Yangquan
阳泉市 Yangchuan | |
|---|---|
 | |
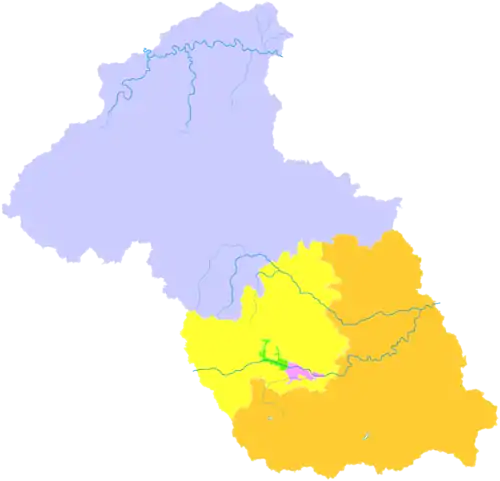
.png.webp) Location of Yangquan City jurisdiction in Shanxi | |
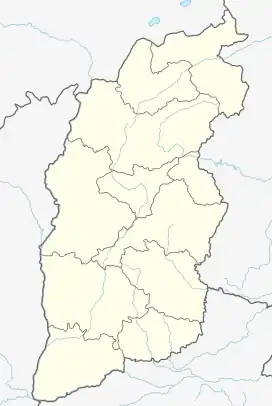 Yangquan Location of the city centre in Shanxi | |
| Coordinates (Yangquan municipal government): 37°51′26″N 113°34′49″E / 37.8571°N 113.5804°E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Shanxi |
| Districts | 3 |
| Counties | 2 |
| Incorporated (prefecture) | 1952 |
| Municipal seat | Chengqu |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 4,563 km2 (1,762 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 656.9 km2 (253.6 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 2,053.9 km2 (793.0 sq mi) |
| Population (2020 census)[2] | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 1,368,502 |
| • Density | 300/km2 (780/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 731,228 |
| • Urban density | 1,100/km2 (2,900/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,037,456 |
| • Metro density | 510/km2 (1,300/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 045000 |
| Area code | 0353 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-SX-03 |
| License Plate Prefix | 晋C |
| Administrative division code | 140300 |
| Website | yq |
Yangquan (simplified Chinese: 阳泉; traditional Chinese: 陽泉; pinyin: Yángquán [jǎŋtɕʰyǎn]) is a prefecture-level city in the east of Shanxi province, People's Republic of China, bordering Hebei province to the east. Situated at the eastern edge of the Loess Plateau and the west side of the Taihang Mountains, known as "Rippling Spring" in ancient times. Yangquan occupies a total area of 4,452 square kilometres (1,719 sq mi). According to the 2020 Census, Yangquan had a population of 1,318,505 inhabitants whom 1,037,456 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of 3 urban Districts plus Pingding County now being conurbated.[2] Yangquan is a new industrial city of Shanxi province. It belongs to the warm temperate semi-humid continental monsoon climate zone. Yangquan City has jurisdiction over two counties and three districts.
Yangquan is the gateway of the Shanxi province, located in the middle of Taiyuan and Shijiazhuang, 100 kilometers apart. Yangquan is also located in the eastern developed areas and the central and western regions of the combination zone, and also located in the reasonable transport sector through Tianjin, Qingdao, Huanghua. There are the ninth pass and Niangzi pass of the Great Wall, the Cangshan tourist Scenic spot, the Guanshan Academy, the former residence of Shi Pingmei, the Liangjiazhai Hot Spring, and the Shinaoshan Forest Park.
In 2017, Yangquan achieved a regional gross domestic product of 67.2 billion yuan, an increase of 6.3 percent at comparable prices. Among them, the added value of the primary industry was 1.04 billion yuan, up 3.0 percent, the added value of the secondary industry was 32.04 billion yuan, an increase of 5.6 percent, and that of the tertiary industry was 34.12 billion yuan, an increase of 7.1 percent. The composition of the three industries was adjusted from 1.7 to 48.0 50.3 in 2016 to 1.5 to 47.7 50.8. The per capita regional GDP was 47790 yuan, or US$7078 at the average exchange rate in 2017.
