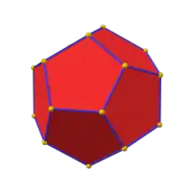
| Snub cube | |
|---|---|
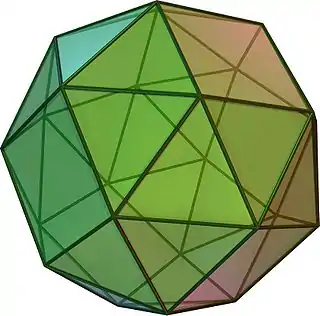 (Click here for rotating model) | |
| Type | Archimedean solid Uniform polyhedron |
| Elements | F = 38, E = 60, V = 24 (χ = 2) |
| Faces by sides | (8+24){3}+6{4} |
| Conway notation | sC |
| Schläfli symbols | sr{4,3} or |
| ht0,1,2{4,3} | |
| Wythoff symbol | | 2 3 4 |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | O, 1/2B3, [4,3]+, (432), order 24 |
| Rotation group | O, [4,3]+, (432), order 24 |
| Dihedral angle | 3-3: 153°14′04″ (153.23°) 3-4: 142°59′00″ (142.98°) |
| References | U12, C24, W17 |
| Properties | Semiregular convex chiral |
 Colored faces |
 3.3.3.3.4 (Vertex figure) |
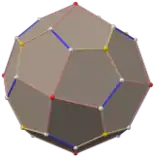 Pentagonal icositetrahedron (dual polyhedron) |
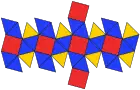 Net |


In geometry, the snub cube, or snub cuboctahedron, is an Archimedean solid with 38 faces: 6 squares and 32 equilateral triangles. It has 60 edges and 24 vertices.
It is a chiral polyhedron; that is, it has two distinct forms, which are mirror images (or "enantiomorphs") of each other. The union of both forms is a compound of two snub cubes, and the convex hull of both sets of vertices is a truncated cuboctahedron.
Kepler first named it in Latin as cubus simus in 1619 in his Harmonices Mundi. H. S. M. Coxeter, noting it could be derived equally from the octahedron as the cube, called it snub cuboctahedron, with a vertical extended Schläfli symbol , and representing an alternation of a truncated cuboctahedron, which has Schläfli symbol .
Dimensions
For a snub cube with edge length , its surface area and volume are:[1]
where t is the tribonacci constant
If the original snub cube has edge length 1, its dual pentagonal icositetrahedron has side lengths
- .
Cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinates for the vertices of a snub cube are all the even permutations of
- (±1, ±1/t, ±t)
with an even number of plus signs, along with all the odd permutations with an odd number of plus signs, where t ≈ 1.83929 is the tribonacci constant. Taking the even permutations with an odd number of plus signs, and the odd permutations with an even number of plus signs, gives a different snub cube, the mirror image. Taking all of them together yields the compound of two snub cubes.
This snub cube has edges of length , a number which satisfies the equation
and can be written as
To get a snub cube with unit edge length, divide all the coordinates above by the value α given above.
Orthogonal projections
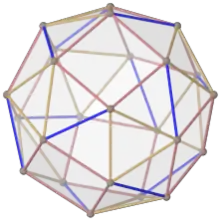
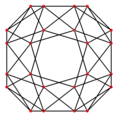
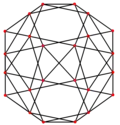
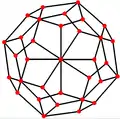
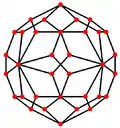
The snub cube has two special orthogonal projections, centered, on two types of faces: triangles, and squares, correspond to the A2 and B2 Coxeter planes.
| Centered by | Face Triangle |
Face Square |
Edge |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid |  |
 |
 |
| Wireframe | 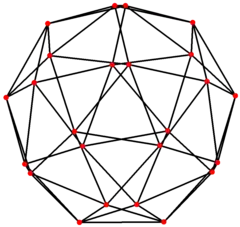 |
 |
 |
| Projective symmetry |
[3] | [4]+ | [2] |
| Dual |  |
 |
 |
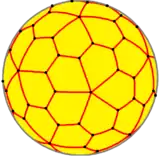
Spherical tiling
The snub cube can also be represented as a spherical tiling, and projected onto the plane via a stereographic projection. This projection is conformal, preserving angles but not areas or lengths. Great circle arcs (geodesics) on the sphere are projected as circular arcs on the plane.
 |
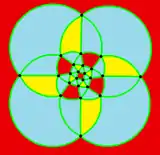 square-centered |
| Orthographic projection | Stereographic projection |
|---|
Geometric relations
The snub cube can be generated by taking the six faces of the cube, pulling them outward so they no longer touch, then giving them each a small rotation on their centers (all clockwise or all counter-clockwise) until the spaces between can be filled with equilateral triangles.
The snub cube can also be derived from the truncated cuboctahedron by the process of alternation. 24 vertices of the truncated cuboctahedron form a polyhedron topologically equivalent to the snub cube; the other 24 form its mirror-image. The resulting polyhedron is vertex-transitive but not uniform.
