Tour. The defending champion was Alejandro Valverde (Movistar Team), who won a solo victory in the 2014 race. (Full article...)
Image 2The 2015 Clásica de San Sebastián was a one-day cycling classic that took place in the Basque Country in Spain on 1 August 2015. It was the 35th edition of the Clásica de San Sebastián and was the nineteenth race of the 2015 UCI World Tour. The defending champion was Alejandro Valverde (Movistar Team), who won a solo victory in the 2014 race. (Full article...) Image 3The Spanish conquest of Chiapas was the campaign undertaken by the Spanish conquistadores against the Late Postclassic Mesoamerican polities in the territory that is now incorporated into the modern Mexican state of Chiapas. The region is physically diverse, featuring a number of highland areas, including the Sierra Madre de Chiapas and the Montañas Centrales (Central Highlands), a southern littoral plain known as Soconusco and a central depression formed by the drainage of the Grijalva River. (Full article...)
Image 3The Spanish conquest of Chiapas was the campaign undertaken by the Spanish conquistadores against the Late Postclassic Mesoamerican polities in the territory that is now incorporated into the modern Mexican state of Chiapas. The region is physically diverse, featuring a number of highland areas, including the Sierra Madre de Chiapas and the Montañas Centrales (Central Highlands), a southern littoral plain known as Soconusco and a central depression formed by the drainage of the Grijalva River. (Full article...) Image 4
Image 4 Plácido painted by his son, Ignacio Zuloaga
Plácido painted by his son, Ignacio Zuloaga
Plácido Maria Martin Zuloaga y Zuloaga (5 October 1834 – 1 July 1910) was a Spanish sculptor and metalworker. He is known for refining damascening, a technique that involves inlaying gold, silver, and other metals into an iron surface, creating an intricate decorative effect. Zuloaga came from a family of Basque metalworkers. He was the son of damascening pioneer Eusebio Zuloaga, the half-brother of the artist Daniel Zuloaga, and the father of the painter Ignacio Zuloaga. Taking over his father's armaments factory, he adapted it to make art pieces which he exhibited at international fairs, winning multiple awards. (Full article...) Image 5The 1977 Atocha massacre was an attack by right-wing extremists in the center of Madrid on January 24, 1977, which saw the assassination of five labor activists from the Communist Party of Spain (PCE) and the workers' federation Comisiones Obreras (CC.OO). The act occurred within the wider context of far-right reaction to Spain's transition to constitutional democracy following the death of dictator Francisco Franco. Intended to provoke a violent left-wing response that would provide legitimacy for a subsequent right-wing counter coup d'état, the massacre had an immediate opposite effect; generating mass popular revulsion of the far-right and accelerating the legalization of the long-banned Communist Party. (Full article...)
Image 5The 1977 Atocha massacre was an attack by right-wing extremists in the center of Madrid on January 24, 1977, which saw the assassination of five labor activists from the Communist Party of Spain (PCE) and the workers' federation Comisiones Obreras (CC.OO). The act occurred within the wider context of far-right reaction to Spain's transition to constitutional democracy following the death of dictator Francisco Franco. Intended to provoke a violent left-wing response that would provide legitimacy for a subsequent right-wing counter coup d'état, the massacre had an immediate opposite effect; generating mass popular revulsion of the far-right and accelerating the legalization of the long-banned Communist Party. (Full article...) Image 6
Image 6 The Moorish Proselytes of Archbishop Ximenes, Granada, 1500 by Edwin Long (1829–1891), depicting a mass baptism of Muslims
The Moorish Proselytes of Archbishop Ximenes, Granada, 1500 by Edwin Long (1829–1891), depicting a mass baptism of Muslims
The forced conversions of Muslims in Spain were enacted through a series of edicts outlawing Islam in the lands of the Spanish Monarchy. This persecution was pursued by three Spanish kingdoms during the early 16th century: the Crown of Castile in 1500–1502, followed by Navarre in 1515–1516, and lastly the Crown of Aragon in 1523–1526. (Full article...) Image 7
Image 7 Clara Stauffer (1931)
Clara Stauffer (1931)
Clara Stauffer (1904–October 4, 1984) was a Spanish Falangist and Nazi ratline operator. She was a member of the Sección Femenina, a women's Falangist group, during the Spanish Civil War. She served as its chief propagandist and later as its head of foreign affairs. She was involved with the group's efforts to strengthen ties between Francoist Spain and Nazi Germany in World War II. After the war, she was one of the most prominent smugglers of Nazi fugitives, giving them shelter in Spain and arranging their travel to Argentina. (Full article...) Image 8
