| Solar eclipse of September 21, 1922 | |
|---|---|
 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | −0.213 |
| Magnitude | 1.0678 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 359 sec (5 m 59 s) |
| Coordinates | 10°42′S 104°30′E / 10.7°S 104.5°E |
| Max. width of band | 226 km (140 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 4:40:31 |
| References | |
| Saros | 133 (40 of 72) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9333 |
A total solar eclipse occurred on September 21, 1922. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The greatest eclipse occurred exactly at perigee.
Totality started in Ethiopia, Italian Somaliland (today's Somalia), and passed British Maldives and Christmas Island in the Straits Settlements (now in Australia) in the Indian Ocean, and Australia. Two large scientific expeditions investigated Einstein's theory of relativity.[1]
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 1921–1924
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[2]
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1921–1924 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||
| 118 | April 8, 1921 Annular |
123 | October 1, 1921 Total | |
| 128 | March 28, 1922 Annular |
133 | September 21, 1922 Total | |
| 138 | March 17, 1923 Annular |
143 | September 10, 1923 Total | |
| 148 | March 5, 1924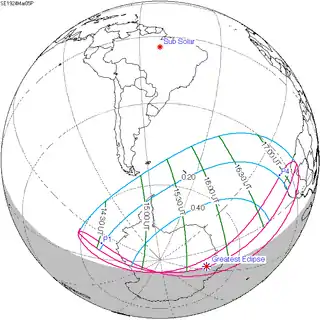 Partial |
153 | August 30, 1924 Partial | |
Saros 133
Solar Saros 133, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, contains 72 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on July 13, 1219. It contains annular eclipses from November 20, 1435, through January 13, 1526, with a hybrid eclipse on January 24, 1544. It has total eclipses from February 3, 1562, through June 21, 2373. The series ends at member 72 as a partial eclipse on September 5, 2499. The longest duration of totality was 6 minutes, 49.97 seconds on August 7, 1850.[3] The total eclipses of this saros series are getting shorter and farther south with each iteration. All eclipses in this series occurs at the Moon’s ascending node.
| Series members 30–56 occur between 1742 and 2211 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 30 | 31 | 32 |
| June 3, 1742 | June 13, 1760 | 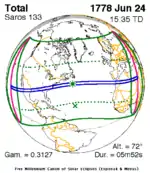 June 24, 1778 |
| 33 | 34 | 35 |
| July 4, 1796 | July 17, 1814 | July 27, 1832 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 |
| August 7, 1850 | 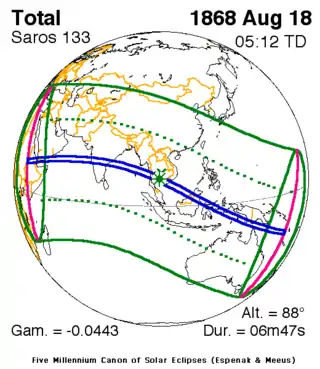 August 18, 1868 |
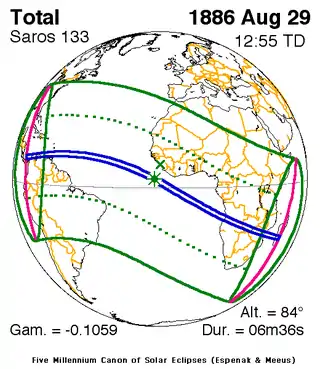 August 29, 1886 |
| 39 | 40 | 41 |
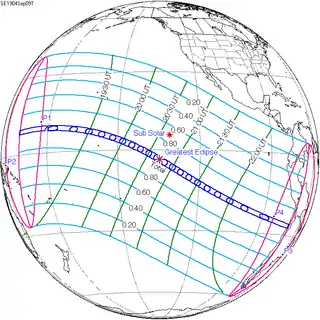 September 9, 1904 |
 September 21, 1922 |
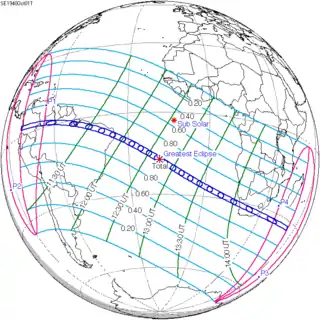 October 1, 1940 |
| 42 | 43 | 44 |
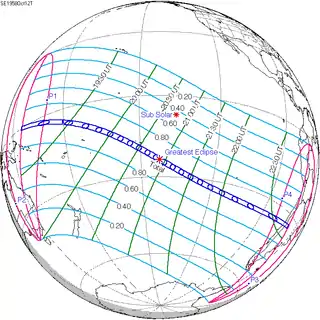 October 12, 1958 |
 October 23, 1976 |
 November 3, 1994 |
| 45 | 46 | 47 |
 November 13, 2012 |
 November 25, 2030 |
 December 5, 2048 |
| 48 | 49 | 50 |
 December 17, 2066 |
 December 27, 2084 |
 January 8, 2103 |
| 51 | 52 | 53 |
 January 19, 2121 |
 January 30, 2139 |
 February 9, 2157 |
| 54 | 55 | 56 |
 February 21, 2175 |
 March 3, 2193 |
 March 15, 2211 |
References
- ↑ "1922 Solar Eclipse in Australia Testing Einstein's Theory". Retrieved 4 June 2011.
- ↑ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ↑ http://eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov/SEsaros/SEsaros133.html
External links
- Fotos of Solar Corona September 21, 1922
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- 1922 Solar Eclipse in Australia
- Wallal: The 1922 Eclipse Expedition
- Photographs from the Wallal Australia expedition from the Lick Observatory Records Digital Archive, UC Santa Cruz Library's Digital Collections Archived 2016-03-05 at the Wayback Machine
.jpg.webp)

