
Road signs in Sweden are regulated in Vägmärkesförordningen, VMF (2007:90), and are to be placed 2 metres from the road with the sign 1.6 m from the base for motorized roads. Except for route numbers, there are a maximum of three signs on a pole, with the most important sign at the top. All signs have a reflective layer added on selected parts of the sign as is custom in European countries; most larger signs also have their own illumination.
Most signs are based on pictograms, with some exceptions like the prohibition-sign for stop at customs and signal and speed limit signs. If the sign includes text, the text is written in Swedish, except the stop sign, which is written in English ("STOP").
Swedish road signs depict people with realistic (as opposed to stylized) silhouettes.
Major differences between Swedish and general European signs
Like other countries in Europe, Swedish signs follow the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals. Whereas European signs usually have white background on warning and prohibition signs, the Swedish signs have a yellow/orange colour. This is for the purpose of enhancing the visibility of the sign during the winter, as white signs would be hard to see in the snow. The prohibition signs have a red line across them if there is a symbol on them, not if it is a numeric value. General European prohibition signs do not usually have such a red line. Swedish warning and prohibition signs also have a thicker border than their European counterparts. Traffic signs in Slovenia and Finland are quite similar.
History
Around 1930 some warning signs and prohibitory signs looking like today's signs with yellow background were introduced. The direction indication signs were however yellow with black text. Around 1965, there was a reform where the colour of those were changed to dark blue with white text. Around 1980, Sweden followed the Vienna convention rule that motorways should have a different colour, so green was introduced for them, and medium blue for ordinary roads.
Private road direction sign
The reason there is a sign indicating private road, is because they are not strictly private. A private road is a road that is not maintained by the state or municipality, but by a private person or association. An owner of a private road in Sweden can prohibit cars (but not people) from using the road. But if the state pays support for the maintenance, cars can't be prohibited. This is mostly the case if several families live along the road. Then they must form an association for it. The Swedish word for this kind of road is "enskild", that can be both translated to "private" and "individual". The background of the sign is yellow, indicating that the quality is often less good, and warning signs might be missing. Signs indicating roads owned by companies or leading to companies usually have white background instead.
Warning signs
Warning signs are triangular and have red borders, but in contrast with those of most other countries that use triangular warning signs, Swedish signs have yellow backgrounds, rather than white. More types of warning signs for animals are used than in most European countries, such as moose, deer, wild boar, reindeer, sheep, horse, and cow appearing alongside roads.
 Dangerous curve to left
Dangerous curve to left Dangerous curve to right
Dangerous curve to right Dangerous curves ahead, first to left
Dangerous curves ahead, first to left Dangerous curves ahead, first to right
Dangerous curves ahead, first to right Steep downhill
Steep downhill Steep uphill
Steep uphill Road narrows on both sides
Road narrows on both sides Road narrows on right sides
Road narrows on right sides Road narrows on left sides
Road narrows on left sides Unprotected quayside or riverbank
Unprotected quayside or riverbank Uneven road
Uneven road Speed refulcation bump
Speed refulcation bump Dip
Dip Slippery road
Slippery road Loose chipings
Loose chipings Falling rocks (from) right
Falling rocks (from) right Falling rocks (from) left
Falling rocks (from) left Pedestrian crossing
Pedestrian crossing Pedestrian
Pedestrian Children
Children Cyclist and mopeds rides on carrigeway
Cyclist and mopeds rides on carrigeway Skiers crossing
Skiers crossing Equestrian
Equestrian Moose
Moose Wild animals
Wild animals Cattle
Cattle Wild horses
Wild horses Reindeer
Reindeer Sheep
Sheep Wild boars
Wild boars Roadworks
Roadworks End of roadworks
End of roadworks Traffic signals
Traffic signals Low-flying aircraft
Low-flying aircraft Side winds
Side winds Two-way traffic
Two-way traffic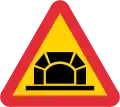 Tunnel
Tunnel Dangerous shoulder
Dangerous shoulder Crossroad intersection
Crossroad intersection Crossroad without priority
Crossroad without priority Right way at crocked intersection
Right way at crocked intersection Right way junction from the left or right winding junction from right
Right way junction from the left or right winding junction from right Right way junction from the left or right winding junction from left
Right way junction from the left or right winding junction from left Side road priority on left
Side road priority on left Side road priority on right
Side road priority on right Skewed side road priority on left
Skewed side road priority on left Skewed side road priority on right
Skewed side road priority on right Roundabout
Roundabout Slow moving vehicles
Slow moving vehicles Horse drawn-carts
Horse drawn-carts Off road-vehicles
Off road-vehicles Traffic congestion
Traffic congestion Level crossing with barrier
Level crossing with barrier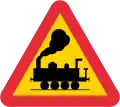 Level crossing without barrier
Level crossing without barrier Tramway
Tramway Level crossing countdown
Level crossing countdown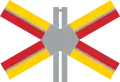 Single track level crossing
Single track level crossing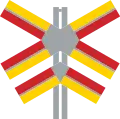 Multi track level crossing
Multi track level crossing Other hazard
Other hazard Accident
Accident
Priority signs
The pedestrian and bicycle crossing signs are priority signs in Sweden, whereas the pedestrian crossing sign is regarded as a special regulation sign in the Vienna convention on road signs and signals. A sign for bicycle crossing is not yet implemented in the Vienna convention.