Administrative divisions
| Map | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Hanzi | Pinyin | Meaning | Population (2010 Census) |
Area (km2) | Density (/km2) |
| Cheng District | 城区 | Chéngqū | Urban District | 193,106 | 19 | 10,163 |
| Kuang District | 矿区 | Kuàngqū | Mining District | 242,994 | 10 | 24,299 |
| Jiao District | 郊区 | Jiāoqū | Suburban District | 286,055 | 633 | 452 |
| Pingding County | 平定县 | Píngdìng Xiàn | 335,265 | 1,350 | 248 | |
| Yu County | 盂县 | Yù Xiàn | 311,082 | 2,439 | 128 | |
Geography and climate
Yangquan has a rather dry, monsoon-influenced humid continental climate /semi-arid climate (Köppen Dwa/BSk),[3] with cold and very dry winters, and hot, somewhat humid summers. The monthly 24-hour average temperature ranges from −3.2 °C (26.2 °F) in January to 24.3 °C (75.7 °F) in July, and the annual mean is 11.5 °C (52.7 °F). The diurnal temperature variation, not exceeding 13 °C (23 °F) in any month, is not large for provincial standards. More than 70% of the annual precipitation, which ranges from 450 to 550 millimetres (18 to 22 in) in the entire prefecture-level city (PLC), occurs from June to September; throughout the PLC, sunshine totals 2700–2900 hours annually, and the frost-free period lasts 130–180 days.
| Climate data for Yangquan (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1971–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 16.3 (61.3) |
24.2 (75.6) |
29.9 (85.8) |
36.9 (98.4) |
37.8 (100.0) |
41.7 (107.1) |
41.5 (106.7) |
37.6 (99.7) |
37.6 (99.7) |
30.1 (86.2) |
26.3 (79.3) |
16.9 (62.4) |
41.7 (107.1) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 2.8 (37.0) |
6.4 (43.5) |
12.9 (55.2) |
20.3 (68.5) |
25.8 (78.4) |
29.3 (84.7) |
29.9 (85.8) |
28.2 (82.8) |
24.1 (75.4) |
18.5 (65.3) |
10.7 (51.3) |
4.3 (39.7) |
17.8 (64.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −3.2 (26.2) |
−0.2 (31.6) |
6.0 (42.8) |
13.2 (55.8) |
19.1 (66.4) |
22.8 (73.0) |
24.2 (75.6) |
22.6 (72.7) |
17.9 (64.2) |
12.0 (53.6) |
4.6 (40.3) |
−1.4 (29.5) |
11.5 (52.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −7.5 (18.5) |
−4.8 (23.4) |
0.8 (33.4) |
7.4 (45.3) |
13.1 (55.6) |
17.3 (63.1) |
19.8 (67.6) |
18.5 (65.3) |
13.3 (55.9) |
7.1 (44.8) |
0.2 (32.4) |
−5.4 (22.3) |
6.6 (44.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −17.5 (0.5) |
−15.4 (4.3) |
−12.6 (9.3) |
−2.5 (27.5) |
3.0 (37.4) |
8.2 (46.8) |
13.1 (55.6) |
9.8 (49.6) |
3.8 (38.8) |
−4.3 (24.3) |
−12.3 (9.9) |
−15.8 (3.6) |
−17.5 (0.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 3.8 (0.15) |
5.7 (0.22) |
10.3 (0.41) |
26.7 (1.05) |
41.5 (1.63) |
67.4 (2.65) |
133.5 (5.26) |
116.7 (4.59) |
66.8 (2.63) |
31.6 (1.24) |
14.7 (0.58) |
3.0 (0.12) |
521.7 (20.53) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 2.5 | 2.9 | 3.5 | 6.1 | 7.1 | 10.8 | 13.7 | 12.0 | 9.1 | 5.9 | 3.9 | 2.0 | 79.5 |
| Average snowy days | 4.0 | 4.3 | 2.8 | 0.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | 2.5 | 3.4 | 18 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 46 | 46 | 42 | 44 | 47 | 56 | 70 | 74 | 68 | 59 | 51 | 45 | 54 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 182.8 | 176.5 | 215.1 | 232.9 | 252.6 | 225.7 | 199.0 | 191.8 | 192.2 | 198.3 | 182.7 | 181.3 | 2,430.9 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 60 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 57 | 51 | 45 | 46 | 52 | 58 | 61 | 61 | 55 |
| Source 1: China Meteorological Administration[4][5] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather China[6] | |||||||||||||
Location domain
Yangquan City is located in the east wing of central Shanxi Province, with geographical coordinates of 112 °5 °114 °4 east longitude and 37 °40 °40 °38 °31 °north latitude. It is located in the west of the middle of Taihang Mountain, north of Dingxiang County and Wutai County of Xinzhou, and east of Pingshan County and Jingxing County of Shijiazhuang, Hebei Province.
Southern Jinzhong Xiyang County, Jinzhong Shouyang County, Taiyuan Yangqu County;
It is about 106 kilometers long from north to south and about 42 kilometers from east to west.
the city has a total land area of 4559 square kilometers.
Geomorphology

Yangquan City is located on the eastern edge of the Loess Plateau and belongs to the eastern mountainous area of Shanxi Province.
The landforms in the territory are mainly mountainous areas, while the rest are hills and plains.
The mountains include nine mountains.
On the northern city boundary is the Niudaoling Mountains, which is located at the junction of Zhoushan and Taihang Mountains.
There are two mountains on the northwest boundary, which is the branch of Zhoushan.
The rest of the mountains are arranged in two rows, east and west.
The eastern train consists of four mountains, from north to south are the Baima Mountains, the Qiulin Mountains, the Mianshan Mountains and the Aishan Mountains. They belong to the middle of the Taihang Mountains, with peaks ranging from 700 to 1700 meters above sea level.
Taihang Mountain is the boundary mountain of Hebei and Jin provinces, its eastern slope is steep, the foothills meet with the North China Plain, which is less than 100 meters above sea level; the western slope is gently inclined, and the mountains and hills are undulating.
The western column consists of three mountains, namely, the Northern Mountains, the Southern Mountains and the Qiling Mountains.
They have gone deep into the interior of the Shanxi Plateau, although the altitude is higher, but the ground fluctuation is slower than that in the east.
Among the mountains, there are some intermountain basins, mainly the Xiyan Basin in the west, the Yucheng Basin in the middle and the Pingding Basin in the south.
Hydrology
Yangquan City, with the exception of 22 square meters in the west belongs to the Yellow River Basin, the rest belong to the Haihe River Basin.
There are more than 60 rivers in the territory, of which 34 have a watershed area of more than 10 square kilometers, and seven have a watershed area of more than 300 square kilometers and a river length of more than 30 kilometers, all of which belong to the Haihe River system.
Hutuo River and Mianhe River are the main rivers in the territory.
Hutuo River flows through the northern part of the city, is the Haihe River system of the five major rivers of the north source of the Ziya River, in the territory of the main tributaries are Wuhe, Longhua River, Shitang River and so on.
The Mianhe River is formed by the confluence of the Wenhe River and the Taohe River, distributed in the middle and south of the city; after leaving the country, it converges with the Gantao River (Songxi River) and flows into the Hutuo River.
There are also a number of rivers that leave the country directly.
History
Yangquan City has a long history, according to the 1950s from Pingding northwest jujube smoke, Daliangding and other places unearthed cultural relics, the Middle Paleolithic Age, there will be human survival and reproduction here.
During the Tang, Yu, Xia and Shang dynasties, Yangquan City was handed down to be the place of ancient Jizhou.
During the Spring and Autumn period, there was a hatred of Judah in Yuxian County.

Zhou Zhending king twelve years (457 years ago), Jinqing Zhibo extermination of feud; sixteen years (453 years ago), Han Zhao Wei three Jin, the city belongs to Zhao. Qin belongs to Taiyuan County.
At the beginning of the Western Han Dynasty, Shangai County was located in the city, and the county governance was in Xincheng Village, Pingding County, which belongs to Taiyuan County.
In the Eastern Han Dynasty, Shangai County belongs to Changshan State of Jizhou.
When the three Kingdoms, the north and south belong to Wei and state Leping County, Xinxing County.
The old system of Cao and Wei was used in the Western Jin Dynasty.
During the Sixteen Kingdoms of the Eastern Jin Dynasty, it belonged to Qian Zhao, Hou Zhao, ran Wei, Qian Yan, Qian Qin, Hou Yan, Northern Wei and other countries. During the Northern Wei Dynasty, the north and south belonged to Shiai County, Leping County, and Dingxiang County, Xinxing County, Wangzhou. After the whole territory belongs to the Eastern Wei Dynasty and the Northern Qi Dynasty. Sui in this Niangzi Wei Ze County, is Jingzhou, after the waste; in this county to buy the original Qiu County (later renamed Yu County), and Shiai County belong to Liaozhou.
In the early Tang Dynasty, the city belonged to the state, and later abandoned by the state. Shiai and Yuxian successively belonged to both prefectures and Taiyuan prefectures. In the first year of Tianbao (742), Shiai changed its name to Guangyang and moved to Guangyang Village.
The five dynasties belong to the late Tang Dynasty, the Post-Jin Dynasty, the Post-Han Dynasty and the Northern Han Dynasty.
In the Northern Song Dynasty, Taiping Xingguo four years (979), changed Guangyang County to Pingding County, the county administration moved back to Pingding Shangcheng, Li Ping Dingjun; Yu County belongs to the state; after that, Pingding County and Yu County both belong to Hedong Road.
Jin Shengping Dingzhou, Yuzhou, is Hedong Road, he Northeast Road.
Yuan belongs to Jining Road.
In the Ming Dynasty, Yuzhou was reduced to a county, and Pingding Prefecture belonged to Taiyuan House in Shanxi Province.
Qing Yongzheng two years (1724), pacified as Zhili Prefecture, the addition of Yu County, Shouyang County, is Shanxi Province.
