| Pha | |
|---|---|
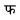 | |
| Example glyphs | |
| Bengali-Assamese | |
| Tibetan | |
| Thai | ผ |
| Malayalam | ഫ |
| Sinhala | ඵ |
| Ashoka Brahmi | |
| Devanagari | |
| Cognates | |
| Hebrew | פ ,ף |
| Greek | Π |
| Latin | P |
| Cyrillic | П |
| Properties | |
| Phonemic representation | /pʰ/ |
| IAST transliteration | ph Ph |
| ISCII code point | C9 (201) |
| Indic letters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consonants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vowels | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other marks | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Punctuation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pha is a consonant of Indic abugidas. In modern Indic scripts, Pha is derived from the early "Ashoka" Brahmi letter ![]() after having gone through the Gupta letter
after having gone through the Gupta letter ![]() .
.
Āryabhaṭa numeration
Aryabhata used Devanagari letters for numbers, very similar to the Greek numerals, even after the invention of Indian numerals. The values of the different forms of फ are:[1]
- फ [pʰə] = 22 (२२)
- फि [pʰɪ] = 2,200 (२ २००)
- फु [pʰʊ] = 220,000 (२ २० ०००)
- फृ [pʰri] = 22,000,000 (२ २० ०० ०००)
- फॢ [pʰlə] = 22×108 (२२×१०८)
- फे [pʰe] = 22×1010 (२२×१०१०)
- फै [pʰɛː] = 22×1012 (२२×१०१२)
- फो [pʰoː] = 22×1014 (२२×१०१४)
- फौ [pʰɔː] = 22×1016 (२२×१०१६)
Historic Pha
There are three different general early historic scripts - Brahmi and its variants, Kharoṣṭhī, and Tocharian, the so-called slanting Brahmi. Pha as found in standard Brahmi, ![]() was a simple geometric shape, with variations toward more flowing forms by the Gupta
was a simple geometric shape, with variations toward more flowing forms by the Gupta ![]() . The Tocharian Pha
. The Tocharian Pha ![]() did not have an alternate Fremdzeichen form. The third form of pha, in Kharoshthi (
did not have an alternate Fremdzeichen form. The third form of pha, in Kharoshthi (![]() ) was probably derived from Aramaic separately from the Brahmi letter.
) was probably derived from Aramaic separately from the Brahmi letter.
Brahmi Pha
The Brahmi letter ![]() , Pha, is probably derived from the altered Aramaic Pe
, Pha, is probably derived from the altered Aramaic Pe ![]() , and is thus related to the modern Latin P and Greek Pi.[2] Several identifiable styles of writing the Brahmi Pha can be found, most associated with a specific set of inscriptions from an artifact or diverse records from an historic period.[3] As the earliest and most geometric style of Brahmi, the letters found on the Edicts of Ashoka and other records from around that time are normally the reference form for Brahmi letters, with vowel marks not attested until later forms of Brahmi back-formed to match the geometric writing style.
, and is thus related to the modern Latin P and Greek Pi.[2] Several identifiable styles of writing the Brahmi Pha can be found, most associated with a specific set of inscriptions from an artifact or diverse records from an historic period.[3] As the earliest and most geometric style of Brahmi, the letters found on the Edicts of Ashoka and other records from around that time are normally the reference form for Brahmi letters, with vowel marks not attested until later forms of Brahmi back-formed to match the geometric writing style.
| Ashoka (3rd-1st c. BCE) | Girnar (~150 BCE) | Kushana (~150-250 CE) | Gujarat (~250 CE) | Gupta (~350 CE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No sample | No sample |
Tocharian Pha
The Tocharian letter ![]() is derived from the Brahmi
is derived from the Brahmi ![]() , but does not have an alternate Fremdzeichen form.
, but does not have an alternate Fremdzeichen form.
| Pha | Phā | Phi | Phī | Phu | Phū | Phr | Phr̄ | Phe | Phai | Pho | Phau | Phä |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Kharoṣṭhī Pha
The Kharoṣṭhī letter ![]() is generally accepted as being derived from the altered Aramaic Pe
is generally accepted as being derived from the altered Aramaic Pe ![]() , and is thus related to P and Pi, in addition to the Brahmi Pha.[2]
, and is thus related to P and Pi, in addition to the Brahmi Pha.[2]
Devanagari Pha
| Devanāgarī |
|---|
 |
Pha (फ) is a consonant of the Devanagari abugida. It ultimately arose from the Brahmi letter ![]() , after having gone through the Gupta letter
, after having gone through the Gupta letter ![]() . Letters that derive from it are the Gujarati letter ફ, and the Modi letter 𑘣.
. Letters that derive from it are the Gujarati letter ફ, and the Modi letter 𑘣.
Devanagari-using Languages
In all languages, फ is pronounced as [pʰə] or [pʰ] when appropriate. Like all Indic scripts, Devanagari uses vowel marks attached to the base consonant to override the inherent /ə/ vowel:
| Pha | Phā | Phi | Phī | Phu | Phū | Phr | Phr̄ | Phl | Phl̄ | Phe | Phai | Pho | Phau | Ph |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| फ | फा | फि | फी | फु | फू | फृ | फॄ | फॢ | फॣ | फे | फै | फो | फौ | फ् |
Conjuncts with फ

Devanagari exhibits conjunct ligatures, as is common in Indic scripts. In modern Devanagari texts, most conjuncts are formed by reducing the letter shape to fit tightly to the following letter, sometimes referred to as a "half form". Most Devanagari letters drop a character's vertical stem to create a half form, but due to its large tail to the right of the stem, the common half form of फ has its tail reduced to attach to the following letter. Some conjunct clusters are always represented by a true ligature, instead of a shape that can be broken into constituent independent letters. Vertically stacked conjuncts are ubiquitous in older texts, while only a few are still used routinely in modern Devanagari texts. The use of ligatures and vertical conjuncts may vary across languages using the Devanagari script, with Marathi in particular preferring the use of half forms where texts in other languages would show ligatures and vertical stacks.[4]
Ligature conjuncts of फ
True ligatures are quite rare in Indic scripts. The most common ligated conjuncts in Devanagari are in the form of a slight mutation to fit in context or as a consistent variant form appended to the adjacent characters. Those variants include Na and the Repha and Rakar forms of Ra. Nepali and Marathi texts use the "eyelash" Ra half form ![]() for an initial "R" instead of repha.
for an initial "R" instead of repha.
- Repha र্ (r) + फ (pʰa) gives the ligature rpʰa: note

- Eyelash र্ (r) + फ (pʰa) gives the ligature rpʰa:

- फ্ (pʰ) + न (na) gives the ligature pʰna:

- फ্ (pʰ) + rakar र (ra) gives the ligature pʰra:

Stacked conjuncts of फ
Vertically stacked ligatures are the most common conjunct forms found in Devanagari text. Although the constituent characters may need to be stretched and moved slightly in order to stack neatly, stacked conjuncts can be broken down into recognizable base letters, or a letter and an otherwise standard ligature.
- छ্ (cʰ) + फ (pʰa) gives the ligature cʰpʰa:

- ढ্ (ḍʱ) + फ (pʰa) gives the ligature ḍʱpʰa:

- ड্ (ḍ) + फ (pʰa) gives the ligature ḍpʰa:

- द্ (d) + फ (pʰa) gives the ligature dpʰa:

- ङ্ (ŋ) + फ (pʰa) gives the ligature ŋpʰa:

- फ্ (pʰ) + ब (ba) gives the ligature pʰba:

- फ্ (pʰ) + च (ca) gives the ligature pʰca:

- फ্ (pʰ) + ड (ḍa) gives the ligature pʰḍa:

- फ্ (pʰ) + ज (ja) gives the ligature pʰja:

- फ্ (pʰ) + ज্ (j) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature pʰjña:

- फ্ (pʰ) + क (ka) gives the ligature pʰka:

- फ্ (pʰ) + ल (la) gives the ligature pʰla:

