.svg.png.webp)
This outline of Australia is an overview of and topical guide to various aspects of the country of Australia.
Australia refers to both the continent of Australia and to the Commonwealth of Australia, the sovereign country.
The continent of Australia, the world's smallest continent, is in the Southern Hemisphere and borders both the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean.
The Commonwealth of Australia comprises the mainland of the Australian continent, the major island of Tasmania, other nearby islands, and various external territories.[1]
Neighbouring countries are Indonesia, East Timor, and Papua New Guinea to the north, the Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, and New Caledonia to the north-east, and New Zealand to the south-east.
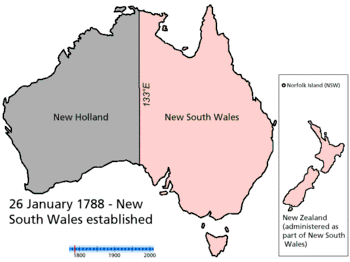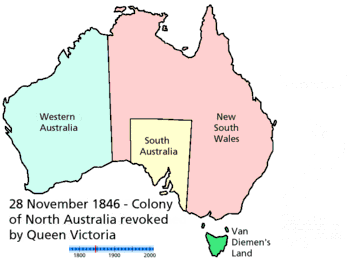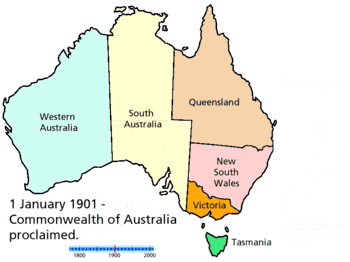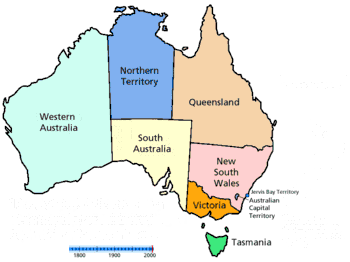
The Australian mainland has been inhabited for at least 50,000 years by Aboriginal Australians.[2] After sporadic visits by fishermen from the north and then European discovery by Dutch explorers in 1606,[3] the eastern half of Australia was later claimed by the British in 1770 and initially settled through penal transportation as part of the colony of New South Wales, commencing on 26 January 1788. As the population grew and new areas were explored, another five largely self-governing Crown colonies were established during the 19th century.
General reference
- Pronunciation: /əˈstreɪliə, ɒ-/ ⓘ
- Common English country name: Australia
- Official English country name: The Commonwealth of Australia
- Common endonym(s): Land Down Under
- Official endonym(s):
- Adjectival(s): Australian
- Demonym(s): Australian, Aussie (Colloquially)
- Etymology: Name of Australia
- International rankings of Australia
- ISO country codes: AU, AUS, 036
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:AU
- Internet country code top-level domain: .au
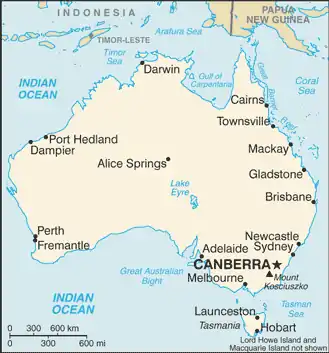
Geography
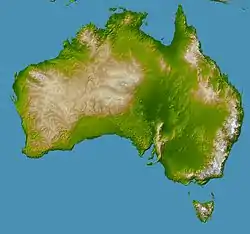
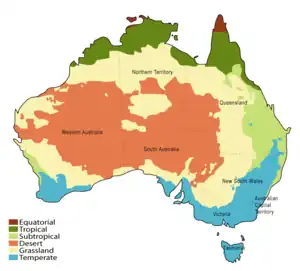
- Australia is...
- Location:
- Australia is a region or subregion of:
- Australia lies between:
- Indian Ocean
- Pacific Ocean
- Southern Ocean by some reckonings
- Time zones:
- Australian Eastern Standard Time (EST) (UTC+10), Australian Eastern Summer Time (EDT) (UTC+11)
- Australian Central Standard Time (CST) (UTC+09:30), Australian Central Summer Time (CDT) (UTC+10:30),
- Australian Western Standard Time (WST) (UTC+08)
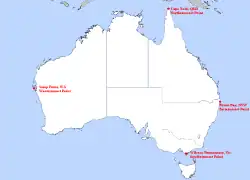
- Extreme points of Australia (mainland)
- Northernmost Point – Cape York, Queensland (10°41' S)
- Southernmost Point – South Point, Wilsons Promontory, Victoria (39°08' S)
- Westernmost Point – Steep Point, Western Australia (113°09' E)
- Easternmost Point – Cape Byron, New South Wales (153°38' E)
- Highest Point – Mount Kosciuszko 2,228 m (7,310 ft)
- Lowest Point – Lake Eyre −15 m (−49 ft)
- Land boundaries: none
- Coastline: 25,760 km
- Population of Australia: 25,694,393 people [4] (December 2020) – 53rd most populous country
- Area of Australia: 7,741,220 km2 (2,988,900 sq mi) – 6th largest country
- Atlas of Australia
- Surveying in Australia
Environment

- Climate of Australia
- Ecoregions of Australia
- Environmental issues in Australia
- Renewable energy in Australia
- Geology of Australia
- National parks of Australia
- Protected areas of Australia
- Wildlife of Australia
- Iconic wildlife of Australia
 A koala.
A koala. A kangaroo.
A kangaroo..jpg.webp) The Saltwater crocodile is the largest species of crocodile in the world.
The Saltwater crocodile is the largest species of crocodile in the world. An emu.
An emu.
