 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | LAE; Lysergic acid ethylamide; d-Lysergic acid ethylamide; d-Ethyllysergamide, |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
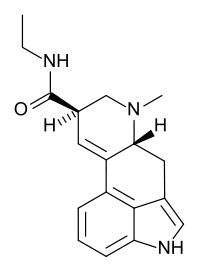
| Formula | C18H21N3O |
| Molar mass | 295.386 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
D-Lysergic acid ethylamide (LAE-32) is a derivative of ergine.[1][2] It is reported to have some LSD-like effects but is weaker and shorter lasting, with an active dose reported to be between 0.5 and 1.5 milligrams.
It was studied by the CIA as part of Project MKULTRA. Documents published by the CIA under the Freedom of Information Act suggest it causes "a schizophrenia-like condition" but it allows people with schizophrenia to remain indifferent to their disorder.
References
- ↑ "N-Ethyllysergamide". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 2022-11-16.
- ↑ Baquiran M, Al Khalili Y (2022). "Lysergic Acid Diethylamide Toxicity". StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMID 31985997. Retrieved 2022-11-18.
| Lysergic acid derivatives |
|
|---|---|
| Psychedelic lysergamides |
|
| Clavines | |
| Other ergolines | |
| Natural sources |
Morning glory: Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian Baby Woodrose), Ipomoea spp.(Morning Glory, Tlitliltzin, Badoh Negro), Rivea corymbosa (Coaxihuitl, Ololiúqui) |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.