- फ্ (pʰ) + ङ (ŋa) gives the ligature pʰŋa:

- फ্ (pʰ) + ञ (ña) gives the ligature pʰña:

- फ্ (pʰ) + व (va) gives the ligature pʰva:

- ठ্ (ṭʰ) + फ (pʰa) gives the ligature ṭʰpʰa:

- ट্ (ṭ) + फ (pʰa) gives the ligature ṭpʰa:

Bengali Pha
The Bengali script ফ is derived from the Siddhaṃ ![]() , and is marked by a similar horizontal head line, but less geometric shape, than its Devanagari counterpart, फ. The inherent vowel of Bengali consonant letters is /ɔ/, so the bare letter ফ will sometimes be transliterated as "pho" instead of "pha". Adding okar, the "o" vowel mark, gives a reading of /pʰo/.
Like all Indic consonants, ফ can be modified by marks to indicate another (or no) vowel than its inherent "a".
, and is marked by a similar horizontal head line, but less geometric shape, than its Devanagari counterpart, फ. The inherent vowel of Bengali consonant letters is /ɔ/, so the bare letter ফ will sometimes be transliterated as "pho" instead of "pha". Adding okar, the "o" vowel mark, gives a reading of /pʰo/.
Like all Indic consonants, ফ can be modified by marks to indicate another (or no) vowel than its inherent "a".
| pha | phā | phi | phī | phu | phū | phr | phr̄ | phe | phai | pho | phau | ph |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ফ | ফা | ফি | ফী | ফু | ফূ | ফৃ | ফৄ | ফে | ফৈ | ফো | ফৌ | ফ্ |
ফ in Bengali-using languages
ফ is used as a basic consonant character in all of the major Bengali script orthographies, including Bengali and Assamese.
Conjuncts with ফ
Bengali ফ exhibits conjunct ligatures, as is common in Indic scripts, with a tendency towards stacked ligatures.[5]
- ল্ (l) + ফ (pʰa) gives the ligature lpʰa:

- ম্ (m) + ফ (pʰa) gives the ligature mpʰa:

- ফ্ (pʰ) + ল (la) gives the ligature pʰla:

- ফ্ (pʰ) + র (ra) gives the ligature pʰra, with the ra phala suffix:

- র্ (r) + ফ (pʰa) gives the ligature rpʰa, with the repha prefix:

- স্ (s) + ফ (pʰa) gives the ligature spʰa:

- ষ্ (ṣ) + ফ (pʰa) gives the ligature ṣpʰa:

Gujarati Pha

Pha (ફ) is the twenty-second consonant of the Gujarati abugida. It is derived from the Devanagari Pha ![]() with the top bar (shiro rekha) removed, and ultimately the Brahmi letter
with the top bar (shiro rekha) removed, and ultimately the Brahmi letter ![]() . ફ (Pha) is similar in appearance to ક (Ka), and care should be taken to avoid confusing the two when reading Gujarati script texts.
. ફ (Pha) is similar in appearance to ક (Ka), and care should be taken to avoid confusing the two when reading Gujarati script texts.
Gujarati-using Languages
The Gujarati script is used to write the Gujarati and Kutchi languages. In both languages, ફ is pronounced as [pʰə] or [pʰ] when appropriate. Like all Indic scripts, Gujarati uses vowel marks attached to the base consonant to override the inherent /ə/ vowel:
| Pha | Phā | Phi | Phī | Phu | Phū | Phr | Phl | Phr̄ | Phl̄ | Phĕ | Phe | Phai | Phŏ | Pho | Phau | Ph |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
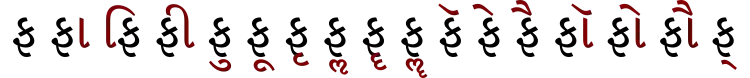 | ||||||||||||||||
| Gujarati Pha syllables, with vowel marks in red. | ||||||||||||||||
Conjuncts with ફ
Gujarati ફ exhibits conjunct ligatures, much like its parent Devanagari Script. While most Gujarati conjuncts can only be formed by reducing the letter shape to create a "half form" that fits tightly to following letter, Pha does not have a half form. A few conjunct clusters can be represented by a true ligature, instead of a shape that can be broken into constituent independent letters, and vertically stacked conjuncts can also be found in Gujarati, although much less commonly than in Devanagari. Lacking a half form, Pha will normally use an explicit virama when forming conjuncts without a true ligature. True ligatures are quite rare in Indic scripts. The most common ligated conjuncts in Gujarati are in the form of a slight mutation to fit in context or as a consistent variant form appended to the adjacent characters. Those variants include Na and the Repha and Rakar forms of Ra.
- ર્ (r) + ફ (pʰa) gives the ligature RPha:

