 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
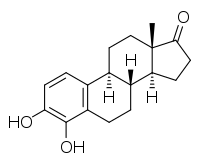
| IUPAC name
3,4-Dihydroxyestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-one | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(3aS,3bR,9bS,11aS)-6,7-Dihydroxy-11a-methyl-2,3,3a,3b,4,5,9b,10,11,11a-decahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-1-one | |
| Other names
4-OHE1; Estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,4-diol-17-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H22O3 | |
| Molar mass | 286.371 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
4-Hydroxyestrone (4-OHE1), also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,4-diol-17-one, is an endogenous, naturally occurring catechol estrogen and a minor metabolite of estrone and estradiol.[1][2][3] It is estrogenic, similarly to many other hydroxylated estrogen metabolites such as 2-hydroxyestradiol, 16α-hydroxyestrone, estriol (16α-hydroxyestradiol), and 4-hydroxyestradiol but unlike 2-hydroxyestrone.[1][4]
| Estrogen | ER RBA (%) | Uterine weight (%) | Uterotrophy | LH levels (%) | SHBG RBA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | – | 100 | – | 100 | – |
| Estradiol (E2) | 100 | 506 ± 20 | +++ | 12–19 | 100 |
| Estrone (E1) | 11 ± 8 | 490 ± 22 | +++ | ? | 20 |
| Estriol (E3) | 10 ± 4 | 468 ± 30 | +++ | 8–18 | 3 |
| Estetrol (E4) | 0.5 ± 0.2 | ? | Inactive | ? | 1 |
| 17α-Estradiol | 4.2 ± 0.8 | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 24 ± 7 | 285 ± 8 | +b | 31–61 | 28 |
| 2-Methoxyestradiol | 0.05 ± 0.04 | 101 | Inactive | ? | 130 |
| 4-Hydroxyestradiol | 45 ± 12 | ? | ? | ? | ? |
| 4-Methoxyestradiol | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 260 | ++ | ? | 9 |
| 4-Fluoroestradiola | 180 ± 43 | ? | +++ | ? | ? |
| 2-Hydroxyestrone | 1.9 ± 0.8 | 130 ± 9 | Inactive | 110–142 | 8 |
| 2-Methoxyestrone | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 103 ± 7 | Inactive | 95–100 | 120 |
| 4-Hydroxyestrone | 11 ± 4 | 351 | ++ | 21–50 | 35 |
| 4-Methoxyestrone | 0.13 ± 0.04 | 338 | ++ | 65–92 | 12 |
| 16α-Hydroxyestrone | 2.8 ± 1.0 | 552 ± 42 | +++ | 7–24 | <0.5 |
| 2-Hydroxyestriol | 0.9 ± 0.3 | 302 | +b | ? | ? |
| 2-Methoxyestriol | 0.01 ± 0.00 | ? | Inactive | ? | 4 |
| Notes: Values are mean ± SD or range. ER RBA = Relative binding affinity to estrogen receptors of rat uterine cytosol. Uterine weight = Percentage change in uterine wet weight of ovariectomized rats after 72 hours with continuous administration of 1 μg/hour via subcutaneously implanted osmotic pumps. LH levels = Luteinizing hormone levels relative to baseline of ovariectomized rats after 24 to 72 hours of continuous administration via subcutaneous implant. Footnotes: a = Synthetic (i.e., not endogenous). b = Atypical uterotrophic effect which plateaus within 48 hours (estradiol's uterotrophy continues linearly up to 72 hours). Sources: See template. | |||||
See also
References
- 1 2 Oettel M, Schillinger E (6 December 2012). Estrogens and Antiestrogens I: Physiology and Mechanisms of Action of Estrogens and Antiestrogens. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 224, 232, 244–245, 249. ISBN 978-3-642-58616-3.
- ↑ Rakel D (2012). Integrative Medicine. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 338–. ISBN 978-1-4377-1793-8.
- ↑ Buchsbaum HJ (6 December 2012). The Menopause. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 64–65. ISBN 978-1-4612-5525-3.
- ↑ Bhavnani BR, Nisker JA, Martin J, Aletebi F, Watson L, Milne JK (2000). "Comparison of pharmacokinetics of a conjugated equine estrogen preparation (premarin) and a synthetic mixture of estrogens (C.E.S.) in postmenopausal women". Journal of the Society for Gynecologic Investigation. 7 (3): 175–83. doi:10.1016/s1071-5576(00)00049-6. PMID 10865186.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.