| Partial Lunar Eclipse July 16, 2019 | |
|---|---|
 Near greatest eclipse from Tilehurst, England, 21:30 UTC | |
 This chart shows the right-to-left hourly motion of the moon through the earth's shadow. | |
| Series (and member) | 139 (22 of 81) |
| Gamma | -0.643 |
| Magnitude | 0.6531 |
| Duration (hr:mn:sc) | |
| Partial | 2:57:56 |
| Penumbral | 5:33:43 |
| Contacts | |
| P1 | 18:43:53 UTC |
| U1 | 20:01:43 |
| Greatest | 21:30:44 |
| U4 | 22:59:39 |
| P4 | 0:17:36 |
A partial lunar eclipse occurred on the 16 and 17 July 2019. The Moon was covered 65.31% by the Earth's umbral shadow at maximum eclipse.
This was the last umbral lunar eclipse until May 2021.
Visibility
It was visible over most of Asia, Australia, Africa, Europe, and South America.[1]
 |
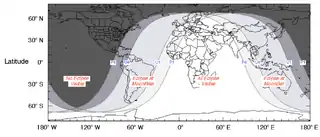 Visibility map |
Gallery
 Hefei, China, 19:56 UTC
Hefei, China, 19:56 UTC Mariupol, Ukraine, 20:25 UTC
Mariupol, Ukraine, 20:25 UTC Tashkent, Uzbekistan, 21:05 UTC
Tashkent, Uzbekistan, 21:05 UTC Moscow, Russia, 21:11 UTC
Moscow, Russia, 21:11 UTC Novate Milanese, Italy, 21:17 UTC
Novate Milanese, Italy, 21:17 UTC Bandung, Indonesia, 21:20 UTC
Bandung, Indonesia, 21:20 UTC.jpg.webp) Farasan Island, Saudi Arabia, 21:25 UTC
Farasan Island, Saudi Arabia, 21:25 UTC Paris, France, 21:27 UTC
Paris, France, 21:27 UTC Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 21:30 UTC
Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 21:30 UTC Munich, Germany, 21:36 UTC
Munich, Germany, 21:36 UTC Prague, Czech Republic, 21:39 UTC
Prague, Czech Republic, 21:39 UTC.jpg.webp) Manuel B. Gonnet, Argentina, 21:43 UTC
Manuel B. Gonnet, Argentina, 21:43 UTC.jpg.webp) London, England, 21:47 UTC
London, England, 21:47 UTC Sayada, Tunisia, 21:55 UTC
Sayada, Tunisia, 21:55 UTC Virovitica, Croatia, 22:12 UTC
Virovitica, Croatia, 22:12 UTC Banjarmasin, Indonesia, Near Moonset, 22:17 UTC
Banjarmasin, Indonesia, Near Moonset, 22:17 UTC.jpg.webp) Krško, Slovenia, 22:19 UTC
Krško, Slovenia, 22:19 UTC Szanda, Hungary, 22:23 UTC
Szanda, Hungary, 22:23 UTC Wrocław, Poland, 22:27 UTC
Wrocław, Poland, 22:27 UTC_1.jpg.webp) Logroño, Spain, 22:32 UTC
Logroño, Spain, 22:32 UTC
Related eclipses
Tzolkinex
- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of 4 June 2012
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of 28 August 2026
Tritos
- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of 16 August 2008
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of 15 June 2030
Inex
- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of 6 August 1990
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of 26 June 2048
Triad
- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of 14 September 1932
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of 17 May 2106
Eclipses of 2019
- A partial solar eclipse on 6 January.
- A total lunar eclipse on 21 January.
- A total solar eclipse on 2 July.
- A partial lunar eclipse on 16 July.
- An annular solar eclipse on 26 December.
Lunar year series
| Lunar eclipse series sets from 2016–2020 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||||
| Saros | Date | Type Viewing |
Gamma | Saros | Date Viewing |
Type Chart |
Gamma | |
| 109 | 2016 Aug 18 |
Penumbral |
1.56406 | 114 |
2017 Feb 11 |
Penumbral |
−1.02548 | |
119 |
2017 Aug 07 |
Partial |
0.86690 | 124 |
2018 Jan 31 |
Total |
−0.30143 | |
129_(43696968392)_(cropped).jpg.webp) |
2018 Jul 27 |
Total |
0.11681 | 134_(cropped).jpg.webp) |
2019 Jan 21 |
Total |
0.36842 | |
139 |
2019 Jul 16 |
Partial |
−0.64300 | 144 |
2020 Jan 10 |
Penumbral |
1.07270 | |
| 149 | 2020 Jul 05 |
Penumbral |
−1.36387 | |||||
| Last set | 2016 Sep 16 | Last set | 2016 Mar 23 | |||||
| Next set | 2020 Jun 05 | Next set | 2020 Nov 30 | |||||
Saros cycle
Lunar Saros series 139, repeating every 18 years and 11 days, has a total of 79 lunar eclipse events including 42 umbral lunar eclipses (15 partial lunar eclipses and 27 total lunar eclipses)..
| Greatest | First | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
The greatest eclipse of the series will occur on 2199 Nov 02, lasting 102 minutes.[2] |
Penumbral | Partial | Total | Central |
| 1658 Dec 09 | 1947 Jun 03 | 2073 Aug 17 | 2109 Sep 09 | |
| Last | ||||
| Central | Total | Partial | Penumbral | |
| 2488 Apr 26 | 2542 May 30 | 2686 Aug 25 | 3065 Apr 13 | |
| 1911 May 13 | 1929 May 23 | 1947 Jun 03 | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 1965 Jun 14 | 1983 Jun 25 | 2001 Jul 05 | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 2019 Jul 16 | 2037 Jul 27 | 2055 Aug 07 | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| 2073 Aug 17 | 2091 Aug 29 | ||||
Half-Saros cycle
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[3] This lunar eclipse is related to two total solar eclipses of Solar Saros 146.
| 11 July 2010 | 22 July 2028 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
See also
References
- ↑ "Lunar eclipse july 2019 timing of all countries". bindassnews.com. Archived from the original on 7 May 2019. Retrieved 7 May 2019.
- ↑ Listing of Eclipses of cycle 139
- ↑ Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros
External links
- Partial Lunar Eclipse 2019
- Saros cycle 139
- Hermit eclipse: 2019-07-16
- 2019 Jul 16 chart: Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
_(cropped).jpg.webp)