 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
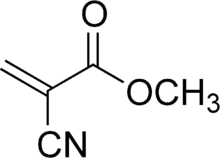
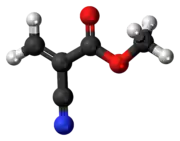
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methyl 2-cyanoprop-2-enoate | |
| Other names
Methyl 2-cyanopropenoate Methyl 2-cyanoacrylate 2-Cyano-2-propenoic acid methyl ester MCA Methyl alpha-cyanoacrylate Mecrylate Ad/here Adhere CA 7 Cemedine 3000 Coapt Cyanobond 5000 Eastman 910 Fimofix P 1048 Mecrilat Mecrilate Sicomet 7000 Three Bond 1701[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.796 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H5NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 111.1 g/mol |
| Density | 1.1 |
| Melting point | −40 °C (−40 °F; 233 K) |
| Boiling point | 48 to 49 °C (118 to 120 °F; 321 to 322 K) (2.5–2.7 mmHg) |
| 30% (20 °C)[2] | |
| Vapor pressure | 0.2 mmHg (25 °C)[2] |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 79 °C; 174 °F; 352 K[2] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) |
None[2] |
REL (Recommended) |
TWA 2 ppm (8 mg/m3) ST 4 ppm (16 mg/m3)[2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) |
N.D.[2] |
| Related compounds | |
Related Cyanoacrylates |
Ethyl cyanoacrylate Butyl cyanoacrylate Octyl cyanoacrylate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Methyl cyanoacrylate (MCA) (also sometimes referred to as α-cyanoacrylate or alpha-cyanoacrylate)[3] is an organic compound that contains several functional groups: a methyl ester, a nitrile, and an alkene. It is a colorless liquid with low viscosity. Its chief use is as the main component of cyanoacrylate glues.[4][5] It can be encountered under many trade names. Methyl cyanoacrylate is less commonly encountered than ethyl cyanoacrylate.
It is soluble in acetone, methyl ethyl ketone, nitromethane, and dichloromethane.[6] MCA polymerizes rapidly in presence of moisture.
Safety
Heating the polymer causes depolymerization of the cured MCA, producing gaseous products which are a strong irritant to the lungs and eyes. With regard to occupational exposure to MCA, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health recommends workers do not exceed exposures over 2 ppm (8 mg/m3) over an eight-hour workshift, or over 4ppm (16 mg/m3) over a short-term exposure.[7]
References
- ↑ Methyl 2-cyanoacrylate at Cameo Chemicals
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0405". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ "Cyanoacrylate Derivative - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics". www.sciencedirect.com. Retrieved 2021-11-09.
- ↑ Ohara, Takashi; Sato, Takahisa; Shimizu, Noboru; Prescher, Günter; Schwind, Helmut; Weiberg, Otto; Marten, Klaus; Greim, Helmut; Shaffer (2020). "Acrylic Acid and Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. pp. 1–21. doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_161.pub4. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ↑ Methyl 2-cyanoacrylate at Inchem.org
- ↑ Palm Labs Adhesives Archived 2008-12-08 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ CDC - NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards