| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
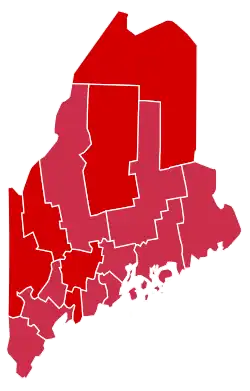 County Results
McKinley 60-70% 70-80%
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elections in Maine |
|---|
 |
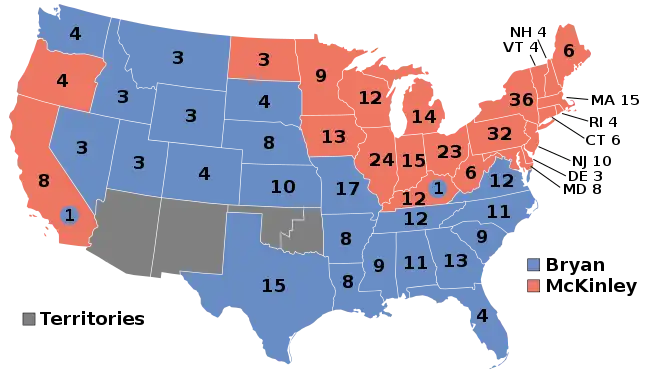
The 1896 United States presidential election in Maine took place on November 3, 1896, as part of the 1896 United States presidential election. Voters chose six representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.
Maine voted for the Republican nominee, former governor of Ohio William McKinley, over the Democratic nominee, former U.S. Representative from Nebraska William Jennings Bryan. McKinley won the state by a margin of 38.69%.
Bryan, running on a platform of free silver, appealed strongly to Western miners and farmers, but had little appeal in the Northeastern states such as Maine.
With 67.90% of the popular vote, Maine would be McKinley's fifth strongest victory in terms of percentage in the popular vote after Vermont, Massachusetts, neighboring New Hampshire and Rhode Island.[1]
Bryan would lose Maine to McKinley again four years later and would later lose the state again in 1908 to William Howard Taft.
Results
| 1896 United States presidential election in Maine[2] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Votes | Percentage | Electoral votes | |
| Republican | William McKinley | 80,403 | 67.90% | 6 | |
| Democratic | William Jennings Bryan | 32,200 | 27.19% | ||
| Populist | William Jennings Bryan | 2,387 | 2.02% | ||
| Total | William Jennings Bryan | 34,587 | 29.21% | 0 | |
| National Democratic | John M. Palmer | 1,867 | 1.58% | 0 | |
| Prohibition | Joshua Levering | 1,562 | 1.32% | 0 | |
| Totals | 118,419 | 100.00% | 6 | ||
| Voter turnout | — | ||||
Results by county
| County | William McKinley Republican |
William Jennings Bryan Democratic |
John McAuley Palmer[3] National Democratic |
Joshua Levering[3] Prohibition |
Margin | Total votes cast[4] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | % | # | % | # | % | # | % | # | % | ||
| Androscoggin | 5,548 | 66.61% | 2,513 | 30.17% | 157 | 1.88% | 111 | 1.33% | 3,035 | 36.44% | 8,329 |
| Aroostook | 4,816 | 74.41% | 1,383 | 21.37% | 42 | 0.65% | 231 | 3.57% | 3,433 | 53.04% | 6,472 |
| Cumberland | 11,017 | 65.32% | 5,175 | 30.68% | 450 | 2.67% | 224 | 1.33% | 5,842 | 34.64% | 16,866 |
| Franklin | 2,578 | 72.60% | 886 | 24.95% | 49 | 1.38% | 38 | 1.07% | 1,692 | 47.65% | 3,551 |
| Hancock | 4,306 | 68.69% | 1,795 | 28.63% | 117 | 1.87% | 51 | 0.81% | 2,511 | 40.06% | 6,269 |
| Kennebec | 7,889 | 71.70% | 2,817 | 25.60% | 106 | 0.96% | 191 | 1.74% | 5,072 | 46.10% | 11,003 |
| Knox | 3,286 | 61.72% | 1,900 | 35.69% | 103 | 1.93% | 35 | 0.66% | 1,386 | 26.03% | 5,324 |
| Lincoln | 2,596 | 66.46% | 1,211 | 31.00% | 62 | 1.59% | 37 | 0.95% | 1,385 | 35.46% | 3,906 |
| Oxford | 4,779 | 71.52% | 1,677 | 25.10% | 159 | 2.38% | 67 | 1.00% | 3,102 | 46.42% | 6,682 |
| Penobscot | 8,414 | 66.42% | 4,031 | 31.82% | 90 | 0.71% | 133 | 1.05% | 4,383 | 34.60% | 12,668 |
| Piscataquis | 2,342 | 70.37% | 904 | 27.16% | 36 | 1.08% | 46 | 1.38% | 1,438 | 43.21% | 3,328 |
| Sagadahoc | 2,725 | 71.60% | 957 | 25.14% | 79 | 2.08% | 45 | 1.18% | 1,768 | 46.46% | 3,806 |
| Somerset | 4,695 | 68.12% | 2,018 | 29.28% | 82 | 1.19% | 97 | 1.41% | 2,677 | 38.84% | 6,892 |
| Waldo | 3,253 | 61.68% | 1,939 | 36.77% | 50 | 0.95% | 32 | 0.61% | 1,314 | 24.91% | 5,274 |
| Washington | 4,627 | 68.93% | 1,925 | 28.68% | 111 | 1.65% | 50 | 0.74% | 2,702 | 40.25% | 6,713 |
| York | 7,532 | 66.44% | 3,456 | 30.49% | 174 | 1.53% | 174 | 1.53% | 4,076 | 35.95% | 11,336 |
| Totals | 80,403 | 67.90% | 34,587 | 29.21% | 1,867 | 1.58% | 1,562 | 1.32% | 45,816 | 38.69% | 118,419 |
See also
References
- ↑ "1896 Presidential Election Statistics". Dave Leip’s Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections. Retrieved March 5, 2018.
- ↑ "1896 Presidential General Election Results – Maine". Dave Leip's U.S. Election Atlas.
- 1 2 Géoelections; Popular Vote at the Presidential Election for 1896 (.xlsx file for €30 including full minor party figures)
- ↑ Robinson, Edgar Eugene; The Presidential Vote 1896-1932, pp. 223-224 ISBN 9780804716963
.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)