 Give way (Yield)
Give way (Yield) Stop
Stop Pedestrian crossing
Pedestrian crossing Pedestrian crossing
Pedestrian crossing Priority road
Priority road End of priority road
End of priority road Priority for oncoming vehicles
Priority for oncoming vehicles Priority over oncoming vehicles
Priority over oncoming vehicles Bike crossing
Bike crossing
Prohibitory signs
Prohibitory signs are round with yellow backgrounds and red borders, except the international standard stop sign that is an octagon with red background and white border and the no parking and no standing signs that have a blue background instead of yellow.
 Do not enter
Do not enter Closed to all motor vehicles in both directions
Closed to all motor vehicles in both directions No motor vehicles
No motor vehicles No motor vehicles with more than two wheels
No motor vehicles with more than two wheels No motorcycles
No motorcycles No towed trailers
No towed trailers No trucks
No trucks No tractors
No tractors No vehicles transporting dangerous goods
No vehicles transporting dangerous goods No bike
No bike No mopeds
No mopeds No horse-drawns
No horse-drawns No snowmobiles
No snowmobiles No horses
No horses No pedestrians
No pedestrians No vehicles exceeding width shown
No vehicles exceeding width shown No vehicles exceeding height shown
No vehicles exceeding height shown No vehicles exceeding length shown
No vehicles exceeding length shown Minimum distance between 2-tracked motor vehicles
Minimum distance between 2-tracked motor vehicles No vehicles exceeding weight shown
No vehicles exceeding weight shown No vehicles or combination of vehicles exceeding weight shown
No vehicles or combination of vehicles exceeding weight shown No vehicles having a weight exceeding weight on 1 axle
No vehicles having a weight exceeding weight on 1 axle No vehicles exceeding weight shown on a tandem axle
No vehicles exceeding weight shown on a tandem axle No turning in a certain direction
No turning in a certain direction No overtaking
No overtaking No overtaking by trucks
No overtaking by trucks Speed limit
Speed limit End of overtaking prohibition
End of overtaking prohibition End of overtaking prohibition by trucks
End of overtaking prohibition by trucks Stop at the sign if the signal shows red
Stop at the sign if the signal shows red
(only applies when driving towards the signal concerned) Stop for police control. There are variants STOPP VAKT (stop for guard) STOPP FÄRJA (stop here when waiting for ferry)
Stop for police control. There are variants STOPP VAKT (stop for guard) STOPP FÄRJA (stop here when waiting for ferry) No parking or waiting
No parking or waiting No parking on odd days
No parking on odd days No parking on even days
No parking on even days Date-based parking
Date-based parking No stopping or standing
No stopping or standing No 2-tracked motor vehicles with studded tires
No 2-tracked motor vehicles with studded tires Restriction zone.
Restriction zone.
In this example, this is no parking zone. However, the restriction doesn't apply when the signs inside the zone says otherwise. End of the restriction zone
End of the restriction zone
Stop at customs
The sign "Stop at customs" ("Stopp vid tull") is multilingual and exists in four variants.