- ફ્ (pʰ) + ર (ra) gives the ligature PhRa:

Javanese Pha
Telugu Pha


Pha (ఫ) is a consonant of the Telugu abugida. It ultimately arose from the Brahmi letter ![]() . It is closely related to the Kannada letter ಫ. Most Telugu consonants contain a v-shaped headstroke that is related to the horizontal headline found in other Indic scripts, although headstrokes do not connect adjacent letters in Telugu. The headstroke is normally lost when adding vowel matras.
Telugu conjuncts are created by reducing trailing letters to a subjoined form that appears below the initial consonant of the conjunct. Many subjoined forms are created by dropping their headline, with many extending the end of the stroke of the main letter body to form an extended tail reaching up to the right of the preceding consonant. This subjoining of trailing letters to create conjuncts is in contrast to the leading half forms of Devanagari and Bengali letters. Ligature conjuncts are not a feature in Telugu, with the only non-standard construction being an alternate subjoined form of Ṣa (borrowed from Kannada) in the KṢa conjunct.
. It is closely related to the Kannada letter ಫ. Most Telugu consonants contain a v-shaped headstroke that is related to the horizontal headline found in other Indic scripts, although headstrokes do not connect adjacent letters in Telugu. The headstroke is normally lost when adding vowel matras.
Telugu conjuncts are created by reducing trailing letters to a subjoined form that appears below the initial consonant of the conjunct. Many subjoined forms are created by dropping their headline, with many extending the end of the stroke of the main letter body to form an extended tail reaching up to the right of the preceding consonant. This subjoining of trailing letters to create conjuncts is in contrast to the leading half forms of Devanagari and Bengali letters. Ligature conjuncts are not a feature in Telugu, with the only non-standard construction being an alternate subjoined form of Ṣa (borrowed from Kannada) in the KṢa conjunct.
Malayalam Pha

Pha (ഫ) is a consonant of the Malayalam abugida. It ultimately arose from the Brahmi letter ![]() , via the Grantha letter
, via the Grantha letter ![]() Pha. Like in other Indic scripts, Malayalam consonants have the inherent vowel "a", and take one of several modifying vowel signs to represent syllables with another vowel or no vowel at all.
Pha. Like in other Indic scripts, Malayalam consonants have the inherent vowel "a", and take one of several modifying vowel signs to represent syllables with another vowel or no vowel at all.
Conjuncts of ഫ
As is common in Indic scripts, Malayalam joins letters together to form conjunct consonant clusters. There are several ways in which conjuncts are formed in Malayalam texts: using a post-base form of a trailing consonant placed under the initial consonant of a conjunct, a combined ligature of two or more consonants joined together, a conjoining form that appears as a combining mark on the rest of the conjunct, the use of an explicit candrakkala mark to suppress the inherent "a" vowel, or a special consonant form called a "chillu" letter, representing a bare consonant without the inherent "a" vowel. Texts written with the modern reformed Malayalam orthography, put̪iya lipi, may favor more regular conjunct forms than older texts in paḻaya lipi, due to changes undertaken in the 1970s by the Government of Kerala.
- പ് (p) + ഫ (pʰa) gives the ligature ppʰa:
Odia Pha

