 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Melting point | 13.7[1] °C (56.7 °F; 286.8 K) |
| Boiling point | 67–68[1] °C (153–154 °F; 340–341 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
1.1 mg/kg (subcutaneous, mice)(hydrochloride salt)[2] 1 mg/kg (subcutaneous, rats)(hydrochloride salt)[2] 0.5 mg/kg (intravenous, rat)(hydrochloride salt)[2] 22 mg/kg (oral, mice)(hydrochloride salt)[2] 0.5 mg/kg (subcutaneous, mice)(hydrochloride salt)[3] 2 mg/kg (subcutaneous, rats)(hydrochloride salt)[3] |
LDLo (lowest published) |
25 mg/kg (oral, rats)(hydrochloride salt)[4] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
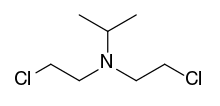
TL-301 is a nitrogen mustard vesicant.[1][2][3]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 "Chemical Warfare Agents, and Related Chemical Problems. Parts I-II". 1958.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Chemical Warfare Agents, and Related Chemical Problems, Parts III-VI-Summary Technical Report".
- 1 2 3 Boyland, E (December 1946). "The toxicity of alkyl-bis(beta-chloroethyl)amines and of the products of their reaction with water". British Journal of Pharmacology and Chemotherapy. 1 (4): 247–54. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.1946.tb00044.x. PMC 1509752. PMID 19108094.
- ↑ Witt, James B. De (1953). Relationship Between Chemical Structure and Toxic Action on Rats. Chemical-Biological Coordination Center, National Research Council.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.