调和矩阵
定义
若G是简单图,G有n个顶点,A是邻接矩阵,D是度数矩阵,则调和矩阵是[1]
举例
| 图 | 度矩阵 | 邻接矩阵 | 调和矩阵 |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
动力学和微分方程
使用矩阵矢量
解是
平衡举动
当的时候,
MATLAB代码
N = 20;%The number of pixels along a dimension of the image
A = zeros(N, N);%The image
Adj = zeros(N*N, N*N);%The adjacency matrix
%Use 8 neighbors, and fill in the adjacency matrix
dx = [-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1];
dy = [-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1];
for x = 1:N
for y = 1:N
index = (x-1)*N + y;
for ne = 1:length(dx)
newx = x + dx(ne);
newy = y + dy(ne);
if newx > 0 && newx <= N && newy > 0 && newy <= N
index2 = (newx-1)*N + newy;
Adj(index, index2) = 1;
end
end
end
end
%%%BELOW IS THE KEY CODE THAT COMPUTES THE SOLUTION TO THE DIFFERENTIAL
%%%EQUATION
Deg = diag(sum(Adj, 2));%Compute the degree matrix
L = Deg - Adj;%Compute the laplacian matrix in terms of the degree and adjacency matrices
[V, D] = eig(L);%Compute the eigenvalues/vectors of the laplacian matrix
D = diag(D);
%Initial condition (place a few large positive values around and
%make everything else zero)
C0 = zeros(N, N);
C0(2:5, 2:5) = 5;
C0(10:15, 10:15) = 10;
C0(2:5, 8:13) = 7;
C0 = C0(:);
C0V = V'*C0;%Transform the initial condition into the coordinate system
%of the eigenvectors
for t = 0:0.05:5
%Loop through times and decay each initial component
Phi = C0V.*exp(-D*t);%Exponential decay for each component
Phi = V*Phi;%Transform from eigenvector coordinate system to original coordinate system
Phi = reshape(Phi, N, N);
%Display the results and write to GIF file
imagesc(Phi);
caxis([0, 10]);
title(sprintf('Diffusion t = %3f', t));
frame = getframe(1);
im = frame2im(frame);
[imind, cm] = rgb2ind(im, 256);
if t == 0
imwrite(imind, cm, 'out.gif', 'gif', 'Loopcount', inf, 'DelayTime', 0.1);
else
imwrite(imind, cm, 'out.gif', 'gif', 'WriteMode', 'append', 'DelayTime', 0.1);
end
end
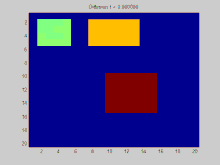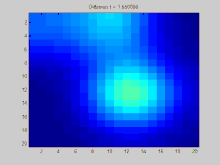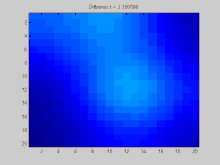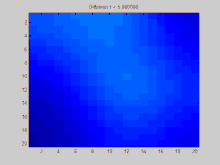
GIF:离散拉普拉斯过程,使用拉普拉斯矩阵
参考文献
- Weisstein, Eric W. (编). . at MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource. Wolfram Research, Inc. [2020-02-14]. (原始内容存档于2019-12-23) (英语).
- . www.quora.com. [2020-02-14].
- Shuman, David I.; Narang, Sunil K.; Frossard, Pascal; Ortega, Antonio; Vandergheynst, Pierre. . IEEE Signal Processing Magazine. 2013-05, 30 (3): 83–98 [2020-02-14]. ISSN 1053-5888. doi:10.1109/MSP.2012.2235192. (原始内容存档于2020-01-11).
- Chung, Fan. . American Mathematical Society. 1997 [1992] [2020-02-14]. ISBN 978-0821803158. (原始内容存档于2020-02-14).
- Newman, Mark. . Oxford University Press. 2010. ISBN 978-0199206650.
阅读
- T. Sunada. . P. Exner, J. P. Keating, P. Kuchment, T. Sunada, A. Teplyaev (编). 77. 2008: 51–86. ISBN 978-0-8218-4471-7.
- B. Bollobás, Modern Graph Theory, Springer-Verlag (1998, corrected ed. 2013), ISBN 0-387-98488-7, Chapters II.3 (Vector Spaces and Matrices Associated with Graphs), VIII.2 (The Adjacency Matrix and the Laplacian), IX.2 (Electrical Networks and Random Walks).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.