At the beginning of the Republic of China, it was Pingding County and Yu County, which belonged to Jining Road in Shanxi Province and was directly under the jurisdiction of Shanxi Province. During the War of Resistance against Japan, Ping (Lubei) County, Ping (Ding) East County and Ping (Ding) West County, Yu County divided into Pen (County) Ping (Shan) County, Pen (County) Yang (qu) County, Pen (County) Shou (Yang) County; To the south of Zhengtai Railway, Ping (Ding) East and Ping (Ding) West two counties belong to the Shanxi-Hebei-Shandong-Henan Border region, and the northern counties belong to the Shanxi-Cr-Hebei Border region. During the War of Liberation, peace, Yu County gradually restored to the original establishment.
On May 4, 1947, Yangquan City was established as part of the original Pingding County, which was later renamed Yangquan Industrial and Mining area. Yangquan City (industrial and mining area) has been under the jurisdiction of the North China Joint Administrative Commission, the North China people's Government and Shanxi Province.
After the founding of New China, Yangquan City (initially industrial and mining area, resumed in 1952) several times by Jinzhong (Yuci) area (special agency), Pingding County, Yu County is Jinzhong (Yuci) area (special agency). It has set up urban areas, suburbs and mining areas.
In September 1983, the city administered the county system, and Pingding County and Yu County were assigned to Yangquan City. Yangquan City became a city with three districts (city, mine and suburb) under the jurisdiction of two counties (Pingding and Yu County) directly under the jurisdiction of Shanxi Province.
Natural resources
Water
The total amount of water resources in Yangquan City is 1.584 billion cubic meters per year.
Among them, the river runoff is 1.382 billion cubic meters per year (including 490 million cubic meters per year in this river and 892 million cubic meters per year in the outer area).
The amount of groundwater resources is 543 million cubic meters per year (including 435 million cubic meters per year for local groundwater resources and 108 million cubic meters per year for incoming groundwater resources in the outer area),
The repeated amount of river runoff and groundwater is 341 million cubic meters per year.

The per capita share of local water resources in Yangquan City is only 562 cubic meters per year, which is slightly higher than that of Shanxi Province, which is 546 cubic meters per year, less than 1 to 4 of the national per capita water resources of 2400 cubic meters per year.
It is only 1 to 8% of the world's per capita water resources.
Flora
Yangquan City has complex habitats and a wide variety of plants.
According to the Engler-Gilger classification system, there are 93 families and 437 species of common plants in China, including 5 families and 5 species of fungi and 4 families and 6 species of ferns.
There are 4 families and 11 species of gymnosperms, 80 families and 415 species of angiosperms (including 72 families and 360 species of dicotyledons and 8 families and 55 species of monocotyledons).
Among the families, the most species are Compositae, Leguminosae, Rosaceae and Gramineae, followed by Liliaceae, Umbelina, Labiatae, Chenopodiaceae, Ranunculaceae, Solanaceae and so on.
Among the plant variety resources, there are more than 160 species of medicinal plants, as well as a variety of food crops, oil crops and vegetable crops.
Yangquan City has 941000 mu of forest, accounting for 13.74% of the total area of Yangquan City, with another 22.05 million trees on the four sides, with a total wood volume of 550000 cubic meters.
In the forestland, the economic forest is 48000 mu.
There are 1.821 million mu of pastoral slope grassland, of which more than 90% are available, and the total output of grass is more than 100m kg.
Fauna
Due to the lack of forests and serious environmental pollution, there are few wild animals in Yangquan.
For example, "Pingding Zhou Zhi" recorded that in the Qing Dynasty, there were tigers and deer nearby. Nowadays, tigers have disappeared and deer can be found only at the Yao Ling Temple Forest Farm and other places with a small amount of artificial breeding.
In addition to wild animals, Yangquan City contains a large number of domesticated animals, such as pigs, cattle, sheep, horses, donkeys, mules, chickens, and rabbits.
Mineral resources
Yangquan City is rich in mineral resources, and as many as 52 kinds of mineral deposits have been proved, especially anthracite, pyrite and bauxite, which are famous for their large reserves, high grade and easy exploitation.
It is one of the largest anthracite production bases in China, one of the three bauxite production bases and one of the five pyrite production bases in China.
The territory contains a coal area of 1051 square kilometers, coal geological reserves of 10.4 billion tons, pyrite 250 million tons, bauxite 227 million tons.
The annual output of raw coal is 35 million tons, the annual production of pyrite is 2 million tons, and the annual output of bauxite clinker is 1.8 million tons.
There are also ceramic raw materials, kaolin, plastic clay, hard clay reserves of 177.409 million tons; feldspar reserves of 43.17 million tons; quartz reserves of 43.2 million tons; diopside reserves of 500 million tons.
Economy
In 2017, Yangquan achieved a regional gross domestic product of 67.2 billion yuan, an increase of 6.3 percent at comparable prices.
