
Road signs in Spain are regulated in Normas y señales reguladores de la circulación vial.[1] They conform to the general pattern of those used in most other European countries. Spain is an original signatory to the 1968 Vienna Convention of Road Signs and Signals.[2] Spain signed this convention on November 8, 1968, but has yet to fully ratify it.
Typeface
In Spain, according to standard 8.1-I.C, two typefaces must be used that are attached sized with the standard. For signage on highways, highways and automobile roads, the alphabet called Autopista will be used; while for conventional roads, the urban environment and the rest of the roads, the Conventional Highway alphabet will be used.
From 1969 (Order of February 4, 1969 of the Ministry of the Interior on traffic rules and signs) until approximately 1991, the Autopista typography was used for highways, French typography and modified Helvetica for the rest of the roads, and a typography with a denomination Commercial Traffic Type Luxembourg to indicate various points, such as railway stations, airports, etc. Order of February 4, 1969 of the Ministry of the Interior on traffic rules and signs Signs in 1962. From 1991 to 2000, the date of publication of the new order, regulatory work was carried out in view of said order, changing the old signs for others; However, there are still a few signs from the 1969 order, perhaps made in the late 1980s and not changed due to their condition.
On April 5, 2014, the new standard 8.1-IC was published in the BOE, which, in relation to typography, establishes that only the "conventional road" alphabet will be used, replacing the "highway" alphabet in the new panels installed since then.[3]
There are commercial versions of both typefaces. The version of the Highway alphabet comes from the typeface known as Highway Gothic, which is a collection of typefaces created by different commissions in the United States. The Interstate commercial typeface, the work of Tobias Frere-Jones, is derived from the Highway Gothic, and the Conventional Highway is an adaptation of Transport.
However, on certain roads such as the AP-7 toll motorway, the Helvetica typeface has been used in various sections within Catalonia.
Language
In Spain, the Catalan (Catalonia and Balearic Islands), Valencian (Valencian Community), Basque (Basque Country and part of Navarre) and Galician (Galicia) speaking regions are officially bilingual.
According to standard 8.1-IC[4] of vertical signage (edited by the General Directorate of Highways (Dirección General de Carreteras)), the proper names of towns, provinces, characteristic points, etc. They will always be written in the official place name.
In the event that there is no official place name, the place name is first written in the regional language followed by a slash (/) and the place name in Spanish. If they are found on two lines, the name in the local language will be placed first, followed by a horizontal line and, finally, the place name in Spanish. No distinction is made in typography between both languages.
In the event that the official place name differs greatly from its Spanish version and the latter appears on the Official Road Map, both are written.
Warning signs
Below is a detailed and specific list of the signs adopted by regulations on public roads in Spain. The danger warning traffic signs approved and in common use in Spain since 1991 are the following:
 P-1
P-1
Intersection with priority P-1a
P-1a
Intersection with priority on the road on the right P-1b
P-1b
Intersection with priority on road on the left P-1c
P-1c
Intersection with priority over merging on the right P-1d
P-1d
Intersection with priority over merge from the left P-1e
P-1e
Section with shortcuts P-2
P-2
Intersection with right priority P-3
P-3
Traffic lights P-4
P-4
Roundabout P-5
P-5
Opening bridge P-6
P-6
Tram crossing P-7
P-7
Level crossing with barriers P-8
P-8
Level crossing without barriers P-9a
P-9a
Proximity of a level crossing or a moving bridge (right side) P-9b
P-9b
Approach of a level crossing or a moving bridge (right side) P-9c