Geographic features
Regions
Multi-state regions
Administrative divisions

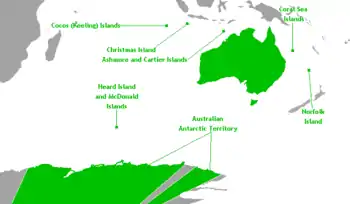
States and territories of Australia
States
Territories
Mainland territories
External territories
Municipalities
Demography
| State/territory | Land area (km2) | Rank | Population (2012)[4] | Rank | Population density (/km2) | Rank | % of population in capital | Rank |
| 800,642 | 5th | 7,348,900 | 1st | 9.18 | 3rd | 63.5% | 5th | |
| 227,416 | 6th | 5,679,600 | 2nd | 24.97 | 2nd | 74.8% | 4th | |
| 1,730,648 | 2nd | 4,610,900 | 3rd | 2.66 | 5th | 47.5% | 7th | |
| 2,529,875 | 1st | 2,472,700 | 4th | 0.98 | 7th | 76.7% | 3rd | |
| 983,482 | 4th | 1,662,200 | 5th | 1.69 | 6th | 76.8% | 2nd | |
| 68,401 | 7th | 512,400 | 6th | 7.49 | 4th | 42.3% | 8th | |
| 2,358 | 8th | 379,600 | 7th | 160.98 | 1st | 98.7% | 1st | |
| 1,349,129 | 3rd | 236,900 | 8th | 0.18 | 8th | 55.6% | 6th |
Government and politics
- Form of government: Federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy
- Capital of Australia: Canberra
- Elections in Australia
- Human rights in Australia
- Political parties in Australia
- Political scandals of Australia
- Republicanism in Australia
- Taxation in Australia
Federal government
Branches of the government
Separation of powers in Australia
Executive branch
- Head of state: King of Australia (King Charles III)
- Head of state's representative: Governor-General (David Hurley)
- Head of government: Prime Minister of Australia (Anthony Albanese)
- Cabinet
- Federal Executive Council
Legislative branch
Judicial branch
Military
Australian Defence Force (ADF)
- Command
- Commander-in-chief: Governor-General as the King's representative.
- Forces
- Army of Australia: Australian Army
- Navy of Australia: Royal Australian Navy
- Air force of Australia: Royal Australian Air Force
- Special forces of Australia
- Military history of Australia
- Australian Defence Force ranks
Foreign relations
International organisation membership
The Commonwealth of Australia is a member of the:[1]
Law and order
- Citizenship
- Cannabis in Australia
- Constitution of Australia
- Crime in Australia
- Law enforcement in Australia
- National law enforcement agencies
- Regional law enforcement agencies – the following policing agencies are regulated by their respective State or Territory Government and are highly visible:
State and territory governments
- Governors of the Australian states
- Parliaments of the Australian states and territories
- Premiers of the Australian states
- Government of New South Wales
- Government of Queensland
- Government of South Australia
- Government of Tasmania
- Government of Victoria
- Government of Western Australia
- Government of the Australian Capital Territory
- Government of the Northern Territory
Local government
History
- Prehistory of Australia
- Australian archaeology
- European exploration of Australia
- History of Australia (1788–1850)
- History of Australia (1851–1900)
- History of Australia (1901–1945)
- History of Australia since 1945
- Constitutional history of Australia
- Immigration history of Australia
- Postage stamps and postal history of Australia
History of states
Culture
- Architecture of Australia
- Australian art
- Cinema of Australia
- Australian cuisine
- Dance in Australia
- Festivals in Australia
- Australian folklore
- Humour in Australia
- Languages of Australia
- Australian literature
- Media of Australia
- Music of Australia
- National symbols of Australia
- Coat of arms of Australia
- Flag of Australia
- National anthems:
- Official national anthem: Advance Australia Fair
- Royal anthem: God Save the King
- People of Australia
- Prostitution in Australia
- Public holidays in Australia
- World Heritage Sites in Australia
- Theatre of Australia
Economy and infrastructure
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 14th (fourteenth)
- Agriculture in Australia
- Telecommunications in Australia
- Reserve Bank of Australia
- Currency of Australia: Dollar
- Economic history of Australia
- Energy in Australia
- Health care in Australia
- Median household income in Australia and New Zealand
- Mining in Australia
- Australian Securities Exchange
- Tourism in Australia
- Transport in Australia
- Water supply and sanitation in Australia
State economies
Education
- Homeschooling and distance education in Australia
- Public and private education in Australia
- Universities in Australia
States education
Religion and belief systems in Australia
Sport
- Australia at the Olympics
- Australia at the Commonwealth Games
- Football in Australia
- Cricket in Australia
- Golf in Australia
- Field hockey in Australia
- Motorsport in Australia
- Tennis in Australia
- Basketball in Australia
- Netball in Australia
- Swimming in Australia
- Skiing in Australia
- Australian horse racing
- Winter sport in Australia
See also
- All pages with titles beginning with Australia
- All pages with titles beginning with Australian
- All pages with titles containing Australia
- All pages with titles containing Australian
- Index of Australia-related articles
- List of Australia-related topics
- List of articles about Australia and New Zealand jointly
- Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations
- Members states of the Group of Twenty
- Member states of the United Nations
- Outline of geography
- Outline of Oceania
- List of place names of Dutch origin
References
- 1 2 "Australia". The World Factbook. United States Central Intelligence Agency. 2 July 2009. Retrieved 23 July 2009.
- ↑ Both Australian Aborigines and Europeans Rooted in Africa – 50,000 years ago
- ↑ MacKnight, CC (1976).The Voyage to Marege: Macassan Trepangers in Northern Australia. Melbourne University Press
- 1 2 "Australian Demographic Statistics December 2020". Retrieved 3 May 2021.

