| Partial Lunar Eclipse 31 December 2009 | |
|---|---|
 Munster, Ireland, 19:43 UT | |
 The southern edge of the Moon will be completely darken as the Moon passes through the Earth's umbral shadow | |
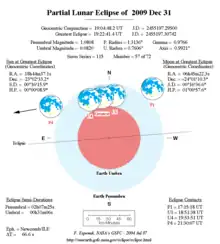
| Series (and member) | 115 (57 of 72) |
| Gamma | 0.9765 |
| Magnitude | 0.0763 |
| Duration (hr:mn:sc) | |
| Partial | 0:59:58 |
| Penumbral | 4:11:03 |
| Contacts (UTC) | |
| P1 | 17:17:08 |
| U1 | 18:52:43 |
| Greatest | 19:22:39 |
| U4 | 19:52:41 |
| P4 | 21:28:11 |
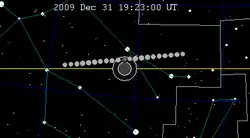 The Moon's hourly motion across the Earth's shadow in the constellation of Gemini | |
A partial lunar eclipse was visible on 31 December 2009. It was the last and largest of four minor lunar eclipses in 2009. This lunar eclipse was also notable, because it occurred during a blue moon (a second full moon in December) and was near perigee (making it a supermoon). The next eclipse on New Year's Eve and blue moon will occur on 31 December 2028.
Only a small portion of the Moon entered the Earth's umbral shadow, but there was a distinct darkening visible over the Moon's southern surface at greatest eclipse.
Visibility
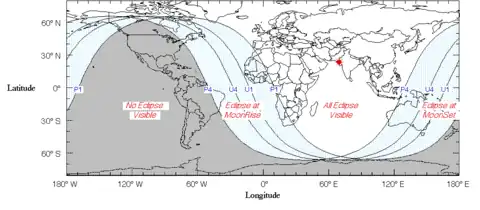
It was visible from all of Africa, Europe, Asia, Middle East and Australia. In the Philippines, the lunar eclipse was started last 1 January 2010, when it was very visible at mid-dawn until before sunrise.
 This simulation shows the view of the Earth as viewed from the center of the Moon at greatest eclipse. The partially eclipsed Sun is visible above the north pole. |
Map
Photos

Progression from Degania A, Israel
 Sheffield, England, 19:14 UTC
Sheffield, England, 19:14 UTC Qingdao, China, 19:16 UTC
Qingdao, China, 19:16 UTC.jpg.webp) Laguja, Estonia, 19:21 UTC
Laguja, Estonia, 19:21 UTC Beijing, China
Beijing, China
At maximum, 19:22 UTC.jpg.webp) Tokyo, Japan, 19:32 UTC
Tokyo, Japan, 19:32 UTC Chennai, India, 19:33 UTC
Chennai, India, 19:33 UTC Barcelona, Spain, 19:34 UTC
Barcelona, Spain, 19:34 UTC.jpg.webp) Athens, Greece, 19:34 UTC
Athens, Greece, 19:34 UTC Helsinki, Finland, 19:47 UTC
Helsinki, Finland, 19:47 UTC Nonthaburi, Thailand, 19:59 UTC
Nonthaburi, Thailand, 19:59 UTC.gif) Belfort, France
Belfort, France
Combined images
Related eclipses
Eclipses of 2009
Lunar year (354 days)
This eclipse is the one of four lunar eclipses in a short-lived series. The lunar year series repeats after 12 lunations or 354 days (Shifting back about 10 days in sequential years). Because of the date shift, the Earth's shadow will be about 11 degrees west in sequential events.
Saros series
It was part of Saros series 115.
| Lunar eclipse series sets from 2009–2013 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||||
| Saros # Photo |
Date Viewing |
Type chart |
Gamma | Saros # Photo |
Date Viewing |
Type chart |
Gamma | |
| 110 | 2009 Jul 07 |
penumbral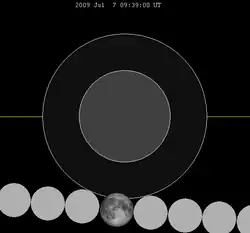 |
−1.4916 | 115 |
2009 Dec 31 |
partial |
0.9766 | |
120 |
2010 Jun 26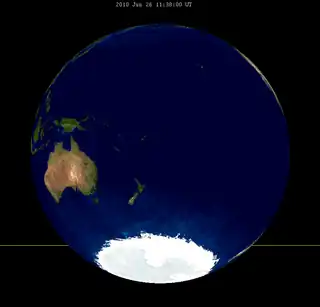 |
partial |
−0.7091 | 125 |
2010 Dec 21 |
total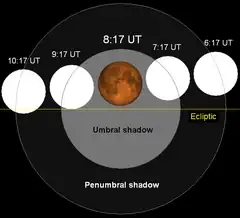 |
0.3214 | |
130 |
2011 Jun 15 |
total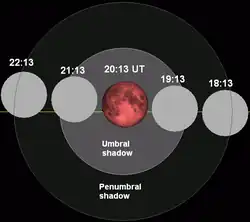 |
0.0897 | 135 |
2011 Dec 10 |
total |
−0.3882 | |
140 |
2012 Jun 04 |
partial |
0.8248 | 145 | 2012 Nov 28 |
penumbral |
−1.0869 | |
| 150 | 2013 May 25 |
penumbral |
1.5351 | |||||
| Last set | 2009 Aug 06 | Last set | 2009 Feb 9 | |||||
| Next set | 2013 Apr 25 | Next set | 2013 Oct 18 | |||||
Half-Saros cycle
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[1] This lunar eclipse is related to two partial solar eclipses of Solar Saros 122.
| 25 December 2000 | 6 January 2019 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Tritos series
- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of January 31, 1999
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of November 30, 2020
Tzolkinex
- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of November 20, 2002
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of February 11, 2017
See also
- List of lunar eclipses
- List of 21st-century lunar eclipses
- File:2009-12-31 Lunar Eclipse Sketch.gif Chart
References
- ↑ Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros
External links
- 2009 Dec 31 chart: Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- Hermit eclipse: 2009-12-31
- Eclipse enthusiasts in Europe, Africa, Australia and Asia can celebrate New Year's Eve by observing a partial lunar eclipse on December 31, 2009. The event's duration will be about four hours.

_(cropped).jpg.webp)