Image 8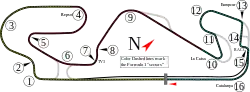 Circuit de Catalunya
Circuit de Catalunya
The 2012 Spanish Grand Prix (formally the Formula 1 Gran Premio de España Santander 2012) was a Formula One motor race held on 13 May 2012, at the Circuit de Catalunya in Montmeló, Spain, attended by 82,000 people. It was the fifth round of the 2012 Formula One World Championship and the 22nd Spanish Grand Prix at the track. Williams's Pastor Maldonado won the 66-lap event from pole position, with Ferrari's Fernando Alonso second and Lotus's Kimi Räikkönen third. (Full article...)![Image 9Bartolomé de las Casas, OP (US: /lɑːs ˈkɑːsəs/ lahss KAH-səss; Spanish: [baɾtoloˈme ðe las ˈkasas] ⓘ; 11 November 1484 – 18 July 1566) was a Spanish clergyman, writer, and activist best known for his work as a historian and social reformer. He arrived in Hispaniola as a layman, then became a Dominican friar. He was appointed as the first resident Bishop of Chiapas, and the first officially appointed "Protector of the Indians". His extensive writings, the most famous being A Short Account of the Destruction of the Indies and Historia de Las Indias, chronicle the first decades of colonization of the West Indies. He described the atrocities committed by the colonizers against the indigenous peoples. (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 9
Image 9
Bartolomé de las Casas, OP (US: /lɑːs ˈkɑːsəs/ lahss KAH-səss; Spanish: [baɾtoloˈme ðe las ˈkasas] ⓘ; 11 November 1484 – 18 July 1566) was a Spanish clergyman, writer, and activist best known for his work as a historian and social reformer. He arrived in Hispaniola as a layman, then became a Dominican friar. He was appointed as the first resident Bishop of Chiapas, and the first officially appointed "Protector of the Indians". His extensive writings, the most famous being A Short Account of the Destruction of the Indies and Historia de Las Indias, chronicle the first decades of colonization of the West Indies. He described the atrocities committed by the colonizers against the indigenous peoples. (Full article...) Image 10
Image 10
The current Basque coat of arms (Spanish: Escudo del País Vasco, Basque: Euskal autonomi erkidegoaren armarria) is the official coat of arms of the Basque Country, Autonomous community of Spain. It consists of a party per cross representing the three historical territories of Álava, Gipuzkoa and Biscay, as well as a fourth, void quarter. The arms are ringed by a regal wreath of oak leaves, symbolic of the Gernikako Arbola. The fourth quarter constituted since the late 19th century the linked chains of Navarre; however, following a legal suit by the Navarre Government claiming that the usage of the arms of a region on the flag of another was illegal, the Constitutional Court of Spain ordered the removal of the chains of Navarre in a judgement of 1986. (Full article...) Image 11The Legazpi-Sikatuna Blood Compact or Sandugo (Spanish: Pacto de Sangre) was a blood compact, performed in the island of Bohol in the Philippines, between the Spanish explorer Miguel López de Legazpi and Datu Sikatuna, chieftain of Bohol, on March 16, 1565, to seal their friendship following tribal tradition. This is considered the first treaty of friendship between the Spaniards and Filipinos. "Sandugo" is a Visayan word which means "one blood". (Full article...)
Image 11The Legazpi-Sikatuna Blood Compact or Sandugo (Spanish: Pacto de Sangre) was a blood compact, performed in the island of Bohol in the Philippines, between the Spanish explorer Miguel López de Legazpi and Datu Sikatuna, chieftain of Bohol, on March 16, 1565, to seal their friendship following tribal tradition. This is considered the first treaty of friendship between the Spaniards and Filipinos. "Sandugo" is a Visayan word which means "one blood". (Full article...) Image 12
Image 12 Illustration of España in 1912
Illustration of España in 1912
España was a Spanish dreadnought battleship, the lead ship of the España class, the two other ships being Alfonso XIII and Jaime I. The ship was built in the early 1910s in the context of a cooperative defensive agreement with Britain and France, as part of a naval construction program to restore the fleet after the losses of the Spanish–American War. She was the only member of the class to be completed before the start of World War I, which significantly delayed completion of the other vessels. The ships were armed with a main battery of eight 305 mm (12 in) guns and were intended to support the French Navy in the event of a major European war. (Full article...) Image 13