P-9c
Proximity of a level crossing or a moving bridge (right side) P-10a
P-10a
Proximity of a level crossing or a moving bridge (left side) P-10b
P-10b
Approach of a level crossing or a moving bridge (left side) P-10c
P-10c
Proximity of a level crossing or a moving bridge (left side) P-11
P-11
Level crossing (single track) P-11a
P-11a
Level crossing (single track) P-12
P-12
Low-flying craft P-13a
P-13a
Dangerous curve to the right P-13b
P-13b
Dangerous curve to the left P-14a
P-14a
Dangerous curves, first to the right P-14b
P-14b
Dangerous curves, first to the left P-15
P-15
Uneven road P-15a
P-15a
Speed bump P-15b
P-15b
Dip P-16a
P-16a
Steep descent P-16b
P-16b
Steep ascent P-17
P-17
Road narrows on both sides P-17a
P-17a
Road narrows on the right P-17b
P-17b
Road narrows on the left P-18
P-18
Roadworks P-19
P-19
Slip road P-20
P-20
Pedestrians P-21
P-21
Children P-22
P-22
Cyclists P-23
P-23
Cattle or livestock P-24
P-24
Deer or wild animals P-25
P-25
Two-way traffic P-26
P-26
Falling rocks P-27
P-27
Unprotected body of water P-28
P-28
Loose surface material P-29
P-29
Crosswind P-30
P-30
Soft or low verges P-31
P-31
Traffic queues P-32
P-32
Accident P-33
P-33
Reduced visibility P-34
P-34
Pavement slippery due to ice or snow P-50
P-50
Other dangers
Regulatory signs
Priority signs
Priority signs force other vehicles to give way in various situations. Due to their importance, these signs have different shapes than all the others. The Stop sign (R-2) is octagonal in shape and is red. The Yield sign (R-1) is shaped like an equilateral triangle with one vertex facing downwards and is white with a red border.
Entry prohibition signs
Prohibition signs prohibit behavior that may cause danger. These signs have a circular shape and their pictogram is black on a white background, edges and band (descending transversal from left to right crossing the pictogram at 45° with respect to the horizontal) red (the red must cover, at least, 35 percent of the sign surface).
No entry signs are those that restrict access to a road. These signs are circular and white with a red border. Due to its importance, the "no entry" sign (R-101) has a red background with a white stripe.
 R-100
R-100
No vehicles R-101
R-101
No entry R-102
R-102
No motor vehicles R-103
R-103
No motor vehicles, except two-wheeled motorcycles R-104
R-104
No motorcycles R-105
R-105
No mopeds (and vehicles for people with reduced mobility) R-106
R-106
No vehicles intended for the transport of goods R-107
R-107
No heavy goods vehicles with a mass greater than indicated in the sign R-108
R-108
No vehicles carrying dangerous goods R-109
R-109
No vehicles transporting explosive or flammable goods R-110
R-110
No vehicles transporting water polluting products (more than 1,000 liters) R-111
R-111
No agricultural motor vehicles R-112
R-112
No motor vehicles with a trailer, other than a semi-trailer or a single-axle trailer R-113
R-113
No animal-drawn vehicles R-114
R-114
No cycles R-115
R-115
No handcarts R-116
R-116
No pedestrians R-117
R-117
No mounted animals
Restriction signs
 R-200
R-200
Passing without stopping prohibited R-200
R-200
Toll R-201
R-201
Mass limitation R-202
R-202
Mass limitation per axle R-203
R-203
Length limitation R-204
R-204
Width limitation R-205
R-205
Height limitation
Other prohibition or restriction signs
 R-300
R-300
Minimum separation R-301
R-301
Maximum speed limit (10 km/h) R-301
R-301
Maximum speed limit (20 km/h) R-301
R-301
Maximum speed limit (30 km/h) R-301
R-301
Maximum speed limit (40 km/h) R-301
R-301
Maximum speed limit (50 km/h) R-301
R-301
Maximum speed limit (60 km/h) R-301
R-301
Maximum speed limit (70 km/h) R-301
R-301
Maximum speed limit (80 km/h) R-301
R-301
Maximum speed limit (90 km/h) R-301
R-301
Maximum speed limit (100 km/h) R-301
R-301
Maximum speed limit (110 km/h) R-301
R-301
Maximum speed limit (120 km/h) R-302
R-302
No right turn R-303
R-303
No left turn R-304
R-304
No U-turn R-305
R-305
No overtaking R-306
R-306
No overtaking by heavy goods vehicles R-307
R-307
No stopping and parking R-308