Among them, the added value of the primary industry was 1.04 billion yuan, up 3.0 percent, the added value of the secondary industry was 32.04 billion yuan, an increase of 5.6 percent, and that of the tertiary industry was 34.12 billion yuan, an increase of 7.1 percent.
The composition of the three industries was adjusted from 1.7 to 48.0 50.3 in 2016 to 1.5 to 47.7 50.8.
The per capita regional GDP was 47790 yuan, or US$7078 at the average exchange rate in 2017.
Consumer prices rose 1.4% year-on-year, with food prices falling 0.9%.
Retail prices rose 0.8%.
The ex-factory prices of industrial producers rose 8.1%, of which the prices of means of production and means of living rose by 7.7% and 7.7%, respectively.
The purchase price of industrial producers rose 14.8 percent.
25326 new jobs were created in cities and towns throughout the year.
11626 rural workers were transferred.
At the end of the year, the registered unemployment rate in cities and towns was 3.11%, below the provincial control target of 4.2%.
In 2017, investment in fixed assets in Yangquan City totaled 24.57 billion yuan, an increase of 6.6 percent over the same caliber.
Of this total, investment in the primary industry was 300 million yuan, down 88.8 percent; investment in the secondary industry was 14.97 billion yuan, up 51.3 percent; and investment in the tertiary industry was 9.3 billion yuan, down 11 percent.
According to the type of registration, the holding investment of the state-owned economy was 14.79 billion yuan, an increase of 29.4 percent.
By major sectors, industrial investment was 14.97 billion yuan, up 51.3 percent; infrastructure investment was 3.61 billion yuan, down 24.9 percent; and other investment was 5.99 billion yuan, down 28.2 percent.
In the whole year, 193 projects with investment in fixed assets (excluding real estate) were completed and put into production, with an investment rate of 53.0%, with a new fixed assets of 10.66 billion yuan and a utilization rate of 49.5%.
In 2017, the general public budget revenue of Yangquan City reached 5 billion yuan, an increase of 21.1 percent.
Of this total, tax revenue was 3.79 billion yuan, an increase of 38.5 percent. Domestic value-added tax, business tax, enterprise income tax, personal income tax, resource tax and urban construction tax totaled 3.09 billion yuan.
They increased by 76.9%, decreased by 99.0%, increased by 175.8%, increased by 56.0%, increased by 65.7% and increased by 19.3%.
The general public budget expenditure was 10.58 billion yuan, an increase of 10.5 per cent.
Of these, expenditure on agriculture, forestry and water services decreased by 1.2%, expenditure on education increased by 4.6%, expenditure on social security and employment increased by 18.8%, expenditure on health and family planning increased by 1.3%, and expenditure on energy conservation and environmental protection increased by 21.4%.
Spending on culture, sports and media increased by 1.8%, spending on urban and rural communities increased by 8.9%, and expenditure on public security increased by 1.0%.
In 2017, the per capita disposable income of urban permanent residents in Yangquan City was 29581 yuan, an increase of 6.4 per cent.
The per capita disposable income of rural permanent residents was 12963 yuan, an increase of 6.5 per cent.
The per capita disposable income of low-income households in cities and towns accounted for 20 per cent of the total households surveyed, up 8.2 per cent, while that in rural areas accounted for 20 per cent of the total households surveyed, accounting for 5553 yuan, an increase of 14.8 per cent.
Primary sector
In 2017, the planting area of crops in Yangquan City decreased by 1.5 per cent to 55000 hectares.
Of this total, grain planting area was 53000 hectares, down 2.5 percent, and oil planting area was 123.5 hectares, an increase of 32.4 percent.
Among the grain acreage, the corn acreage was 45000 hectares, down 3.4 per cent.
The total grain output for the whole year was 260000 tons, an increase of 0.4 percent.
Of this total, corn was 239000 tons, an increase of 0.2 per cent.
In 2017, Yangquan's total meat output was 21000 tons, an increase of 5.1 per cent.
Of this total, pork production was 16000 tons, up 4.7 per cent; beef production was 400 tons, up 70.2 per cent; and mutton production was 1000 tons, up 17.4 per cent.
Milk production was 6000 tons, down 18.2 per cent.
Egg production was 33000 tons, down 2.2 per cent.
The output of aquatic products was 701 tons, an increase of 12.8 percent.
In 2017, Yangquan City completed afforestation area of 3.7 thousand hectares, an increase of 21.1 percent, of which the artificial afforestation area was 3.3 thousand hectares, an increase of 18.8 percent.
Barren mountains and wasteland afforested an area of 3.3 thousand hectares.
By the end of 2017, the total power of agricultural machinery in Yangquan City was 331000 kilowatts, down 21.5 percent.