 Danish
Danish Finnish
Finnish German
German Norwegian
Norwegian
Mandatory signs
Mandatory signs are always round blue signs with white border.
 Direction to be followed
Direction to be followed Keep right
Keep right Keep left
Keep left Pass either side
Pass either side Roundabout
Roundabout Track for cycles and mopeds
Track for cycles and mopeds Footpath
Footpath Compulsory track for pedestrians, cyclists and moped drivers.
Compulsory track for pedestrians, cyclists and moped drivers. Compulsory track for pedestrians, cyclists and moped drivers. Dual track
Compulsory track for pedestrians, cyclists and moped drivers. Dual track Compulsory track for pedestrians, cyclists and moped drivers. Dual track
Compulsory track for pedestrians, cyclists and moped drivers. Dual track Track for rider on horseback (and pedestrians)
Track for rider on horseback (and pedestrians) Track for off-road vehicles
Track for off-road vehicles Beginning of lane reserved for public transport (and cycles and mopeds Class II).
Beginning of lane reserved for public transport (and cycles and mopeds Class II). End of lane reserved for public transport (and cycles and mopeds Class II).
End of lane reserved for public transport (and cycles and mopeds Class II).
Special regulation signs
 Motorway
Motorway End of motorway
End of motorway Expressway
Expressway End of expressway
End of expressway Built-up area
Built-up area End of built-up area
End of built-up area Pedestrian area
Pedestrian area End of pedestrian area
End of pedestrian area Residential area
Residential area End of residential area
End of residential area Low-speed road (recommended top speed)
Low-speed road (recommended top speed) End of low-speed road
End of low-speed road Maximum recommended speed (in km/h)
Maximum recommended speed (in km/h) End of maximum recommended speed (in km/h)
End of maximum recommended speed (in km/h) One-way traffic
One-way traffic Dead end
Dead end Passing place
Passing place Parking (max 24 hours on weekdays except weekday before Sunday or holiday).
Parking (max 24 hours on weekdays except weekday before Sunday or holiday). Bus stop
Bus stop Taxi rank
Taxi rank Toll road
Toll road
Signs giving information
 Sign when entering Sweden from another country
Sign when entering Sweden from another country Post office
Post office Telephone
Telephone Radio station for road and traffic information
Radio station for road and traffic information First aid
First aid Industrial zone
Industrial zone Information
Information Workshop area
Workshop area Petrol station
Petrol station Cafe
Cafe Restaurant
Restaurant Hotel
Hotel Rest site
Rest site Holiday chalets
Holiday chalets Camping site
Camping site Caravan site
Caravan site Park
Park Toilet
Toilet Bathing
Bathing Open-air recreation
Open-air recreation Hiking trail
Hiking trail Chair lift
Chair lift Tow lift
Tow lift Golf course
Golf course Fishing licences on sale here
Fishing licences on sale here National heritage
National heritage.svg.png.webp) Park and ride
Park and ride.svg.png.webp) The long turn — mandatory turning manoeuvre for pedal cycles and mopeds.