Pha (ଫ) is a consonant of the Odia abugida. It ultimately arose from the Brahmi letter ![]() , via the Siddhaṃ letter
, via the Siddhaṃ letter ![]() Pha. Like in other Indic scripts, Odia consonants have the inherent vowel "a", and take one of several modifying vowel signs to represent syllables with another vowel or no vowel at all.
Pha. Like in other Indic scripts, Odia consonants have the inherent vowel "a", and take one of several modifying vowel signs to represent syllables with another vowel or no vowel at all.
| Pha | Phā | Phi | Phī | Phu | Phū | Phr̥ | Phr̥̄ | Phl̥ | Phl̥̄ | Phe | Phai | Pho | Phau | Ph |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ଫ | ଫା | ଫି | ଫୀ | ଫୁ | ଫୂ | ଫୃ | ଫୄ | ଫୢ | ଫୣ | ଫେ | ଫୈ | ଫୋ | ଫୌ | ଫ୍ |
Conjuncts of ଫ
As is common in Indic scripts, Odia joins letters together to form conjunct consonant clusters. The most common conjunct formation is achieved by using a small subjoined form of trailing consonants. Most consonants' subjoined forms are identical to the full form, just reduced in size, although a few drop the curved headline or have a subjoined form not directly related to the full form of the consonant. The second type of conjunct formation is through pure ligatures, where the constituent consonants are written together in a single graphic form. This ligature may be recognizable as being a combination of two characters or it can have a conjunct ligature unrelated to its constituent characters.
- ମ୍ (m) + ଫ (pʰa) gives the ligature mpʰa:

Kaithi Pha

Pha (𑂤) is a consonant of the Kaithi abugida. It ultimately arose from the Brahmi letter ![]() , via the Siddhaṃ letter
, via the Siddhaṃ letter ![]() Pha. Like in other Indic scripts, Kaithi consonants have the inherent vowel "a", and take one of several modifying vowel signs to represent syllables with another vowel or no vowel at all.
Pha. Like in other Indic scripts, Kaithi consonants have the inherent vowel "a", and take one of several modifying vowel signs to represent syllables with another vowel or no vowel at all.
| Pha | Phā | Phi | Phī | Phu | Phū | Phe | Phai | Pho | Phau | Ph |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 𑂤 | 𑂤𑂰 | 𑂤𑂱 | 𑂤𑂲 | 𑂤𑂳 | 𑂤𑂴 | 𑂤𑂵 | 𑂤𑂶 | 𑂤𑂷 | 𑂤𑂸 | 𑂤𑂹 |
Conjuncts of 𑂤
As is common in Indic scripts, Kaithi joins letters together to form conjunct consonant clusters. The most common conjunct formation is achieved by using a half form of preceding consonants, although several consonants use an explicit virama. Most half forms are derived from the full form by removing the vertical stem. As is common in most Indic scripts, conjucts of ra are indicated with a repha or rakar mark attached to the rest of the consonant cluster. In addition, there are a few vertical conjuncts that can be found in Kaithi writing, but true ligatures are not used in the modern Kaithi script.
- 𑂩୍ (r) + 𑂤 (pʰa) gives the ligature rpʰa:

Comparison of Pha
The various Indic scripts are generally related to each other through adaptation and borrowing, and as such the glyphs for cognate letters, including Pha, are related as well.
| Comparison of Pha in different scripts |
|---|
|
Notes
|
Character encodings of Pha
Most Indic scripts are encoded in the Unicode Standard, and as such the letter Pha in those scripts can be represented in plain text with unique codepoint. Pha from several modern-use scripts can also be found in legacy encodings, such as ISCII.
| Preview | ఫ | ଫ | ಫ | ഫ | ફ | ਫ | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | DEVANAGARI LETTER PHA | BENGALI LETTER PHA | TELUGU LETTER PHA | ORIYA LETTER PHA | KANNADA LETTER PHA | MALAYALAM LETTER PHA | GUJARATI LETTER PHA | GURMUKHI LETTER PHA | ||||||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 2347 | U+092B | 2475 | U+09AB | 3115 | U+0C2B | 2859 | U+0B2B | 3243 | U+0CAB | 3371 | U+0D2B | 2731 | U+0AAB | 2603 | U+0A2B |
| UTF-8 | 224 164 171 | E0 A4 AB | 224 166 171 | E0 A6 AB | 224 176 171 | E0 B0 AB | 224 172 171 | E0 AC AB | 224 178 171 | E0 B2 AB | 224 180 171 | E0 B4 AB | 224 170 171 | E0 AA AB | 224 168 171 | E0 A8 AB |
| Numeric character reference | फ | फ | ফ | ফ | ఫ | ఫ | ଫ | ଫ | ಫ | ಫ | ഫ | ഫ | ફ | ફ | ਫ | ਫ |
| ISCII | 201 | C9 | 201 | C9 | 201 | C9 | 201 | C9 | 201 | C9 | 201 | C9 | 201 | C9 | 201 | C9 |
| Preview | Ashoka Kushana Gupta | 𐨥 | 𑌫 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | BRAHMI LETTER PHA | KHAROSHTHI LETTER PHA | SIDDHAM LETTER PHA | GRANTHA LETTER PHA | ||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 69672 | U+11028 | 68133 | U+10A25 | 71075 | U+115A3 | 70443 | U+1132B |
| UTF-8 | 240 145 128 168 | F0 91 80 A8 | 240 144 168 165 | F0 90 A8 A5 | 240 145 150 163 | F0 91 96 A3 | 240 145 140 171 | F0 91 8C AB |
| UTF-16 | 55300 56360 | D804 DC28 | 55298 56869 | D802 DE25 | 55301 56739 | D805 DDA3 | 55300 57131 | D804 DF2B |
| Numeric character reference | 𑀨 | 𑀨 | 𐨥 | 𐨥 | 𑖣 | 𑖣 | 𑌫 | 𑌫 |
| Preview | ྥ | ꡍ | 𑨟 | 𑐦 | 𑰣 | 𑆦 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | TIBETAN LETTER PHA | TIBETAN SUBJOINED LETTER PHA | PHAGS-PA LETTER PHA | ZANABAZAR SQUARE LETTER PHA | NEWA LETTER PHA | BHAIKSUKI LETTER PHA | SHARADA LETTER PHA | |||||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 3925 | U+0F55 | 4005 | U+0FA5 | 43085 | U+A84D | 72223 | U+11A1F | 70694 | U+11426 | 72739 | U+11C23 | 70054 | U+111A6 |
| UTF-8 | 224 189 149 | E0 BD 95 | 224 190 165 | E0 BE A5 | 234 161 141 | EA A1 8D | 240 145 168 159 | F0 91 A8 9F | 240 145 144 166 | F0 91 90 A6 | 240 145 176 163 | F0 91 B0 A3 | 240 145 134 166 | F0 91 86 A6 |
| UTF-16 | 3925 | 0F55 | 4005 | 0FA5 | 43085 | A84D | 55302 56863 | D806 DE1F | 55301 56358 | D805 DC26 | 55303 56355 | D807 DC23 | 55300 56742 | D804 DDA6 |
| Numeric character reference | ཕ | ཕ | ྥ | ྥ | ꡍ | ꡍ | 𑨟 | 𑨟 | 𑐦 | 𑐦 | 𑰣 | 𑰣 | 𑆦 | 𑆦 |