The area of mechanical cultivated land was 42000 hectares, down 0.7 percent, the mechanical sown area was 44000 hectares, and the mechanical harvest area was 17000 hectares, up 1.1 percent and 0.8 percent respectively over the previous year.
The total income of agricultural mechanization in the city reached 210 million yuan, an increase of 5.0 per cent.
Huayang New Material Technology Group (Chinese: 华阳新材料科技集团), until 2021 was known as Yangquan Coal Industry Group Company Limited, is a coal mining and energy company. Founded in 1950, transformed into a joint-stock company in 1999, headquartered in Yangquan.[7]
Secondary sector
In 2017, the number of industrial enterprises above the scale of Yangquan reached 123, with an industrial added value of 21.7 billion yuan, an increase of 5.5 percent.
The raw coal output of industrial enterprises above scale was 51.326 million tons, an increase of 1.1 per cent.
Coal washing was 23.881 million tons, down 29.9 percent, and electricity was 12.55 billion kilowatt hours, up 27.7 percent.
In 2017, industrial enterprises above the scale of Yangquan achieved 73.91 billion yuan in main business income, an increase of 21.3 percent, and 4.01 billion yuan in profits and taxes, an increase of 91 percent. Of these, the total profits were-1.64 billion yuan, 180 million yuan more than the same period last year.
The tax reached 5.65 billion yuan, an increase of 44.1 per cent.
The "two funds" of enterprises occupied 14.47 billion yuan, down 9.7 percent, of which accounts receivable totaled 11.81 billion yuan, down 14.3 percent, and finished goods totaled 2.66 billion yuan, an increase of 18.8 percent.
There were 54 loss-making enterprises, with a loss of 43.9 percent, and a loss of 3.41 billion yuan, an increase of 30.7 percent.
In 2017, the added value of the construction industry in Yangquan reached 5.08 billion yuan, an increase of 6.2 per cent.
The total profits of general contracting and professional contracting enterprises with construction qualifications were 30 million yuan, down 83.9 percent, and the tax paid was 460 million yuan, an increase of 96.7 percent.
Tertiary sector
In 2017, investment in real estate development in Yangquan City totaled 3.03 billion yuan, down 52.7 percent.
According to the purpose of the project,
Society
Science
In 2017, the number of patent applications in Yangquan City was 1107, a decrease of 21.6 percent, of which the number of invention patent applications was 439, an increase of 7.6 percent.
The number of patents granted in the city was 360, a decrease of 5.7 percent, of which the number of patents granted for invention was 18, a decrease of 21.7 percent.
A total of 41 scientific research achievements at or above the municipal level were achieved in the whole year, including 37 at the municipal level and 4 at the provincial level.
In the whole year, a total of 154technical contracts were signed, with a total transaction value of 250 million yuan.
In 2001, 26 scientific and technological achievements were newly registered.
Won 4 provincial science and technology awards.
There are 1 enterprise technology center, 10 provincial enterprise technology center and 30 municipal enterprise technology center.
There are 42 high-tech enterprises in the city.
By the end of 2017, there were 2 ordinary colleges and universities in Yangquan City, with 67000 people trained in practical skills for farmers in the whole year.

Culture
By the end of 2017, there were 6 mass art centers, 6 cultural centers, 6 art performing groups and 6 public libraries in Yangquan City.
At the end of the year, there were 332000 cable TV subscribers.
A total of 6.21 million copies of Yangquan Daily were distributed throughout the year.
Medical and health
By the end of 2017, there were 1548 health institutions (including clinics and village clinics) in Yangquan City, with a total of 6957 beds.
There are 6 Maternal and Child Health Hospitals (stations and stations).
There are a total of 10162 health technical personnel in health institutions in the city.
Sports cause.
In 2017, Yangquan athletes won 36 gold, 33 silver and 53 bronze medals (including non-Olympic events) in major competitions at home and abroad.
The city sold 118 million yuan in sports lottery tickets, nearly double the previous year.
Infrastructure
In 2017, the total energy consumption of Yangquan City was 8.5951 million tons of standard coal, an increase of 2.87 percent over the previous year, and the gross domestic product of 10,000 yuan consumed 1.3130 tons of standard coal, down 3.21 percent.
For the whole year, industrial comprehensive energy consumption was reduced by 5.6588 million tons of standard coal, an increase of 0.7 per cent.
The energy consumption per unit product of the main energy-consuming industrial enterprises is as follows: the comprehensive energy consumption per ton of raw coal production is 6.27 kg standard coal / ton, down 10.6%, and the unit energy consumption of coking process is 147.74 kg standard coal / ton, down 3.6%.
The standard coal consumption of thermal power plant is 300.47 g standard coal / kWh, up 0.4%, and the comprehensive energy consumption per unit alumina is 422.14 kg standard coal / ton, up 3.0%.
