| Total eclipse | |||||||||||||||||
| Date | 24 March 1978 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma | −0.21402 | ||||||||||||||||
| Magnitude | 1.45179 | ||||||||||||||||
| Saros cycle | 122 (54 of 75) | ||||||||||||||||
| Totality | 90 minutes, 40.2 seconds | ||||||||||||||||
| Partiality | 218 minutes, 34.5 seconds | ||||||||||||||||
| Penumbral | 345 minutes, 2.2 seconds | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
A total lunar eclipse took place on Friday, March 24, 1978, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 1978. The moon passed through the center of the Earth's shadow. The Moon was plunged into darkness for 1 hour, 30 minutes and 40.2 seconds, in a deep total eclipse which saw the Moon 45.179% of its diameter inside the Earth's umbral shadow. The visual effect of this depends on the state of the Earth's atmosphere, but the Moon may have been stained a deep red colour. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 38 minutes and 34.5 seconds in total.[1]
This is the 54th member of Lunar Saros 122. The previous event is the March 1960 lunar eclipse. The next event is the April 1996 lunar eclipse.
Visibility
It was seen completely over Asia and Australia, and rising over Africa and Europe. It was seen setting over Pacific Ocean on the morning of Friday 24 March, 1978.
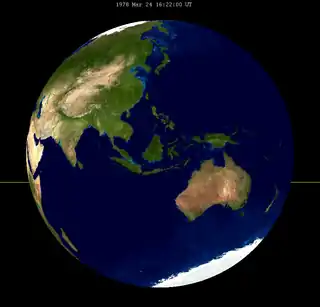
Related lunar eclipses
Eclipses in 1978
- A total lunar eclipse on Friday, 24 March 1978.
- A partial solar eclipse on Friday, 7 April 1978.
- A total lunar eclipse on Saturday, 16 September 1978.
- A partial solar eclipse on Monday, 2 October 1978.
Lunar year series
| Lunar eclipse series sets from 1977–1980 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||||
| Saros | Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Gamma | Saros | Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Gamma | |
| 112 | 1977 Apr 04 |
Partial |
−0.91483 | 117 | 1977 Sep 27 |
Penumbral |
1.07682 | |
| 122 | 1978 Mar 24 |
Total |
−0.21402 | 127 | 1978 Sep 16 |
Total |
0.29510 | |
| 132 | 1979 Mar 13 |
Partial |
0.52537 | 137 | 1979 Sep 06 |
Total |
−0.43050 | |
| 142 | 1980 Mar 01 |
Penumbral |
1.22701 | 147 | 1980 Aug 26 |
Penumbral |
−1.16082 | |
| Last set | 1976 May 13 | Last set | 1976 Nov 06 | |||||
| Next set | 1981 Jan 20 | Next set | 1980 Jul 27 | |||||
Tritos series
The tritos series repeats 31 days short of 11 years at alternating nodes. Sequential events have incremental Saros cycle indices.
This series produces 20 total eclipses between April 24, 1967 and August 11, 2185, only being partial on November 19, 2021.
| Tritos eclipse series (subset 1901–2087) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
| Saros | Date Viewing |
Type chart |
Saros | Date Viewing |
Type chart | |
| 115 | 1901 Oct 27 |
Partial |
116 | 1912 Sep 26 |
Partial | |
| 117 | 1923 Aug 26 |
Partial |
118 | 1934 Jul 26 |
Partial | |
| 119 | 1945 Jun 25 |
Partial |
120 | 1956 May 24 |
Partial | |
| 121 | 1967 Apr 24 |
Total |
122 | 1978 Mar 24 |
Total | |
| 123 | 1989 Feb 20 |
Total |
124 | 2000 Jan 21 |
Total | |
| 125 | 2010 Dec 21 |
Total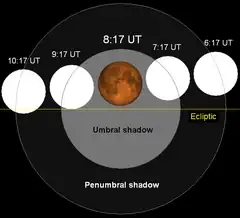 |
126 | 2021 Nov 19 |
Partial | |
| 127 | 2032 Oct 18 |
Total |
128 | 2043 Sep 19 |
Total | |
| 129 | 2054 Aug 18 |
Total |
130 | 2065 Jul 17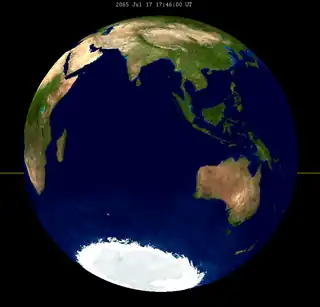 |
Total | |
| 131 | 2076 Jun 17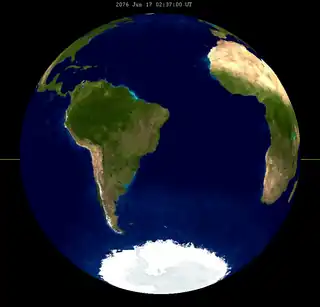 |
Total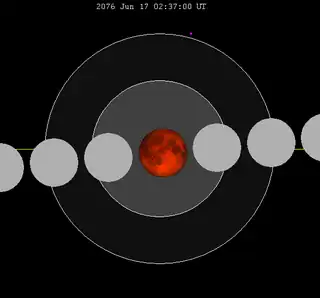 |
132 | 2087 May 17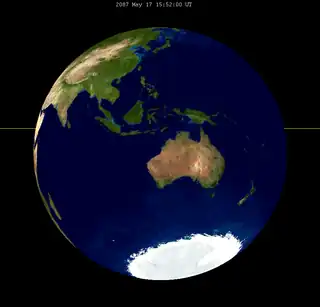 |
Total | |
| 133 | 2098 Apr 15 |
Total | ||||
Half-Saros cycle
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[2] This lunar eclipse is related to two solar eclipses of Solar Saros 129.
| March 18, 1969 | March 29, 1987 |
|---|---|
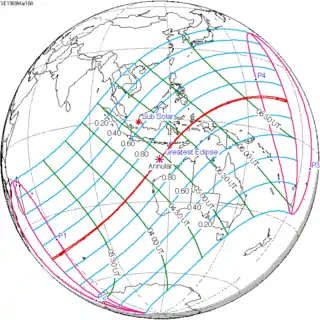 |
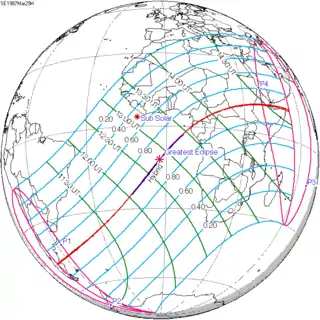 |
See also
Notes
- ↑ Hermit Eclipse: Saros cycle 122
- ↑ Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros
External links
- 1978 Mar 24 chart Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC

_(cropped).jpg.webp)