The long turn — mandatory turning manoeuvre for pedal cycles and mopeds. Advance direction sign, diagrammatic type
Advance direction sign, diagrammatic type Advance direction sign, stack type
Advance direction sign, stack type Lane preselection sign
Lane preselection sign.svg.png.webp) Lane merge
Lane merge Lane ends
Lane ends Temporary sign, left most lane ends
Temporary sign, left most lane ends Temporary sign, Lane merges with oncoming traffic
Temporary sign, Lane merges with oncoming traffic Temporary sign, oncoming traffic merges with this lane
Temporary sign, oncoming traffic merges with this lane Advance direction sign diagrammatic indicating prohibition of left turning
Advance direction sign diagrammatic indicating prohibition of left turning Direction sign flag type
Direction sign flag type.svg.png.webp) Direction to motorway or expressway
Direction to motorway or expressway Sign to specific district or area
Sign to specific district or area Sign to place reached by a private road
Sign to place reached by a private road Sign to local amenities
Sign to local amenities Lane assignment type
Lane assignment type Advance direction sign exit ahead from motorway or expressway
Advance direction sign exit ahead from motorway or expressway Advance direction sign exit ahead from other road than motorway or expressway
Advance direction sign exit ahead from other road than motorway or expressway Direction sign exit sign
Direction sign exit sign Number of exit
Number of exit Lorries
Lorries Car
Car Airfield
Airfield Airfield straight ahead
Airfield straight ahead Ferry
Ferry Place indication sign
Place indication sign Road number sign European highway
Road number sign European highway Main highways (other than European highways) numbered 1-499
Main highways (other than European highways) numbered 1-499 Road number sign. Direction to a numbered road
Road number sign. Direction to a numbered road Road number sign for traffic diversion
Road number sign for traffic diversion Confirmatory sign
Confirmatory sign Grouped destinations (i.e. For Pajala and Övertorneå, follow signs for Kiruna)
Grouped destinations (i.e. For Pajala and Övertorneå, follow signs for Kiruna) Recommended route for vehicles carrying dangerous goods
Recommended route for vehicles carrying dangerous goods Tourist route
Tourist route Tourist attraction area
Tourist attraction area.svg.png.webp) Landmark
Landmark Sign to temporary event
Sign to temporary event.svg.png.webp) Recommended route for pedal cycles and mopeds
Recommended route for pedal cycles and mopeds Recommended route for pedestrians
Recommended route for pedestrians Disabled persons
Disabled persons Stack type design
Stack type design Flag type sign
Flag type sign Place indication sign
Place indication sign Confirmatory sign
Confirmatory sign Bike track
Bike track
Other signs
 End of road works
End of road works Limited access on side marker
Limited access on side marker Limited access marker
Limited access marker Limited access arrow marker
Limited access arrow marker Marking for sharp bends, bridge parapets, abutment, walls, tunnel mouths etc. Arrow marker
Marking for sharp bends, bridge parapets, abutment, walls, tunnel mouths etc. Arrow marker
 Exit
Exit
Additional panels
 High voltage cable
High voltage cable Distance to
Distance to Stop and give way at specified distance ahead
Stop and give way at specified distance ahead Lateral clearance
Lateral clearance Total weight
Total weight Times the restriction applies. Weekday; Weekday before Sunday or public holiday in brackets; Sunday and public holiday in red.
Times the restriction applies. Weekday; Weekday before Sunday or public holiday in brackets; Sunday and public holiday in red. Parking permitted for specified period between times shown
Parking permitted for specified period between times shown No parking between times indicated
No parking between times indicated Blind persons crossing or in the vicinity of the road
Blind persons crossing or in the vicinity of the road Deaf persons crossing or in the vicinity of the road
Deaf persons crossing or in the vicinity of the road All way stop
All way stop Parking configuration
Parking configuration Parking configuration
Parking configuration Parking configuration
Parking configuration Parking configuration
Parking configuration Parking garage
Parking garage.svg.png.webp) Length of stretch of road beginning at specified distance from sign
Length of stretch of road beginning at specified distance from sign.svg.png.webp) Length of stretch of road beginning at sign
Length of stretch of road beginning at sign.svg.png.webp) Prohibition effective in both directions of the sign
Prohibition effective in both directions of the sign.svg.png.webp) Prohibition end at sign
Prohibition end at sign.svg.png.webp) Prohibition effective in the direction of arrow
Prohibition effective in the direction of arrow Parking, effective in both directions of the sign
Parking, effective in both directions of the sign Parking ends at sign
Parking ends at sign Parking, effective in direction of arrow
Parking, effective in direction of arrow Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (lorry)
Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (lorry) Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (lorry)
Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (lorry) Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (handicapped)
Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (handicapped) Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (car)
Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (car) Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (car)
Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (car) Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (bus)
Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (bus) Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (bus)
Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (bus) Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (motorbike)
Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (motorbike) Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (bike)
Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (bike) Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (caravan)
Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (caravan) Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (caravan)
Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (caravan) Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (car + caravan)
Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (car + caravan) Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (car + caravan)
Symbol plate for specified vehicle or road user category (car + caravan) Soft verges
Soft verges Forestry vehicle crossing ahead
Forestry vehicle crossing ahead.svg.png.webp) Direction sign
Direction sign.svg.png.webp) Direction sign
Direction sign Direction sign
Direction sign Direction of priority road at intersection
Direction of priority road at intersection.svg.png.webp) Two-way traffic on cycle and moped track
Two-way traffic on cycle and moped track
A Supreme Court case has clarified that if there are multiple individually framed additional panels for a road sign, they add information to the road sign, not to each other. The two panels in the case was Avgift (fee) and the other 4 hours 9-18, which means that there is mandatory fee anytime and maximum 4 hours 9 am-6 pm.[1]
Traffic light signals
Note: tip-down triangles indicates blinking/flashing light.