R-308
Parking prohibited R-308a
R-308a
No parking on odd days R-308b
R-308b
No parking on even days R-308c
R-308c
Alternate parking R-308d
R-308d
Alternate parking R-308e
R-308e
No parking in crossing R-309
R-309
Restricted parking zone R-310
R-310
No honking
Mandatory signs
 R-400a
R-400a
Turn right R-400b
R-400b
Turn left R-400c
R-400c
Go straight R-400d
R-400d
Turn right R-400e
R-400e
Turn left R-401a
R-401a
Keep right R-401b
R-401b
Keep left R-401c
R-401c
May pass on either side R-402
R-402
Roundabout R-403a
R-403a
Go straight or turn right R-403b
R-403b
Go straight or turn left R-403c
R-403c
Turn right or left R-404
R-404
Car mandatory R-405
R-405
Motorcycles without sidecar mandatory R-406
R-406
Trucks and vans mandatory R-407
R-407
Cycle path R-408
R-408
Road for animal traction vehicles R-409
R-409
Road for mounted animals R-410
R-410
Road reserved for pedestrians R-411
R-411
Minimum speed limit R-412
R-412
Snow chains mandatory R-413
R-413
Headlamps R-414
R-414
Road for vehicles transporting dangerous goods R-415
R-415
Road for vehicles transporting water polluting products. R-416
R-416
Lane for vehicles transporting explosive or flammable materials.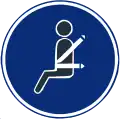 R-417
R-417
Mandatory use of seat belts R-418
R-418
Exclusive lane for vehicles equipped with operational electronic tolling equipment. Mandatory electronic toll
De-restriction signs
De-restriction signs inform that the prohibition or limitation section has ended. These signs are round and white with one or more diagonal black lines (one in France, three in the Netherlands, five in Spain and Germany).
 R-500
R-500
End of all previously signed restrictions R-501
R-501
End of speed limit R-502
R-502
End of no overtaking R-503
R-503
End of no overtaking for trucks R-504
R-504
End of limited parking zone R-505b
R-505b
End of cycle road R-505
R-505
End of no honking R-506
R-506
End of minimum speed limit
Indication signs
Indication signs inform the driver about something of interest. These signs are square or rectangular, blue with white elements and border. The signs are listed below along with their reference and corresponding legend as described in the General Traffic Regulations (Reglamento General de la Circulación).[5]
General indication signs
 S-1
S-1
Motorway S-1a
S-1a
Dual carriageway S-2
S-2
End of motorway S-2a
S-2a
End of dual carriageway S-3
S-3
Limited-access highway S-4
S-4
End of limited-access highway S-5
S-5
Tunnel S-6
S-6
End of tunnel S-7
S-7
Recommended maximum speed S-8
S-8
End of recommended maximum speed S-9
S-9
Recommended speed range S-10
S-10
End of recommended speed range S-11
S-11
One-way road S-11a
S-11a
One-way road (two lanes) S-11b
S-11b
One-way road (three lanes) S-12
S-12
Section of one-way road S-13
S-13
Pedestrian crossing S-14a
S-14a
Pedestrian overpass S-14b
S-14b
Pedestrian underpass S-15a
S-15a
Dead end S-15b
S-15b
Dead end S-15c
S-15c
Dead end S-15d
S-15d
Dead end S-16
S-16
Emergency braking zone S-17
S-17
Parking S-18
S-18
Reserved place for taxis S-19
S-19
Bus stop S-20
S-20
Tram stop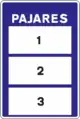 S-21
S-21
Name S-22
S-22
U-turn permitted S-23
S-23
Hospital S-24
S-24
End of short-range headlamps obligation S-25
S-25
Change of direction at different level S-26a
S-26a
Countdown beacon (300 m) S-26b
S-26b
Countdown beacon (200 m) S-26c
S-26c
Countdown beacon (100 m) S-27
S-27
Roadside assistance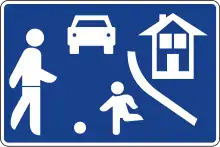 S-28
S-28
Residential area S-29
S-29
End of residential area S-30
S-30
Speed limit zone S-31
S-31
End of speed limit zone S-32
S-32
Electronic toll S-33
S-33
Cycle path S-34
S-34
Siding in tunnels S-34a
S-34a
Siding in tunnels (SOS) Sign indicating the beginning of a section of concentration of accidents
Sign indicating the beginning of a section of concentration of accidents Sign indicating the end of a section of concentration of accidents
Sign indicating the end of a section of concentration of accidents
Lane signs
Lane signs indicate the purpose of the lanes or the passage from one to several, etc.
