 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Drug class | Nonsteroidal androgen; Selective androgen receptor modulator |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
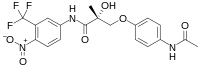
| Formula | C19H18F3N3O6 |
| Molar mass | 441.363 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Acetoxolutamide is a nonsteroidal androgen and selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) which was described in 2000 and was never developed or marketed for medical use.[1] It was derived from structural modification of the nonsteroidal antiandrogen bicalutamide and the nonsteroidal SARM acetothiolutamide.[1] Acetoxolutamide shows greatly improved pharmacokinetic properties and anabolic and androgenic potency relative to acetothiolutamide in animals.[1] It is the (2R) enantiomer of andarine (also known as acetamidoxolutamide or androxolutamide).[1]
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.