Image 13 The States' army in Noordhorn defeated by Verdugo, 1581. Simon Frisius, 1613–1615.
The States' army in Noordhorn defeated by Verdugo, 1581. Simon Frisius, 1613–1615.
The Battle of Noordhorn, fought on 30 September 1581, was a pitched battle of the Dutch Revolt, fought between a Spanish army commanded by Colonel Francisco Verdugo – consisting of Walloon, German, Spanish, and Albanian soldiers – and a Dutch States rebel army under the Englishman John Norreys – comprising English, Scottish, Dutch, and Walloon troops – in the province of Groningen. In 1580, the Dutch stadtholder of Groningen, George van Lalaing, Count of Rennenberg, had shifted its allegiance from the Dutch to the Spanish side. This opened a new front at the back door of the Dutch Republic, forcing the States-General to dispatch forces to the north. That year the Dutch, under the leadership of John Norreys, succeeded in relieving the town of Steenwijk. In July 1581, Rennenberg died and was replaced by the Spaniard Francisco Verdugo, whose arrival in Groningen with reinforcements changed the situation. On 30 September Verdugo forced Norreys to give battle using a strategy of attrition. (Full article...)![Image 14Bust of Hadrian, c. 130Hadrian (/ˈheɪdriən/, HAY-dree-ən; Latin: Hadrianus [(h)adriˈjaːnus]; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. Hadrian was born in Italica, close to modern Seville in Spain, an Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his branch of the Aelia gens, the Aeli Hadriani, came from the town of Hadria in eastern Italy. He was a member of the Nerva-Antonine dynasty. (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 14
Image 14 Bust of Hadrian, c. 130
Bust of Hadrian, c. 130
Hadrian (/ˈheɪdriən/, HAY-dree-ən; Latin: Hadrianus [(h)adriˈjaːnus]; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. Hadrian was born in Italica, close to modern Seville in Spain, an Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his branch of the Aelia gens, the Aeli Hadriani, came from the town of Hadria in eastern Italy. He was a member of the Nerva-Antonine dynasty. (Full article...) Image 15
Image 15 Monbar Hotel in 2007
Monbar Hotel in 2007
The Monbar Hotel attack was carried out by the Grupos Antiterroristas de Liberación (GAL), a Spanish state-sponsored death squad, on 25 September 1985 in Bayonne, Pyrénées-Atlantiques, France. The targets were four members of the Basque separatist terrorist group Euskadi Ta Askatasuna (ETA), whom the Spanish government believed to be senior figures in the organization, itself proscribed as a terrorist group in Spain and France. All four people were killed, with a fifth person, apparently unconnected to ETA, injured in the shooting. This represented the deadliest attack carried out by the GAL. Although two of the participants were apprehended shortly after the shooting, controversy surrounded the possible involvement of senior figures in the Spanish police. (Full article...) Image 16"Esperanza" (English: "Hope") is a song by Spanish singer Enrique Iglesias for his third studio album Cosas del Amor (1998). It was co-written by Igleias and Chein García-Alonso with Rafael Pérez-Botija handling its production. A power ballad, it is a confessional song of love and forgiveness. Upon "Esperanza"'s release, one reviewer lauded Iglesias's vocals and the song's arrangements while another found it too similar to his debut single "Si Tú Te Vas". Filmed in Malibu, California, the accompanying music video for "Esperanza" was directed by Emmanuel Lubezki, which won Video of the Year at the 11th Annual Lo Nuestro Awards in 1999. "Esperanza" also won "Song of the Year" and an American Society of Composers, Authors and Publishers (ASCAP) Latin Award in the same year. Commercially, it reached number one in Guatemala, Nicaragua, and Panama as well as the Billboard Hot Latin Songs and Latin Pop Airplay charts in the United States, while becoming top-five hit in Colombia, Costa Rica, Honduras and El Salvador. (Full article...)
Image 16"Esperanza" (English: "Hope") is a song by Spanish singer Enrique Iglesias for his third studio album Cosas del Amor (1998). It was co-written by Igleias and Chein García-Alonso with Rafael Pérez-Botija handling its production. A power ballad, it is a confessional song of love and forgiveness. Upon "Esperanza"'s release, one reviewer lauded Iglesias's vocals and the song's arrangements while another found it too similar to his debut single "Si Tú Te Vas". Filmed in Malibu, California, the accompanying music video for "Esperanza" was directed by Emmanuel Lubezki, which won Video of the Year at the 11th Annual Lo Nuestro Awards in 1999. "Esperanza" also won "Song of the Year" and an American Society of Composers, Authors and Publishers (ASCAP) Latin Award in the same year. Commercially, it reached number one in Guatemala, Nicaragua, and Panama as well as the Billboard Hot Latin Songs and Latin Pop Airplay charts in the United States, while becoming top-five hit in Colombia, Costa Rica, Honduras and El Salvador. (Full article...)