 S-50a
S-50a
Lanes reserved for traffic based on the minimum speed S-50b
S-50b
Lanes reserved for traffic based on the minimum speed S-50c
S-50c
Lanes reserved for traffic based on the minimum speed S-50d
S-50d
Lanes reserved for traffic based on the minimum speed S-50e
S-50e
Lanes reserved for traffic based on the minimum speed S-51
S-51
Reserved lane for buses S-52
S-52
End of lane intended for circulation S-52a
S-52a
End of lane intended for circulation S-52b
S-52b
End of lane intended for circulation S-53
S-53
Transition from one to two traffic lanes S-53b
S-53b
Transition from two to three traffic lanes S-60a
S-60a
Fork to the left on a two-lane road S-60b
S-60b
Fork to the right on a two-lane road S-61a
S-61a
Fork to the left on a three-lane road S-61b
S-61b
Fork to the right on a three-lane road.svg.png.webp) S-61c
S-61c
Double fork on a three-lane road S-62a
S-62a
Fork to the left on a four-lane road S-62b
S-62b
Fork to the right on a four-lane road S-62с
S-62с
Double fork to the right on a four-lane road S-63
S-63
Double fork to the left and right on a four-lane road S-64a
S-64a
Bike lane or cycle path attached to the road S-64b
S-64b
Bike lane or cycle path attached to the road
Service signs
Service signs indicate the location of a roadside service.
 S-100
S-100
Aid station S-101
S-101
Ambulance base S-102
S-102
Vehicle technical inspection service S-103
S-103
Repair station S-104
S-104
Telephone S-105
S-105
Fuel pump S-106
S-106
Repair station and fuel pump S-107
S-107
Camp S-108
S-108
Water S-109
S-109
Picturesque place S-110
S-110
Hotel or motel S-111
S-111
Restaurant S-112
S-112
Cafeteria S-113
S-113
Land for trailers-housing S-114
S-114
Picnic area S-115
S-115
Starting point for walking tours S-116
S-116
Camping and land for trailers-housing S-117
S-117
Youth hostel S-118
S-118
Tourist information S-119
S-119
Fishing preserve S-120
S-120
National park S-121
S-121
Monument S-122
S-122
Other services S-123
S-123
Rest area S-124
S-124
Parking for railway users S-125
S-125
Parking for lower rail users S-126
S-126
Parking for bus users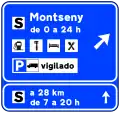 S-127
S-127
Service area
Oritentation signs
Pre-signaling signs
The signs indicate the location of an intersection at an adequate distance for it to be effective, being a minimum of 500 m on highways and highways, and can be reduced to 50 m in towns and repeated several times at another distance. Sometimes they can be seen in different colors to differentiate them.