In 2017, the total amount of electricity used by the whole society in Yangquan City was 8.29 billion kilowatt hours, an increase of 16.5 per cent.
Among them, electricity consumption in the primary industry was 60 million kilowatt hours, up 8.3 percent, and that in the secondary industry was 6.69 billion kilowatt hours, up 18.1 percent, of which industrial power consumption was 6.64 billion kilowatt hours, an increase of 18.0 percent.
Electricity consumption in the tertiary industry was 930 million kWh, an increase of 14.3 per cent, and that of urban and rural residents was 610 million kWh, an increase of 4.4 per cent.
The proportion of electricity consumption of primary, secondary, tertiary industry and urban and rural residents in the whole society was 0.8%, 79.6%, 11.4% and 8.2%, respectively.
Social security
By the end of 2017, 310900 people in Yangquan City had participated in basic old-age insurance for urban workers, an increase of 22300 over the previous year, and 440900 had participated in old-age insurance for urban and rural residents, an increase of 300 over the previous year.
386000 urban workers participated in basic medical insurance, 815600 urban and rural residents participated in basic medical insurance, 260000 participated in industrial injury insurance, an increase of 2200 over the previous year, and 251200 participated in unemployment insurance, the same as the previous year.
246700 people participated in maternity insurance, an increase of 900 over the previous year.
The minimum wage for three districts and two counties in the city is 1700 yuan in urban areas, mining areas and suburbs, and 1500 yuan in Pingding County and Yu County, an increase of 80 yuan over the previous year.
In 2017, Yangquan City had a total of 34300 urban minimum living security objects, a decrease of 999 over the previous year, and 40800 rural minimum living security objects, an increase of 217 over the previous year, and 6300 people were included in the five guarantees in rural areas.
A total of 245 million yuan of minimum guaranteed funds were disbursed throughout the year, an increase of 24 million yuan over the previous year.
By the end of 2017, there were three rescue stations in Yangquan.
A total of 28 social service institutions provide accommodation, the number of beds in old-age service institutions is 1995, the number of beds in various welfare homes is 350, and the number of adoptions is 102.
There are 576 community service facilities in cities and towns, including 90 comprehensive community service centers.
In the whole year, 199 million yuan of welfare lottery tickets were sold and 100000 yuan of donations were received from the community.
Transportation
In 2017, the added value of transportation, warehousing and postal services in Yangquan reached 5 billion yuan, an increase of 12.1 per cent. The mileage of highway lines is 5660.4 km at the end of the year, an increase of 2.2 km over the end of last year. For the whole year, the railway freight volume was 44.971 million tons, an increase of 3.7 percent, and the railway passenger volume was 2.64 million, an increase of 1.3 percent. The number of civilian vehicles in the city reached 217000 (including three-wheeled vehicles and low-speed trucks), an increase of 9.9 percent, of which 190000 were private cars, an increase of 11.3 percent. The number of cars was 134000, an increase of 10.9 percent, of which 126000 were private cars, an increase of 11.7 percent.
Aviation
Yangquan City is located between Taiyuan and Shijiazhuang, the urban area is about 140 kilometers away from Shijiazhuang Zhengding International Airport in the east, and about 100 kilometers away from Taiyuan Wusu International Airport in the west. There are a number of air ticket outlets in the city, quick and convenient to inquire and book flights. In 2016, the Yangquan City Terminal of Taiyuan Wusu International Airport officially opened, providing ticket purchase and airport shuttle services. In 2017, the Yangquan Terminal of Shijiazhuang Zhengding International Airport officially opened, providing ticket purchase and airport pick-up services.
Railway

China's first electrified railway double line, the Shijiazhuang–Taiyuan railway, runs through the urban area.
In 2009, Yangquan North railway station was opened on the Shijiazhuang–Taiyuan high-speed railway. Most services to the older station were canceled leading to complaints from residents as it took 90 minutes by road to reach Yangquan North railway station from downtown Yangquan, and that journeys were less convenient.[8]
Construction started in 2016 on the Yangquan–Dazhai railway. As well as carrying freight, it will allow faster journeys from downtown Yingquan to Yingquan North railway station as well as south to Dazhai. The first section, from Yangquan North to Yangquan East, opened in 2020.
