| Total eclipse | |||||||||||||||||
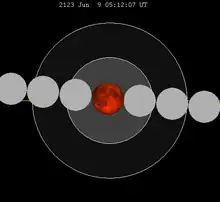 | |||||||||||||||||
| Date | 9 June 2123 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma | 0.0406[1] | ||||||||||||||||
| Magnitude | 1.7487[2] | ||||||||||||||||
| Saros cycle | 132 (36) | ||||||||||||||||
| Totality | 106 min 6 secs[1] | ||||||||||||||||
| Partiality | 236 min[1] | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
A total lunar eclipse will occur on Wednesday, June 9, 2123, with maximum eclipse at 05:06 UTC. A dramatic total eclipse lasting 106 minutes and 6 seconds will plunge the full Moon into deep darkness, as it passes right through the centre of the Earth's umbral shadow. While the visual effect of a total eclipse is variable, the Moon may be stained a deep orange or red colour at maximum eclipse. This will be a great spectacle for everyone who sees it. The partial eclipse will last for 3 hours and 56 minutes in total. The penumbral eclipse lasts for 6 hours and 14 minutes. Maximum eclipse is at 05:06:28 UT. This will be the longest Total Lunar Eclipse since 16 July 2000 (106 minutes, 25 seconds), and the longest one until 12 May 2264 (106 minutes, 13 seconds) and 27 July 3107 (106 minutes, 21 seconds), though the eclipse on June 19, 2141 will be nearly identical in all aspects.[3] This will also be the longest of the 22nd century and the second longest of the 3rd millennium.[4] The eclipse on June 19, 2141 will be the second longest of the 22nd century and the third longest of the third millennium (at 106 minutes 5 seconds).
Related lunar eclipses
Lunar eclipses are related by many different eclipse cycles. The Saros cycle (18 years and 10 days) repeats the most consistently due three coinciding periods, and continue over 70 events (1200+ years). Eclipses are identified by a Saros number and a member index within each series. The lunar year (354 days) and Metonic cycles (19 years) are short period last only 8 to 10 events. The Metonic cycle is equal to one Saros cycle plus one lunar year, and so the two series progress in parallel. The Inex cycle (29 years minus 20 days) can last tens of thousands of years, so long that long perturbations in the moon's path must be taken into account for prediction. Also the eclipse qualities are less inconsistent because the moon is at different significantly positions in its elliptical orbit in sequential events. Similarly for the shorter Tritos cycle (10 years and 31 days), repeats less consistently for the same reason.
Saros series
Lunar saros series 132, repeating every 18 years and 11 days, has a total of 71 lunar eclipse events including 44 umbral lunar eclipses (32 partial lunar eclipses and 12 total lunar eclipses).
| Greatest | First | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 The greatest eclipse of the series will occur on 2123 Jun 9, lasting 106 minutes.[5] |
Penumbral | Partial | Total | Central |
1492 May 12 |
1636 Aug 16 |
2015 Apr 4 |
2069 May 6 | |
| Last | ||||
| Central | Total | Partial | Penumbral | |
2177 Jul 11 |
2213 Aug 2 |
2429 Dec 11 |
2754 Jun 26 | |
There are 11 series events between 1901 and 2100, grouped into threes (called an exeligmos), each column with approximately the same viewing longitude on earth.
| 1907 Jan 29 | 1925 Feb 8 | 1943 Feb 20 | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 1961 Mar 2 | 1979 Mar 13 | 1997 Mar 24 | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 2015 Apr 4 | 2033 Apr 14 | 2051 Apr 26 | |||
 |
 |
 |
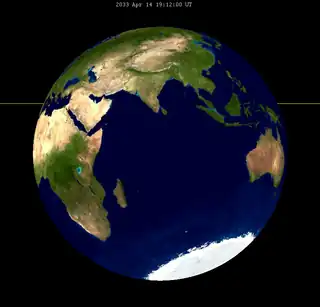 |
 |
 |
| 2069 May 6 | 2087 May 17 | ||||
 |
 |
 |
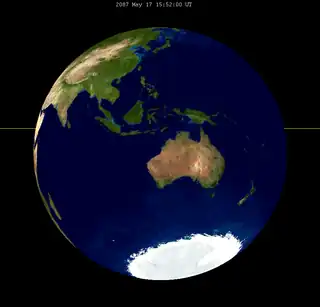 | ||
Half-Saros cycle
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[6] This lunar eclipse is related to two total solar eclipses of Solar Saros 139.
| June 3, 2114 | June 13, 2132 |
|---|---|
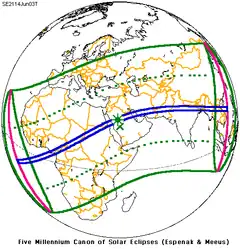 |
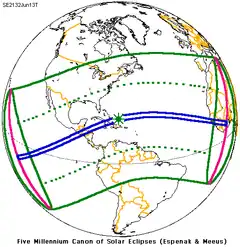 |
References
- 1 2 3 "LE2123-06-09T.gif".
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "Total Lunar Eclipse on June 8–9, 2123 – Where and When to See". www.timeanddate.com. Retrieved 2021-01-22.
- ↑ "EclipseWise - Catalog of Lunar Eclipses of Saros 166".
- ↑ "EclipseWise - Six Millennium Catalog of Lunar Eclipses".
- ↑ Listing of Eclipses of series 132
- ↑ Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros

_(cropped).jpg.webp)
