 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Benfuran, Bentos, Betaclar, Glauconex |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
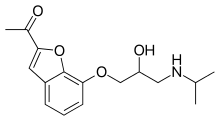
| Formula | C16H21NO4 |
| Molar mass | 291.347 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Befunolol (INN) is a beta blocker with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity used in the management of open-angle glaucoma.[1] It also acts as a β adrenoreceptor partial agonist.[2][3] Befunolol was introduced in Japan in 1983 by Kakenyaku Kako Co. under the trade name Bentos.[4]
References
- ↑ Reichl S, Müller-Goymann CC (January 2003). "The use of a porcine organotypic cornea construct for permeation studies from formulations containing befunolol hydrochloride". International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 250 (1): 191–201. doi:10.1016/S0378-5173(02)00541-0. PMID 12480285.
- ↑ Koike K, Takayanagi I (October 1986). "A beta-adrenergic partial agonist (befunolol) discriminates two different affinity sites". Japanese Journal of Pharmacology. 42 (2): 325–8. doi:10.1254/jjp.42.325. PMID 2879061.
- ↑ Takayanagi I, Koike K (January 1985). "A beta-adrenoceptor blocking agent, befunolol as a partial agonist in isolated organs". General Pharmacology. 16 (3): 265–7. doi:10.1016/0306-3623(85)90080-1. PMID 2862092.
- ↑ Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia (3rd revised ed.). Norwich, N.Y.: William Andrew Publishing. January 14, 2008. p. 542. ISBN 978-0815515265.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.