 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Xermelo |
| Other names | LX1032, LX1606 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a617029 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth (tablets) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | >99% (both telotristat ethyl and telotristat) |
| Metabolism | Hydrolysis via carboxylesterases |
| Metabolites | Telotristat |
| Elimination half-life | 0.6 hours (telotristat ethyl), 5 hours (telotristat) |
| Excretion | Feces (92.8%), urine (less than 0.4%)[2] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
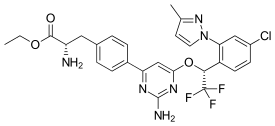
| Formula | C27H26ClF3N6O3 |
| Molar mass | 574.99 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
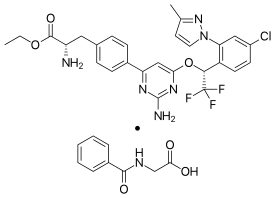
Telotristat ethyl (USAN, brand name Xermelo) is a prodrug of telotristat, which is an inhibitor of tryptophan hydroxylase. It is formulated as telotristat etiprate — a hippurate salt of telotristat ethyl.[2]
On February 28, 2017, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved telotristat ethyl in combination with somatostatin analog (SSA) therapy for the treatment of adults with diarrhea associated with carcinoid syndrome that SSA therapy alone has inadequately controlled.[4][5] Telotristat ethyl was approved for use in the European Union in September 2017.[3]
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers it to be a first-in-class medication.[6]
Pharmacology
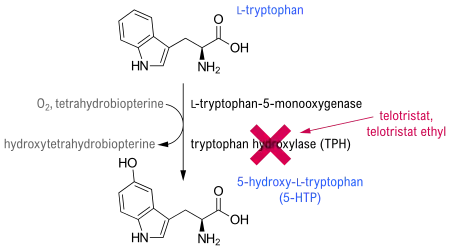
Telotristat is an inhibitor of tryptophan hydroxylase,[7] which mediates the rate-limiting step in serotonin biosynthesis.[2]
Adverse effects
Common adverse effects noted in clinical trials include nausea, headache, elevated liver enzymes, depression, accumulation of fluid causing swelling (peripheral edema), flatulence, decreased appetite, and fever. Constipation is also common, and may be serious or life-threatening (especially in overdose).[4]
Formulations
It is marketed by Lexicon Pharmaceuticals (as telotristat etiprate). 328 mg telotristat etiprate is equivalent to 250 mg telotristate ethyl.[2]
References
- ↑ "Summary Basis of Decision (SBD) for Xermelo". Health Canada. 23 October 2014. Retrieved 29 May 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Xermelo- telotristat ethyl tablet". DailyMed. 30 October 2020. Retrieved 11 November 2020.
- 1 2 "Xermelo EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- 1 2 "FDA Approves Xermelo for Carcinoid Syndrome Diarrhea" (Press release). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). February 28, 2017. Retrieved 1 March 2017.
- ↑ "Xermelo (telotristat ethyl) Tablets". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 4 April 2017. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- ↑ New Drug Therapy Approvals 2017 (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Report). January 2018. Retrieved 16 September 2020.
- ↑ Kulke M, Hörsch D, Caplin M, Anthony L, Bergsland E, Oberg K, et al. (1 October 2016). "Integrated Placebo-Controlled Safety Analysis from Clinical Studies of Telotristat Ethyl for the Treatment of Carcinoid Syndrome". Annals of Oncology. 27 (6): 136–48. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdw369.07.
Further reading
- Kulke MH, O'Dorisio T, Phan A, Bergsland E, Law L, Banks P, et al. (October 2014). "Telotristat etiprate, a novel serotonin synthesis inhibitor, in patients with carcinoid syndrome and diarrhea not adequately controlled by octreotide". Endocrine-Related Cancer. 21 (5): 705–14. doi:10.1530/ERC-14-0173. PMC 4295770. PMID 25012985.
External links
- "Telotristat ethyl". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Telotristat etiprate". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.