 S-200
S-200
Roundabout pre-signaling S-220
S-220
Pre-signaling of directions to a conventional road S-222
S-222
Pre-signaling of directions to a highway or highway S-222a
S-222a
Pre-signaling of directions to a highway or dual carriageway and own direction S-225
S-225
Pre-signaling of directions on a highway or dual carriageway to any road S-230
S-230
Pre-signaling with signs on the carriageway on a conventional road towards a conventional road S-230a
S-230a
Pre-signaling with signs on the carriageway on a conventional road towards a conventional road and its own direction S-232
S-232
Pre-signaling with signs on the carriageway on a conventional road towards a highway or dual carriageway S-232a
S-232a
Pre-signaling with signs on the carriageway on a conventional road towards a highway or dual carriageway and its own direction S-235
S-235
Pre-signaling with signs on the highway or dual carriageway to any road S-235a
S-235a
Pre-signaling with signs on the highway or dual carriageway road towards any road and its own direction S-242
S-242
Pre-signaling on the highway or dual carriageway of two exits very close to any road..svg.png.webp) S-242a
S-242a
Pre-signaling on the highway or dual carriageway of two exits very close to any road and its own direction S-250
S-250
Route pre-signaling S-260
S-260
Lane pre-signaling S-261
S-261
Pre-signaling on conventional roads of service zone or area S-261
S-261
Pre-signaling on conventional roads of service zone or area S-263
S-263
Pre-signaling on the highway or dual carriageway of an area or service area with shared exit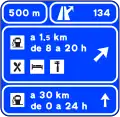 S-263
S-263
Pre-signaling on the highway or dual carriageway of an area or service area with exclusive exit S-264
S-264
Pre-signaling on a conventional road for a service road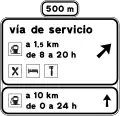 S-264
S-264
Pre-signaling on a conventional road for a service road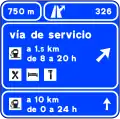 S-266
S-266
Pre-signaling on a highway or dual carriageway of a service road, with a shared exit S-266
S-266
Pre-signaling on a highway or dual carriageway of a service road, with a shared exit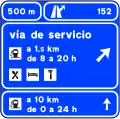 S-266a
S-266a
Pre-signaling on a highway or dual carriageway of a service road, with an exclusive exit S-270
S-270
Pre-signaling of two very close exits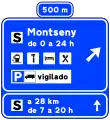 S-271
S-271
Service area pre-signaling
Direction signs
 S-300
S-300
Towns on a conventional road route S-301
S-301
Towns on a highway or dual carriageway route S-310
S-310
Towns on various routes S-320
S-320
Places of interest by conventional road S-321
S-321
Places of interest by highway or dual carriageway S-322
S-322
Destination sign towards a cycle route or cycle path S-341
S-341
Immediate exit destination signs towards conventional highway S-342
S-342
Destination signs for immediate exit to the highway or dual carriageway S-344
S-344
Destination signs for immediate exit to a zone, area or service road S-347
S-347
Destination signs for immediate exit to a zone, area or service road, with shared exit to a highway or dual carriageway S-348
S-348
Detour destination sign S-348b
S-348b
Variable destination signal S-350
S-350
Sign on the road, in conventional road. Immediate departure to conventional road S-351
S-351
Sign on the highway and highway road. Immediate departure to conventional road S-354
S-354
Sign on the road, in conventional road. Immediate exit to the highway or dual carriageway S-355
S-355
Sign on the road, on the highway, highway and expressway. Immediate exit to highway or dual carriageway S-360
S-360
Signs on the road on conventional roads. Immediate exit to conventional road and own direction S-362
S-362
Signs on the road on conventional roads. Immediate exit to the highway or dual carriageway and own direction S-366
S-366
Signs on the highway or dual carriageway road. Immediate exit to conventional road and own direction S-368
S-368
Signs on the highway or dual carriageway road. Exit to the highway or highway and own direction S-373
S-373
Signs on the highway or dual carriageway road. Two immediate exits very close to a conventional highway and its own direction S-375
S-375
Signs on the highway or dual carriageway road. Two immediate exits very close to the highway or highway and own direction
Route number signs
Route number signs are intended to identify the roads by their number, made up of figures, letters or a combination of both, or by their name. They are made up of this number or this name framed in a rectangle or a shield.
 S-400
S-400
European route S-410
S-410
Highway or dual carriageway route S-410
S-410
Highway or dual carriageway route S-410
S-410
Highway or dual carriageway route S-410a
S-410a
Toll road S-420
S-420
State general network road S-430
S-430
First level autonomous highway S-440
S-440
Second level autonomous highway S-450
S-450
Third level autonomous highway
Location signs
Location signs are used to indicate:
- The border between two regions;
- The limit between two administrative divisions of the same region;
- The name of a town, a river, a port, a place or other circumstance of an analogous nature.