![Image 17Gómez de Alvarado y Contreras (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈɡomeθ ðe alβaˈɾaðoj konˈtɾeɾas]; 1482 – September 1542) was a Spanish conquistador and explorer. He was a member of the Alvarado family and the older brother of the famous conquistador Pedro de Alvarado. (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 17Gómez de Alvarado y Contreras (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈɡomeθ ðe alβaˈɾaðoj konˈtɾeɾas]; 1482 – September 1542) was a Spanish conquistador and explorer. He was a member of the Alvarado family and the older brother of the famous conquistador Pedro de Alvarado. (Full article...)
Image 17Gómez de Alvarado y Contreras (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈɡomeθ ðe alβaˈɾaðoj konˈtɾeɾas]; 1482 – September 1542) was a Spanish conquistador and explorer. He was a member of the Alvarado family and the older brother of the famous conquistador Pedro de Alvarado. (Full article...) Image 18
Image 18.jpg.webp) Muhammad I of Granada (in red tunic and shield) leading his troops during the rebellion, illustrated in the contemporary Cantigas de Santa Maria.
Muhammad I of Granada (in red tunic and shield) leading his troops during the rebellion, illustrated in the contemporary Cantigas de Santa Maria.
The Mudéjar revolt of 1264–1266 was a rebellion by the Muslim populations (Mudéjares) in the Lower Andalusia and Murcia regions of the Crown of Castile. The rebellion was in response to Castile's policy of relocating Muslim populations from these regions and was partially instigated by Muhammad I of Granada. The rebels were aided by the independent Emirate of Granada, while the Castilians were allied with Aragon. Early in the uprising, the rebels managed to capture Murcia and Jerez, as well as several smaller towns, but were eventually defeated by the royal forces. Subsequently, Castile expelled the Muslim populations of the reconquered territories and encouraged Christians from elsewhere to settle their lands. Granada became a vassal of Castile and paid an annual tribute. (Full article...)![Image 19Main façade of La MasiaLa Masia de Can Planes, usually shortened to La Masia (Catalan pronunciation: [lə məˈzi.ə]; English: "The Farmhouse"), is a term used for FC Barcelona's youth academy. The academy includes more than 300 young players. It has been an instrumental factor in Barcelona's European success, and produced several world class players in the early 2000s. (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 19
Image 19_(Barcelona)_-_1.jpg.webp) Main façade of La Masia
Main façade of La Masia
La Masia de Can Planes, usually shortened to La Masia (Catalan pronunciation: [lə məˈzi.ə]; English: "The Farmhouse"), is a term used for FC Barcelona's youth academy. The academy includes more than 300 young players. It has been an instrumental factor in Barcelona's European success, and produced several world class players in the early 2000s. (Full article...) Image 20"Amiga Mía" (transl. "My Friend") is a song by Spanish singer Alejandro Sanz from his fifth studio album, Más (1997). WEA Latina released it as the album's fourth single in the same year. The song was written by Sanz and produced by Miguel Angel Arenas and Emanuele Ruffinengo. The rock ballad carries a message of unrequited love and was inspired by a close friend of Sanz. The song received positive reactions from music critics who regarded it as one of his best songs. A music video for "Amiga Mía" features the artist performing on top of a building while the townspeople watch and his love interest leaves with her fiancé. (Full article...)
Image 20"Amiga Mía" (transl. "My Friend") is a song by Spanish singer Alejandro Sanz from his fifth studio album, Más (1997). WEA Latina released it as the album's fourth single in the same year. The song was written by Sanz and produced by Miguel Angel Arenas and Emanuele Ruffinengo. The rock ballad carries a message of unrequited love and was inspired by a close friend of Sanz. The song received positive reactions from music critics who regarded it as one of his best songs. A music video for "Amiga Mía" features the artist performing on top of a building while the townspeople watch and his love interest leaves with her fiancé. (Full article...) Image 21
Image 21 Bust in the Louvre, originally from the Jacobin convent which housed Philip's heart
Bust in the Louvre, originally from the Jacobin convent which housed Philip's heart
