 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
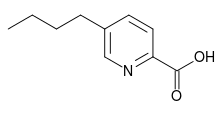
| Preferred IUPAC name
5-Butylpyridine-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
5-Butylpicolinic acid Fusarinic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.859 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | D005669 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H13NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 179.219 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 97 to 98 °C (207 to 208 °F; 370 to 371 K) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds |
picolinic acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Fusaric acid is a picolinic acid derivative and an antibiotic (wilting agent) first isolated from the fungus Fusarium heterosporium.[1]
It is typically isolated from various Fusarium species, and has been proposed for a various therapeutic applications. However, it is primarily used as a research tool.
Its mechanism of action is not well understood. It likely inhibits Dopamine beta-hydroxylase (the enzyme that converts dopamine to norepinephrine). It may also have other actions, such as the inhibition of cell proliferation and DNA synthesis. Fusaric acid and analogues also reported as quorum sensing inhibitors.[2]
It is used to make bupicomide.
References
- ↑ Yabuta et al., J. Agric. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 10, 1059 (1934).
- ↑ Tung et al., Eur. J. Med. Chem. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.11.044.
External links
 Media related to Fusaric acid at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Fusaric acid at Wikimedia Commons
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.