 S-500
S-500
Entrance to town S-510
S-510
Exit from town S-520
S-520
Location of characteristic point of the road S-540
S-540
Entrance to province S-550
S-550
Entrance to autonomous community S-560
S-560
Entrance to autonomous community S-570
S-570
Kilometer marker on highway and dual carriageway S-570a
S-570a
Kilometer marker on toll highway S-571
S-571
Kilometer marker on the highway and dual carriageway that is also part of a European route S-572
S-572
Kilometer marker on conventional road S-573
S-573
Kilometer marker on the European route S-574
S-574
Miriametric marker on a highway or dual carriageway S-574a
S-574a
Miriametric marker on a conventional road S-574b
S-574b
Miriametric marker on toll highway S-575
S-575
Miriametric marker
Confirmation signs
 S-600
S-600
Confirmation of towns on a conventional road route S-602
S-602
Confirmation of towns on a highway or dual carriageway
Signs for specific use in the town
 S-700
S-700
Places on the urban road network S-710
S-710
Places of interest for travelers S-720
S-720
Places of sporting or recreational interest S-730
S-730
Places of geographical or ecological nature S-740
S-740
Places of monumental or cultural interest S-750
S-750
Industrial use areas S-760
S-760
Highways and dual carriageways S-770
S-770
Other places and routes
Additional panels
 S-800
S-800
Distance to the beginning of the danger or prescription S-810
S-810
Length of the dangerous section or subject to prescription S-820
S-820
Extension of the ban, to the right S-821
S-821
Extension of the ban, to the left S-830
S-830
Extension of the ban, on both sides S-840
S-840
STOP presignaling S-850
S-850
Direction of priority road S-851
S-851
Direction of priority road S-852
S-852
Direction of priority road S-853
S-853
Direction of priority road S-860
S-860
Generic S-870
S-870
Signage application S-880
S-880
Signaling application to certain vehicles S-890
S-890
Complementary panel of a vertical sign
Other signs
 S-900
S-900
Fire danger S-910
S-910
Extinguisher S-920
S-920
Entry to Spain S-930
S-930
Country confirmation S-940
S-940
General speed limit in Spain S-950
S-950
Radio frequency of specific road information stations S-960
S-960
Emergency phone S-970
S-970
Fire extinguisher location and emergency phone S-980
S-980
Emergency exit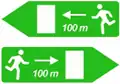 S-990
S-990
Indicative arrow sign emergency sign in tunnels
Construction signs
The construction traffic signs in Spain are signs, generally similar to the rest, with a yellow background used to signal detours or temporary changes due to works on the road.[6]
The different works signs are listed below, accompanied by their reference and a legend. Temporary signs shown below differ from permanent ones in that they have a yellow background instead of white.
Warning signs
 TP-1
TP-1
Intersection with priority TP-1a
TP-1a
Intersection with priority on the road on the right TP-1b
TP-1b
Intersection with priority on the road on the left TP-1c
TP-1c
Intersection with priority over incorporation from the right TP-1d
TP-1d
Intersection with priority over incorporation from the left TP-2
TP-2
Intersection with right priority TP-3
TP-3
Traffic lights TP-4
TP-4
Intersection with rotary circulation TP-13a
TP-13a
Dangerous curve to the right TP-13b
TP-13b
Dangerous curve to the left TP-14a
TP-14a
Dangerous curves to the right TP-14b
TP-14b
Dangerous curves to the left TP-15
TP-15
Irregular profile TP-15a
TP-15a
Highlight TP-15b
TP-15b
Badén TP-17
TP-17
Road narrows on both sides TP-17a
TP-17a
Road narrows on the right TP-17b
TP-17b
Road narrows on the left TP-18
TP-18