An "improved" snub cube, with a slightly smaller square face and slightly larger triangular faces compared to Archimedes' uniform snub cube, is useful as a spherical design.[2]
Related polyhedra and tilings
The snub cube is one of a family of uniform polyhedra related to the cube and regular octahedron.
| Uniform octahedral polyhedra | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry: [4,3], (*432) | [4,3]+ (432) |
[1+,4,3] = [3,3] (*332) |
[3+,4] (3*2) | |||||||
| {4,3} | t{4,3} | r{4,3} r{31,1} |
t{3,4} t{31,1} |
{3,4} {31,1} |
rr{4,3} s2{3,4} |
tr{4,3} | sr{4,3} | h{4,3} {3,3} |
h2{4,3} t{3,3} |
s{3,4} s{31,1} |
= |
= |
= |
||||||||
| Duals to uniform polyhedra | ||||||||||
| V43 | V3.82 | V(3.4)2 | V4.62 | V34 | V3.43 | V4.6.8 | V34.4 | V33 | V3.62 | V35 |
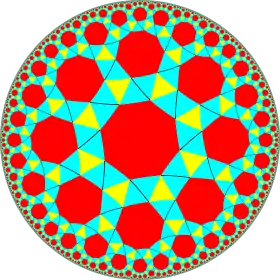
This semiregular polyhedron is a member of a sequence of snubbed polyhedra and tilings with vertex figure (3.3.3.3.n) and Coxeter–Dynkin diagram ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() . These figures and their duals have (n32) rotational symmetry, being in the Euclidean plane for n = 6, and hyperbolic plane for any higher n. The series can be considered to begin with n=2, with one set of faces degenerated into digons.
. These figures and their duals have (n32) rotational symmetry, being in the Euclidean plane for n = 6, and hyperbolic plane for any higher n. The series can be considered to begin with n=2, with one set of faces degenerated into digons.
| n32 symmetry mutations of snub tilings: 3.3.3.3.n | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry n32 |
Spherical | Euclidean | Compact hyperbolic | Paracomp. | ||||
| 232 | 332 | 432 | 532 | 632 | 732 | 832 | ∞32 | |
| Snub figures |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
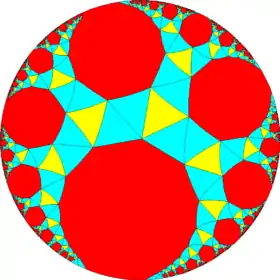 |
| Config. | 3.3.3.3.2 | 3.3.3.3.3 | 3.3.3.3.4 | 3.3.3.3.5 | 3.3.3.3.6 | 3.3.3.3.7 | 3.3.3.3.8 | 3.3.3.3.∞ |
| Gyro figures |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Config. | V3.3.3.3.2 | V3.3.3.3.3 | V3.3.3.3.4 | V3.3.3.3.5 | V3.3.3.3.6 | V3.3.3.3.7 | V3.3.3.3.8 | V3.3.3.3.∞ |
The snub cube is second in a series of snub polyhedra and tilings with vertex figure 3.3.4.3.n.
| 4n2 symmetry mutations of snub tilings: 3.3.4.3.n | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetry 4n2 |
Spherical | Euclidean | Compact hyperbolic | Paracomp. | ||||
| 242 | 342 | 442 | 542 | 642 | 742 | 842 | ∞42 | |
| Snub figures |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Config. | 3.3.4.3.2 | 3.3.4.3.3 | 3.3.4.3.4 | 3.3.4.3.5 | 3.3.4.3.6 | 3.3.4.3.7 | 3.3.4.3.8 | 3.3.4.3.∞ |
| Gyro figures |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||||
| Config. | V3.3.4.3.2 | V3.3.4.3.3 | V3.3.4.3.4 | V3.3.4.3.5 | V3.3.4.3.6 | V3.3.4.3.7 | V3.3.4.3.8 | V3.3.4.3.∞ |
Snub cubical graph
| Snub cubical graph | |
|---|---|
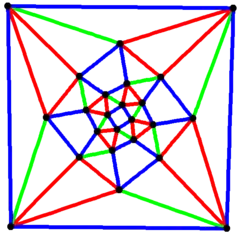 4-fold symmetry | |
| Vertices | 24 |
| Edges | 60 |
| Automorphisms | 24 |
| Properties | Hamiltonian, regular |
| Table of graphs and parameters | |
In graph theory, a snub cubical graph is the graph of vertices and edges of the snub cube, one of the Archimedean solids. It has 24 vertices and 60 edges, and is an Archimedean graph.[3]
 |
See also
References
- ↑ "Snub Cube - Geometry Calculator". rechneronline.de. Retrieved 2020-05-26.
- ↑ "Spherical Designs" by R.H. Hardin and N.J.A. Sloane
- ↑ Read, R. C.; Wilson, R. J. (1998), An Atlas of Graphs, Oxford University Press, p. 269
- Jayatilake, Udaya (March 2005). "Calculations on face and vertex regular polyhedra". Mathematical Gazette. 89 (514): 76–81. doi:10.1017/S0025557200176818. S2CID 125675814.
- Williams, Robert (1979). The Geometrical Foundation of Natural Structure: A Source Book of Design. Dover Publications, Inc. ISBN 0-486-23729-X. (Section 3-9)
- Cromwell, P. (1997). Polyhedra. United Kingdom: Cambridge. pp. 79–86 Archimedean solids. ISBN 0-521-55432-2.
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Snub cube" ("Archimedean solid") at MathWorld.
- Klitzing, Richard. "3D convex uniform polyhedra s3s4s - snic".
- The Uniform Polyhedra
- Virtual Reality Polyhedra The Encyclopedia of Polyhedra
- Editable printable net of a Snub Cube with interactive 3D view