Philip III (Basque: Filipe, Spanish: Felipe, French: Philippe; 27 March 1306 – 16 September 1343), called the Noble or the Wise, was King of Navarre from 1328 until his death. He was born a minor member of the French royal family but gained prominence when the Capetian main line went extinct, as he and his wife and cousin, Joan II of Navarre, acquired the Iberian kingdom and a number of French fiefs. (Full article...) Image 22
Image 22 A depiction of medieval naval combat from Jean Froissart's Chronicles, 14th centuryA depiction of medieval naval combat from Jean Froissart's Chronicles, 14th century
A depiction of medieval naval combat from Jean Froissart's Chronicles, 14th centuryA depiction of medieval naval combat from Jean Froissart's Chronicles, 14th century
The Battle of Winchelsea or the Battle of Les Espagnols sur Mer ("the Spaniards on the Sea") was a naval battle that took place on 29 August 1350 as part of the Hundred Years' War between England and France. It was a victory for an English fleet of 50 ships, commanded by King Edward III, over a Castilian fleet of 47 larger vessels, commanded by Charles de la Cerda. Between 14 and 26 Castilian ships were captured, and several were sunk. Only two English vessels are known to have been sunk, but there was a significant loss of life. (Full article...) Image 23
Image 23 2011 memorial to two of those executed
2011 memorial to two of those executed
The last use of capital punishment in Spain took place on 27 September 1975 when two members of the armed Basque nationalist and separatist group ETA political-military and three members of the Revolutionary Antifascist Patriotic Front (FRAP) were executed by firing squads after having been convicted and sentenced to death by military tribunals for the murder of policemen and civil guards. Spain was Western Europe's only dictatorship at the time and had been unpopular and internationally isolated in the post-war period due to its relations with Nazi Germany in the 1930s and 1940s and the fact that its autocratic leader, Francisco Franco, had come to power by overthrowing a democratically elected government. As a result, the executions resulted in substantial criticism of the Spanish government, both domestically and abroad. Reactions included street protests, attacks on Spanish embassies, international criticism of the Spanish government and diplomatic measures, such as the withdrawal of the ambassadors of fifteen European countries. (Full article...)![Image 24De Lucía performing in 2007Francisco Sánchez Gómez (Spanish: [fɾanˈθisko ˈsantʃeθ ˈɣomeθ]; 21 December 1947 – 25 February 2014), known as Paco de Lucía (/ˈpɑːkoʊ dɛ luːˈtʃiːə/ PAH-koh deh loo-CHEE-ə, Spanish: [ˈpako ðe luˈθi.a]), was a Spanish virtuoso flamenco guitarist, composer, and record producer. A leading proponent of the new flamenco style, he was one of the first flamenco guitarists to branch into classical and jazz. Richard Chapman and Eric Clapton, authors of Guitar: Music, History, Players, describe de Lucía as a "titanic figure in the world of flamenco guitar", and Dennis Koster, author of Guitar Atlas, Flamenco, has referred to de Lucía as "one of history's greatest guitarists". (Full article...)](../I/Blank.png.webp) Image 24
Image 24 De Lucía performing in 2007
De Lucía performing in 2007
Francisco Sánchez Gómez (Spanish: [fɾanˈθisko ˈsantʃeθ ˈɣomeθ]; 21 December 1947 – 25 February 2014), known as Paco de Lucía (/ˈpɑːkoʊ dɛ luːˈtʃiːə/ PAH-koh deh loo-CHEE-ə, Spanish: [ˈpako ðe luˈθi.a]), was a Spanish virtuoso flamenco guitarist, composer, and record producer. A leading proponent of the new flamenco style, he was one of the first flamenco guitarists to branch into classical and jazz. Richard Chapman and Eric Clapton, authors of Guitar: Music, History, Players, describe de Lucía as a "titanic figure in the world of flamenco guitar", and Dennis Koster, author of Guitar Atlas, Flamenco, has referred to de Lucía as "one of history's greatest guitarists". (Full article...)
General images
 Image 11894 satirical cartoon depicting the tacit accord for seamless government change (turnismo) between the leaders of two dynastic parties (Sagasta and Cánovas del Castillo), with the country being lied in an allegorical fashion. (from History of Spain)
Image 11894 satirical cartoon depicting the tacit accord for seamless government change (turnismo) between the leaders of two dynastic parties (Sagasta and Cánovas del Castillo), with the country being lied in an allegorical fashion. (from History of Spain) Image 2Visigothic Hispania and its regional divisions in 700, prior to the Muslim conquest (from History of Spain)
Image 2Visigothic Hispania and its regional divisions in 700, prior to the Muslim conquest (from History of Spain)