Works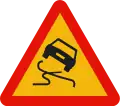 TP-19
TP-19
Slip pavement TP-25
TP-25
Traffic in both directions TP-26
TP-26
Detachment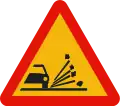 TP-28
TP-28
Gravel projection TP-30
TP-30
Side step TP-31
TP-31
Congestion TP-50
TP-50
Other dangers
Regulation and priority signs
 TR-1
TR-1
Yield TR-5
TR-5
Give way to oncoming traffic TR-6
TR-6
Priority over oncoming traffic TR-101
TR-101
No entry TR-106
TR-106
No goods transport vehicles TR-201
TR-201
Weight limitation TR-204
TR-204
Width limitation TR-205
TR-205
Height limitation TR-302
TR-302
No right turn TR-303
TR-303
No left turn TR-305
TR-305
No overtaking TR-306
TR-306
No overtaking by heavy goods vehicles TR-308
TR-308
No parking TR-400a
TR-400a
Turn right TR-400b
TR-400b
Turn left TR-401a
TR-401a
Keep right TR-401b
TR-401b
Keep left
Speed limit signs
 TR-301-20
TR-301-20
Speed limit (20 km/h) TR-301-30
TR-301-30
Speed limit (30 km/h) TR-301-40
TR-301-40
Speed limit (40 km/h) TR-301-50
TR-301-50
Speed limit (50 km/h) TR-301-60
TR-301-60
Speed limit (60 km/h) TR-301-70
TR-301-70
Speed limit (70 km/h) TR-301-80
TR-301-80
Speed limit (80 km/h) TR-301-90
TR-301-90
Speed limit (90 km/h) TR-301-100
TR-301-100
Speed limit (100 km/h)
De-restriction signs
 TR-500
TR-500
End of all previously signed restrictions
Indication signs
 TS-52
TS-52
Convergence of a lane on the right (from 3 to 2)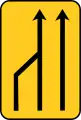 TS-53
TS-53
Convergence of one lane on the left (from 3 to 2)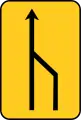 TS-54
TS-54
Convergence of one lane on the right (from 2 to 1)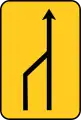 TS-55
TS-55
Convergence of one lane on the left (from 2 to 1)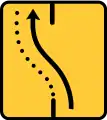 TS-60
TS-60
Detour of one lane onto the opposite road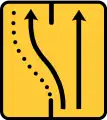 TS-61
TS-61
Detour of one lane onto the opposite road, keeping another on the construction road TS-62
TS-62
Detour of two lanes on the opposite road TS-210
TS-210
Sketch of detour at work TS-210
TS-210
Sketch of detour at work TS-220
TS-220
Address pre-signaling TS-800
TS-800
Distance to the beginning of the danger or prescription TS-810
TS-810
Length of dangerous section or subject to prescription
Reflective marking signs
 TB-1
TB-1
Wide directional panel TB-2
TB-2
Narrow directional panel TB-3
TB-3
Wide directional double panel TB-4
TB-4
Narrow double directional panel TB-5
TB-5
Excluded traffic zone panel TB-6
TB-6
Traffic cone TB-7
TB-7
Picket TB-8
TB-8
Right edge beacon TB-9
TB-9
Left edge beacon TB-10
TB-10
Captafaro TB-11
TB-11
Luminous and reflective beacon TB-12
TB-12
Provisional road marking TB-13
TB-13
Garland TB-14
TB-14
Mobile frame
References
- ↑ "Normas y señales reguladoras de la circulación vial - DGT" (PDF). sede.dgt.gob.es. 2020.
- ↑ "United Nations Treaty Collection". treaties.un.org. Retrieved 2023-11-08.
- ↑ "Disposición 3654 del BOE núm. 83 de 2014" (PDF). www.boe.es (in Spanish). 2014-04-05.
- ↑ "BOE 025 de 29/01/2000 Sec 1 Pag 4049 a 4106" (PDF). boe.es (in Spanish). 2000-01-29.
- ↑ Ministerio de la Presidencia (2003-12-23), Real Decreto 1428/2003, de 21 de noviembre, por el que se aprueba el Reglamento General de Circulación para la aplicación y desarrollo del texto articulado de la Ley sobre tráfico, circulación de vehículos a motor y seguridad vial, aprobado por el Real Decreto Legislativo 339/1990, de 2 de marzo (in Spanish), pp. 45684–45772, retrieved 2023-11-17
- ↑ "Instrucción 8.3-IC. Señalización, balizamiento, defensa, limpieza y terminación de obras fijas fuera de poblado (Orden de 31 de agosto de 1987)" (PDF) (in Spanish). ORDEN MINISTERIAL. 1987-08-31.