Highway
The highway traffic has formed the highway network which runs through the east and the west, longitudinally through the north and south, the trunk and branch crisscross, the layout is reasonable, take the city as the center to radiate to two counties and three districts. East to Hebei, west to Taiyuan, south to Changzhi, north to five, extending in all directions. The first high-grade highway in Shanxi Province, Taijiu Expressway, passes through the border and runs through the Beijing-Shenzhen Expressway and the Beijing-Tianjin-Tang Expressway, which has greatly improved the investment environment in Yangquan and made it very convenient to go east and west. In 2013, Yangquan City, county and county access asphalt road, township access road, village access motor vehicles. Highway traffic is developing in the direction of wide roadbed, large tonnage and high speed. Yangquan Expressway is more developed. The Beijing-Shenzhen high-speed and the Beijing-Tianjin-Tangshan high-speed all connect with its main line too old high-speed. It is only an hour's drive from Taijiao Expressway across Yangquan to Shijiazhuang Airport or Taiyuan Airport, while it takes only more than three hours to get to Beijing via Taijiu Expressway and Jingshi Expressway. The 207 National Highway and 307 National Highway also pass through Yangquan, making the traffic of Yangquan Highway easy to reach all directions. Yangquan City bus terminal every day to Zhengzhou, Taiyuan, Shijiazhuang, Beijing, Jinzhong and other places of the bus.
Specialty
Walnut and their oil, pepper, dried cucumber, coal carving, casserole and vinegar is the specialty goods of Yangquan.
Tourism
Park
Nanshan Park, Taohe Park, Beishan Park, Yangquan Botanical Garden, City Central Park are the main park and tourist attractions.
Historical Site
Yangquan contains the ruins of the ancient city of Zhao Jianzi at the end of the Spring and Autumn period, the site of the garrison of Han Xin in the Han, Huaiyin, and Hou, and the site where the princess of Pingyang led the army to garrison Niangziguan in the Tang Dynasty.
In Dongfu Mountain, in the south of Pingding, Nu WA is said to have built a stove here to make up the sky, making the whole stone of Dongfu Mountain brown and red, floating but not sinking after it has been thrown into the water. Up to now, the cooker still exists, as well as the inscription of Lu Shen in the Ming Dynasty.
The Cang mountain, 60 kilometers north of the city, is said to have been hidden here by Zhao orphans in the Spring and Autumn period. There is a legend of the Canggu cave, and the name of the Cang mountain is interpreted here.
In addition, Yangquan also preserves many ancient cultural sites, such as the Northern Wei Grottoes, the cliff stone carvings of the Southern and Northern dynasties, the main hall of Lin Li Guandi Temple rebuilt in the Song Dynasty, and the ancient architectural groups since the Jin and Yuan dynasty.
Memorial site
The site of the pacified armed uprising led by the Chinese Communist Party in 1931 and the site of Shinao Mountain, the main battlefield of the "hundred League War" in 1940.
(100 Patriotic Education bases).
The Monument to the "hundred League War" (the main monument) is 40 meters high and is shaped like a sharp bayonet.
Peng Zhen inscribed on the front of the inscription: "brilliant achievements, forever in the annals of history";
On both sides are Xu Qian's inscriptions: "the martyrs who took part in the hundred League War are immortal." Bo Yibo wrote: "the hundred League War, the most brilliant page in the War of Resistance against Japan, will certainly go down in the annals of history and shine forever."
Cultural relics and monuments
In addition, there are many ancient temples and temples, stele inscriptions, ancient tombs and other cultural footprints.
Liangjiazhai Hot Spring, Yaolin Temple and Niangziguan Falls with medical value, and the rare wonders of large stalactite cave in the north, such as Lianhua Cave, Wuhuadong and so on.
Yao Lin Temple is located in Pingding County, Yangquan City, 20 kilometers south of the city, is a provincial forest park in Pingding County.
Notable people
- Co-founder of Baidu; Robin Li (李彦宏) was born and raised in Yangquan.
- Author of The Three-Body Problem; Liu Cixin (刘慈欣) was born and raised in Yangquan.
Twinned cities
 Chesterfield, Derbyshire, England, United Kingdom[9]
Chesterfield, Derbyshire, England, United Kingdom[9] Mount Vernon, New York, United States
Mount Vernon, New York, United States
References
- ↑ Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, ed. (2019). China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook 2017. Beijing: China Statistics Press. p. 46. Retrieved 11 January 2020.
- 1 2 "China: Shānxī (Prefectures, Cities, Districts and Counties) - Population Statistics, Charts and Map".
- ↑ Peel, M. C., Finlayson, B. L., and McMahon, T. A.: Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification, Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci., 11, 1633-1644, doi:10.5194/hess-11-1633-2007, 2007.
- ↑ 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 26 August 2023.
- ↑ 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 26 August 2023.
- ↑ 阳泉 - 气象数据 -中国天气网 (in Chinese). Weather China. Retrieved 29 November 2022.
- ↑ "Yangquan Coal Industry Group". Fortune. Retrieved 2023-09-29.
- ↑ "阳泉市民"疏远"动车组事出有因政府已有行动?_新闻中心_新浪网". news.sina.com.cn. 22 May 2009. Retrieved 9 October 2020.
- ↑ "Chesterfield Twinning Links". Chesterfield Borough Council. Retrieved 2013-07-27.