.jpg.webp) Image 5Christopher Columbus leads expedition to the New World, 1492, sponsored by Spanish crown (from History of Spain)
Image 5Christopher Columbus leads expedition to the New World, 1492, sponsored by Spanish crown (from History of Spain)_-_Fondo_Car-Kutxa_Fototeka.jpg.webp)

 Image 8Two women and a man during the siege of the Alcázar (from History of Spain)
Image 8Two women and a man during the siege of the Alcázar (from History of Spain)
 Image 10People's militias attacking on a Rebel position in Somosierra in the early stages of the war. (from History of Spain)
Image 10People's militias attacking on a Rebel position in Somosierra in the early stages of the war. (from History of Spain)

.jpg.webp)
 Image 15The Iberian Peninsula in the 3rd century BC (from History of Spain)
Image 15The Iberian Peninsula in the 3rd century BC (from History of Spain) Image 16Felipe González signing the treaty of accession to the European Economic Community on 12 June 1985. (from History of Spain)
Image 16Felipe González signing the treaty of accession to the European Economic Community on 12 June 1985. (from History of Spain)

.jpg.webp) Image 19Members of the provisional government after the 1868 Glorious Revolution, by Jean Laurent. (from History of Spain)
Image 19Members of the provisional government after the 1868 Glorious Revolution, by Jean Laurent. (from History of Spain) Image 20Louis XIV of France and Philip IV of Spain at the Meeting on the Isle of Pheasants in June 1660, part of the process to put an end to the Franco-Spanish War (1635–59). (from History of Spain)
Image 20Louis XIV of France and Philip IV of Spain at the Meeting on the Isle of Pheasants in June 1660, part of the process to put an end to the Franco-Spanish War (1635–59). (from History of Spain)![Image 21Detail of the votive crown of Recceswinth from the Treasure of Guarrazar, (Toledo-Spain) hanging in Madrid. The hanging letters spell [R]ECCESVINTHVS REX OFFERET [King R. offers this]. (from History of Spain)](../I/Corona_de_(29049230050).jpg.webp) Image 21Detail of the votive crown of Recceswinth from the Treasure of Guarrazar, (Toledo-Spain) hanging in Madrid. The hanging letters spell [R]ECCESVINTHVS REX OFFERET [King R. offers this]. (from History of Spain)
Image 21Detail of the votive crown of Recceswinth from the Treasure of Guarrazar, (Toledo-Spain) hanging in Madrid. The hanging letters spell [R]ECCESVINTHVS REX OFFERET [King R. offers this]. (from History of Spain)
 Image 23The explosion of the USS Maine launched the Spanish–American War in April 1898 (from History of Spain)
Image 23The explosion of the USS Maine launched the Spanish–American War in April 1898 (from History of Spain)