| Preview | ဖ | ᨹ | ᨺ | ᦕ | ᦚ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | MYANMAR LETTER PHA | TAI THAM LETTER HIGH PHA | TAI THAM LETTER HIGH FA | NEW TAI LUE LETTER HIGH PHA | NEW TAI LUE LETTER HIGH FA | |||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 4118 | U+1016 | 6713 | U+1A39 | 6714 | U+1A3A | 6549 | U+1995 | 6554 | U+199A |
| UTF-8 | 225 128 150 | E1 80 96 | 225 168 185 | E1 A8 B9 | 225 168 186 | E1 A8 BA | 225 166 149 | E1 A6 95 | 225 166 154 | E1 A6 9A |
| Numeric character reference | ဖ | ဖ | ᨹ | ᨹ | ᨺ | ᨺ | ᦕ | ᦕ | ᦚ | ᦚ |
| Preview | ផ | ຜ | ຝ | ผ | ฝ | ꪞ | ꪟ | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | KHMER LETTER PHA | LAO LETTER PHO SUNG | LAO LETTER FO TAM | THAI CHARACTER PHO PHUNG | THAI CHARACTER FO FA | TAI VIET LETTER LOW PHO | TAI VIET LETTER HIGH PHO | |||||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 6037 | U+1795 | 3740 | U+0E9C | 3741 | U+0E9D | 3612 | U+0E1C | 3613 | U+0E1D | 43678 | U+AA9E | 43679 | U+AA9F |
| UTF-8 | 225 158 149 | E1 9E 95 | 224 186 156 | E0 BA 9C | 224 186 157 | E0 BA 9D | 224 184 156 | E0 B8 9C | 224 184 157 | E0 B8 9D | 234 170 158 | EA AA 9E | 234 170 159 | EA AA 9F |
| Numeric character reference | ផ | ផ | ຜ | ຜ | ຝ | ຝ | ผ | ผ | ฝ | ฝ | ꪞ | ꪞ | ꪟ | ꪟ |
| Preview | ඵ | ꤖ | 𑄜 | ᥚ | 𑜇 | 𑤡 | ꢧ | ꨜ | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | SINHALA LETTER MAHAAPRAANA PAYANNA | KAYAH LI LETTER PHA | CHAKMA LETTER PHAA | TAI LE LETTER PHA | AHOM LETTER PHA | DIVES AKURU LETTER PHA | SAURASHTRA LETTER PHA | CHAM LETTER PHA | ||||||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 3509 | U+0DB5 | 43286 | U+A916 | 69916 | U+1111C | 6490 | U+195A | 71431 | U+11707 | 71969 | U+11921 | 43175 | U+A8A7 | 43548 | U+AA1C |
| UTF-8 | 224 182 181 | E0 B6 B5 | 234 164 150 | EA A4 96 | 240 145 132 156 | F0 91 84 9C | 225 165 154 | E1 A5 9A | 240 145 156 135 | F0 91 9C 87 | 240 145 164 161 | F0 91 A4 A1 | 234 162 167 | EA A2 A7 | 234 168 156 | EA A8 9C |
| UTF-16 | 3509 | 0DB5 | 43286 | A916 | 55300 56604 | D804 DD1C | 6490 | 195A | 55301 57095 | D805 DF07 | 55302 56609 | D806 DD21 | 43175 | A8A7 | 43548 | AA1C |
| Numeric character reference | ඵ | ඵ | ꤖ | ꤖ | 𑄜 | 𑄜 | ᥚ | ᥚ | 𑜇 | 𑜇 | 𑤡 | 𑤡 | ꢧ | ꢧ | ꨜ | ꨜ |
| Preview | 𑘣 | 𑧃 | 𑩱 | ꠚ | 𑶆 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | MODI LETTER PHA | NANDINAGARI LETTER PHA | SOYOMBO LETTER PHA | SYLOTI NAGRI LETTER PHO | GUNJALA GONDI LETTER PHA | KAITHI LETTER PHA | ||||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 71203 | U+11623 | 72131 | U+119C3 | 72305 | U+11A71 | 43034 | U+A81A | 73094 | U+11D86 | 69796 | U+110A4 |
| UTF-8 | 240 145 152 163 | F0 91 98 A3 | 240 145 167 131 | F0 91 A7 83 | 240 145 169 177 | F0 91 A9 B1 | 234 160 154 | EA A0 9A | 240 145 182 134 | F0 91 B6 86 | 240 145 130 164 | F0 91 82 A4 |
| UTF-16 | 55301 56867 | D805 DE23 | 55302 56771 | D806 DDC3 | 55302 56945 | D806 DE71 | 43034 | A81A | 55303 56710 | D807 DD86 | 55300 56484 | D804 DCA4 |
