| Total eclipse | |||||||||||||||||
| Date | September 15, 1913 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma | −0.2109 | ||||||||||||||||
| Magnitude | 1.4304 | ||||||||||||||||
| Saros cycle | 126 (39 of 70) | ||||||||||||||||
| Totality | 93 minutes and 29 seconds | ||||||||||||||||
| Partiality | 230 minutes and 33 seconds | ||||||||||||||||
| Penumbral | 373 minutes and 1 second | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
A total lunar eclipse took place on Monday, September 15, 1913. The moon passed through the center of the Earth's shadow.[1]
Visibility


Related lunar eclipses
Inex series
The inex series repeats eclipses 20 days short of 29 years, repeating on average every 10571.95 days. This period is equal to 358 lunations (synodic months) and 388.5 draconic months. Saros series increment by one on successive Inex events and repeat at alternate ascending and descending lunar nodes.
This period is 383.6734 anomalistic months (the period of the Moon's elliptical orbital precession). Despite the average 0.05 time-of-day shift between subsequent events, the variation of the Moon in its elliptical orbit at each event causes the actual eclipse time to vary significantly. It is a part of Lunar Inex series 40.
All events in this series shown (from 1000 to 2500) are central total lunar eclipses.
| Descending node | Ascending node | Descending node | Ascending node | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Date | Saros | Date | Saros | Date | Saros | Date |
| 95 | 1016 May 24 | 96 | 1045 May 3 | 97 | 1074 Apr 14 | 98 | 1103 Mar 25 |
| 99 | 1132 Mar 3 | 100 | 1161 Feb 12 | 101 | 1190 Jan 23 | 102 | 1219 Jan 2 |
| 103 | 1247 Dec 13 | 104 | 1276 Nov 23 | 105 | 1305 Nov 2 | 106 | 1334 Oct 13 |
| 107 | 1363 Sep 23 | 108 | 1392 Sep 2 | 109 | 1421 Aug 13 | 110 | 1450 Jul 24 |
| 111 | 1479 Jul 4 | 112 | 1508 Jun 13 |
113 | 1537 May 24 | 114 | 1566 May 4 |
| 115 | 1595 Apr 24 | 116 | 1624 Apr 3 | 117 | 1653 Mar 14 | 118 | 1682 Feb 21 |
| 119 | 1711 Feb 3 | 120 | 1740 Jan 13 | 121 | 1768 Dec 23 | 122 | 1797 Dec 4 |
| 123 | 1826 Nov 14 | 124 | 1855 Oct 25 | 125 | 1884 Oct 4 | 126 | 1913 Sep 15 |
| 127 | 1942 Aug 26 |
128 | 1971 Aug 6 |
129 | 2000 Jul 16 |
130 | 2029 Jun 26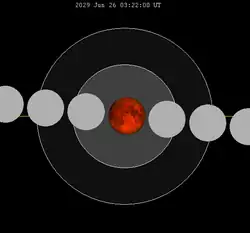 |
| 131 | 2058 Jun 6 |
132 | 2087 May 17 |
133 | 2116 Apr 27 | 134 | 2145 Apr 7 |
| 135 | 2174 Mar 18 | 136 | 2203 Feb 26 | 137 | 2232 Feb 7 | 138 | 2261 Jan 17 |
| 139 | 2289 Dec 27 | 140 | 2318 Dec 9 | 141 | 2347 Nov 19 | 142 | 2376 Oct 28 |
| 143 | 2405 Oct 8 | 144 | 2434 Sep 18 | 145 | 2463 Aug 29 | 146 | 2492 Aug 8 |
Saros series
It is part of saros series 126.
Lunar saros series 126, repeating every 18 years and 11 days, has a total of 70 lunar eclipse events including 14 total lunar eclipses. Solar Saros 133 interleaves with this lunar saros with an event occurring every 9 years 5 days alternating between each saros series.
First penumbral lunar eclipse: 18 July 1228
First partial lunar eclipse: 24 March 1625
First total lunar eclipse: 19 June 1769
First central lunar eclipse: 11 July 1805
Greatest eclipse of the lunar saros 126: 13 August 1859, lasting 106 minutes.
Last central lunar eclipse: 26 September 1931
Last total lunar eclipse: 9 November 2003
Last partial lunar eclipse: 5 June 2346
Last penumbral lunar eclipse: 19 August 2472
1901-2100
11 December 2057
22 December 2075
1 January 2094
Half-Saros cycle
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[2] This lunar eclipse is related to two total solar eclipses of Solar Saros 133.
| September 9, 1904 | September 21, 1922 |
|---|---|
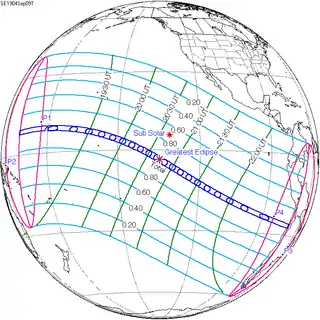 |
 |
See also
Notes
- ↑ Saros series 126
- ↑ Mathematical Astronomy Morsels, Jean Meeus, p.110, Chapter 18, The half-saros
External links
- 1913 Sep 15 chart Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC

_(cropped).jpg.webp)
