 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral, Insufflated, Rectal |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
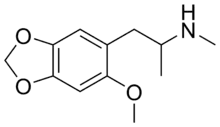
| Formula | C12H17NO3 |
| Molar mass | 223.272 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
N-Methyl-2-methoxy-4,5-methylenedioxyamphetamine (methyl-MMDA-2; 6-methoxy-MDMA) is a psychedelic drug of the amphetamine class.[1] It is the N-methylated derivative of MMDA-2, and it is also an analog of MDMA and 6-methyl-MDA.[1]
Methyl-MMDA-2 was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and was described in his book PiHKAL. He states that it is essentially inactive at a dose of 70 mg, and he did not try any higher;[1] however, Methyl-MMDA-2 is still likely to be active, perhaps in the 125-250 mg range. This reduction in hallucinogenic activity relative to MMDA-2 parallels that of MDA and MDMA, indicating that with phenethylamines, N-methylation substantially reduces 5-HT2A receptor affinity.[1][2]
See also
References
External links
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.