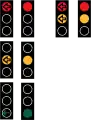 Standard & arrow Red: Stop.
Standard & arrow Red: Stop.
Red + yellow: The light is turning to green.
Green: Proceed.
Yellow: Stop, but only if safe to do so. Flashing yellow: Traffic light malfunction or out of service.
Flashing yellow: Traffic light malfunction or out of service. Cycles and moped lights.
Cycles and moped lights. Pedestrian lights.
Pedestrian lights.
Red: Don't walk.
Green: Walk. Public transport lights.
Public transport lights.
"S": Stop.
"S" + "–": The light is turning to "I" / arrow.
"I" (or arrow): Proceed (for indicated direction).
"–": Stop, but only if safe to do so. Lane-control signals.
Lane-control signals.
Red cross: Lane closed.
Yellow arrow(s): Lane closed ahead, change to indicated lane(s).
Green arrow: Lane open. Lights at level crossing.
Lights at level crossing.
Flashing reds: Stop.
Flashing white (optional): Signals are operational. Light signals at opening or swing bridges, ferries, airfields, emergency service stations etc.
Light signals at opening or swing bridges, ferries, airfields, emergency service stations etc.
Flashing reds: Stop. Flashing yellow(s), accompanied with a sign: Drive with extra caution.
Flashing yellow(s), accompanied with a sign: Drive with extra caution.
Road markings
 Centre line
Centre line No overtaking line
No overtaking line Warning line
Warning line Centre line and no overtaking line
Centre line and no overtaking line Centre line and warning line
Centre line and warning line Warning line and no overtaking line
Warning line and no overtaking line Double no overtaking line
Double no overtaking line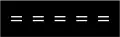 Reversible lane markings (lane that may be used for alternating direction of traffic flow)
Reversible lane markings (lane that may be used for alternating direction of traffic flow) Guide line
Guide line Reserved lane line
Reserved lane line Bike lane marking
Bike lane marking Broken edge line
Broken edge line Continuous edge line
Continuous edge line Stop line
Stop line Give way line
Give way line Zebra crossing
Zebra crossing Bike crossing
Bike crossing Lane selection arrows
Lane selection arrows Deflecting arrow
Deflecting arrow Obstruction marking; no crossing on or over that marking
Obstruction marking; no crossing on or over that marking Text conforming bus and taxi lane, text conforming stop line
Text conforming bus and taxi lane, text conforming stop line Parking bay
Parking bay Standing and parking prohibited
Standing and parking prohibited Parking prohibited
Parking prohibited Parking prohibited
Parking prohibited Bike and moped route
Bike and moped route Advance warning of obligation to give way
Advance warning of obligation to give way Wheelchair persons
Wheelchair persons
Signals by police officers
 Control
Control Advance direction sign control
Advance direction sign control 13.3.1 Slow down
13.3.1 Slow down
13.3.2 Follow the police car and pull up behind it when it stops
13.3.3 Slow down
13.3.4 Drive off the road and stop in front of the police car
Retired signs
.svg.png.webp) Road works (1951-1967)
Road works (1951-1967).svg.png.webp) Stop (1951–1975)
Stop (1951–1975) Derestriction (1951-1967)
Derestriction (1951-1967).svg.png.webp) Turn left (1937-1951)
Turn left (1937-1951).svg.png.webp) Turn right (1937-1951)
Turn right (1937-1951).svg.png.webp) Keep left (1937-1951)
Keep left (1937-1951).svg.png.webp) Built-up area, slow down (1937-1955)
Built-up area, slow down (1937-1955).svg.png.webp) Residential area (1998-2007)
Residential area (1998-2007).svg.png.webp) End of residential area (1998-2007)
End of residential area (1998-2007)