 Image 27Visigothic church, San Pedro de la Nave. Zamora. Spain (from History of Spain)
Image 27Visigothic church, San Pedro de la Nave. Zamora. Spain (from History of Spain) Image 28The Christian kingdoms of Hispania and the Islamic Almohad empire c. 1210
Image 28The Christian kingdoms of Hispania and the Islamic Almohad empire c. 1210

 Image 31Cabeza de Luis Buñuel, sculptor's work by Iñaki, in the center Buñuel Calanda. (from Culture of Spain)
Image 31Cabeza de Luis Buñuel, sculptor's work by Iñaki, in the center Buñuel Calanda. (from Culture of Spain)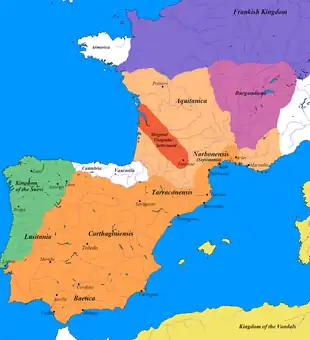 Image 32The greatest extent of the Visigothic Kingdom of Toulouse, c. 500, showing Territory lost after Vouillé in light orange (from History of Spain)
Image 32The greatest extent of the Visigothic Kingdom of Toulouse, c. 500, showing Territory lost after Vouillé in light orange (from History of Spain)
 Image 34Recognition of the Duke of Anjou as King of Spain, under the name of Philip V , November 16, 1700 (from History of Spain)
Image 34Recognition of the Duke of Anjou as King of Spain, under the name of Philip V , November 16, 1700 (from History of Spain) Image 35The successful 1925 Alhucemas landing turned the luck in the Rif War towards Spain's favour. (from History of Spain)
Image 35The successful 1925 Alhucemas landing turned the luck in the Rif War towards Spain's favour. (from History of Spain) Image 36Celebrations of the proclamation of the 2nd Republic in Barcelona. (from History of Spain)
Image 36Celebrations of the proclamation of the 2nd Republic in Barcelona. (from History of Spain) Image 37Proclamation of the Spanish Republic in Madrid (from History of Spain)
Image 37Proclamation of the Spanish Republic in Madrid (from History of Spain) Image 38The Conquest of Tenochtitlán (from History of Spain)
Image 38The Conquest of Tenochtitlán (from History of Spain)

_en_Prins_Juan_Carlos%252C_Bestanddeelnr_254-9762.jpg.webp) Image 41Francisco Franco and his appointed successor Prince Juan Carlos de Borbón. (from History of Spain)
Image 41Francisco Franco and his appointed successor Prince Juan Carlos de Borbón. (from History of Spain).svg.png.webp) Image 42Map of territories that were once part of the Spanish Empire (from History of Spain)
Image 42Map of territories that were once part of the Spanish Empire (from History of Spain)
 Image 44The Second of May 1808 was the beginning of the popular Spanish resistance against Napoleon. (from History of Spain)
Image 44The Second of May 1808 was the beginning of the popular Spanish resistance against Napoleon. (from History of Spain) Image 45In ictu oculi ("In the blink of an eye"), a vanitas by Juan de Valdés Leal (from Spanish Golden Age)
Image 45In ictu oculi ("In the blink of an eye"), a vanitas by Juan de Valdés Leal (from Spanish Golden Age)

 Image 48Charles I of Spain (better known in the English-speaking world as the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V) was the most powerful European monarch of his day. (from History of Spain)
Image 48Charles I of Spain (better known in the English-speaking world as the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V) was the most powerful European monarch of his day. (from History of Spain).jpg.webp) Image 49Visigothic King Roderic haranguing his troops before the Battle of Guadalete (from History of Spain)
Image 49Visigothic King Roderic haranguing his troops before the Battle of Guadalete (from History of Spain).JPG.webp) Image 50Episode of the 1854 Spanish Revolution in the Puerta del Sol, by Eugenio Lucas Velázquez. (from History of Spain)
Image 50Episode of the 1854 Spanish Revolution in the Puerta del Sol, by Eugenio Lucas Velázquez. (from History of Spain)