| Numeric character reference | 𑘣 | 𑘣 | 𑧃 | 𑧃 | 𑩱 | 𑩱 | ꠚ | ꠚ | 𑶆 | 𑶆 | 𑂤 | 𑂤 |
| Preview | 𑒤 | ᰐ | ᤑ | ꯐ | 𑱿 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | TIRHUTA LETTER PHA | LEPCHA LETTER PHA | LIMBU LETTER PHA | MEETEI MAYEK LETTER PHAM | MARCHEN LETTER PHA | |||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 70820 | U+114A4 | 7184 | U+1C10 | 6417 | U+1911 | 43984 | U+ABD0 | 72831 | U+11C7F |
| UTF-8 | 240 145 146 164 | F0 91 92 A4 | 225 176 144 | E1 B0 90 | 225 164 145 | E1 A4 91 | 234 175 144 | EA AF 90 | 240 145 177 191 | F0 91 B1 BF |
| UTF-16 | 55301 56484 | D805 DCA4 | 7184 | 1C10 | 6417 | 1911 | 43984 | ABD0 | 55303 56447 | D807 DC7F |
| Numeric character reference | 𑒤 | 𑒤 | ᰐ | ᰐ | ᤑ | ᤑ | ꯐ | ꯐ | 𑱿 | 𑱿 |
| Preview | 𑚟 | 𑠟 | 𑈠 | 𑋓 | 𑅩 | 𑊜 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | TAKRI LETTER PHA | DOGRA LETTER PHA | KHOJKI LETTER PHA | KHUDAWADI LETTER PHA | MAHAJANI LETTER PHA | MULTANI LETTER PHA | ||||||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 71327 | U+1169F | 71711 | U+1181F | 70176 | U+11220 | 70355 | U+112D3 | 69993 | U+11169 | 70300 | U+1129C |
| UTF-8 | 240 145 154 159 | F0 91 9A 9F | 240 145 160 159 | F0 91 A0 9F | 240 145 136 160 | F0 91 88 A0 | 240 145 139 147 | F0 91 8B 93 | 240 145 133 169 | F0 91 85 A9 | 240 145 138 156 | F0 91 8A 9C |
| UTF-16 | 55301 56991 | D805 DE9F | 55302 56351 | D806 DC1F | 55300 56864 | D804 DE20 | 55300 57043 | D804 DED3 | 55300 56681 | D804 DD69 | 55300 56988 | D804 DE9C |
| Numeric character reference | 𑚟 | 𑚟 | 𑠟 | 𑠟 | 𑈠 | 𑈠 | 𑋓 | 𑋓 | 𑅩 | 𑅩 | 𑊜 | 𑊜 |
| Preview | ᬨ | ꦦ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | BALINESE LETTER PA KAPAL | JAVANESE LETTER PA MURDA | ||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 6952 | U+1B28 | 43430 | U+A9A6 |
| UTF-8 | 225 172 168 | E1 AC A8 | 234 166 166 | EA A6 A6 |
| Numeric character reference | ᬨ | ᬨ | ꦦ | ꦦ |
| Preview | 𑴡 | |
|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | MASARAM GONDI LETTER PHA | |
| Encodings | decimal | hex |
| Unicode | 72993 | U+11D21 |
| UTF-8 | 240 145 180 161 | F0 91 B4 A1 |
| UTF-16 | 55303 56609 | D807 DD21 |
| Numeric character reference | 𑴡 | 𑴡 |
References
- ↑ Ifrah, Georges (2000). The Universal History of Numbers. From Prehistory to the Invention of the Computer. New York: John Wiley & Sons. pp. 447–450. ISBN 0-471-39340-1.
- 1 2 Bühler, Georg (1898). "On the Origin of the Indian Brahmi Alphabet". archive.org. Karl J. Trübner. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- ↑ Evolutionary chart, Journal of the Asiatic Society of Bengal Vol 7, 1838
- ↑ Pall, Peeter. "Microsoft Word - kblhi2" (PDF). Eesti Keele Instituudi kohanimeandmed. Eesti Keele Instituudi kohanimeandmed. Retrieved 19 June 2020.
- ↑ "The Bengali Alphabet" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-09-28.