.jpg.webp) Image 54Execution of Torrijos and his men in 1831. Ferdinand VII took repressive measures against the liberal forces in his country. (from History of Spain)
Image 54Execution of Torrijos and his men in 1831. Ferdinand VII took repressive measures against the liberal forces in his country. (from History of Spain)
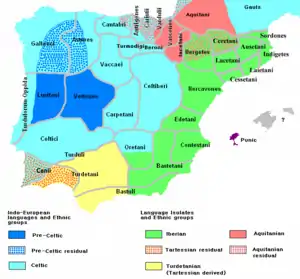 Image 56Ethnology of the Iberian Peninsula c. 200 BC (from History of Spain)
Image 56Ethnology of the Iberian Peninsula c. 200 BC (from History of Spain)


 Image 60The promulgation of the Constitution of 1812, oil painting by Salvador Viniegra. (from History of Spain)
Image 60The promulgation of the Constitution of 1812, oil painting by Salvador Viniegra. (from History of Spain) Image 61Wedding portrait of the Catholic Monarchs (from History of Spain)
Image 61Wedding portrait of the Catholic Monarchs (from History of Spain) Image 62The title page of the Gramática de la lengua castellana (1492), the first grammar of a modern European language to be published. (from History of Spain)
Image 62The title page of the Gramática de la lengua castellana (1492), the first grammar of a modern European language to be published. (from History of Spain) Image 63Illustration depicting the (now lost) Luzaga's Bronze, an example of the Celtiberian script. (from History of Spain)
Image 63Illustration depicting the (now lost) Luzaga's Bronze, an example of the Celtiberian script. (from History of Spain).jpg.webp) Image 64El paseo de las Delicias, a 1784–1785 painting by Ramón Bayeu depicting a meeting of members of the aristocracy in the aforementioned location. (from History of Spain)
Image 64El paseo de las Delicias, a 1784–1785 painting by Ramón Bayeu depicting a meeting of members of the aristocracy in the aforementioned location. (from History of Spain) Image 65The Port of Seville in the late 16th century. Seville became one of the most populous and cosmopolitan European cities after the expeditions to the New World. (from History of Spain)
Image 65The Port of Seville in the late 16th century. Seville became one of the most populous and cosmopolitan European cities after the expeditions to the New World. (from History of Spain).jpg.webp) Image 66The pro-independence forces delivered a crushing defeat to the royalists and secured the independence of Peru in the 1824 battle of Ayacucho. (from History of Spain)
Image 66The pro-independence forces delivered a crushing defeat to the royalists and secured the independence of Peru in the 1824 battle of Ayacucho. (from History of Spain) Image 67Las Meninas (1656, English: The Maids of Honour) by Diego Velázquez (from Spanish Golden Age)
Image 67Las Meninas (1656, English: The Maids of Honour) by Diego Velázquez (from Spanish Golden Age)
In the news
No recent news
No recent news
Spain topics
| History |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geography | |||||||
| Politics | |||||||
| Economy | |||||||
| Society |
| ||||||
Categories
WikiProjects
- Main project
WikiProject Spain
- Related projects
WikiProject Basque • WikiProject Catalan-speaking Countries • WikiProject Galicia • Spanish Translation of the Week
Things you can do

- Add {{WikiProject Spain}} to article talk pages which have some relation to Spain
- Help write new Spain-related articles and improve and expand existent ones
- Assess: unassessed Spain-related articles
- Suggest: selected articles, biographies, pictures, did you knows? and quotes for this Portal
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wikivoyage
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
-
 List of all portals
List of all portals -

-

-

-

-

-

-
-

-

-
 Random portal
Random portal -
 WikiProject Portals
WikiProject Portals
- ↑ "Atlantic hurricane best track (HURDAT version 2)" (Database). United States National Hurricane Center. April 5, 2023. Retrieved January 14, 2024.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.

