 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.070.679 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
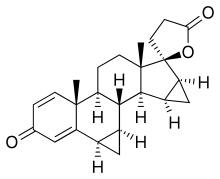
| Formula | C24H28O3 |
| Molar mass | 364.485 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Spirorenone (INN) (developmental code name ZK-35973) is a steroidal antimineralocorticoid of the spirolactone group that was never marketed.[1][2] Spirorenone possesses 5–8 times the antimineralocorticoid activity of spironolactone in animal studies.[3] The initial discovery of spirorenone was deemed a great success, as no compound with greater antimineralocorticoid activity had been developed since spironolactone in 1957.[4] Moreover, spirorenone itself has virtually no affinity for the androgen receptor while its progestogenic activity shows species differences, being somewhat greater than that of spironolactone in rabbits but absent in mice and rats.[3] As such, it was characterized as a highly potent antimineralocorticoid with far fewer hormonal side effects relative to spironolactone.[4]
In clinical trials, spirorenone was found to be 4- to 10-fold as potent as spironolactone as an antimineralocorticoid, and is said to be the most active antimineralocorticoid identified to date.[3] However, it was serendipitously and unexpectedly found that low doses of spirorenone lowered testosterone levels in men during clinical studies.[4][5] This was determined to be due to metabolic conversion of spirorenone into drospirenone (1,2-dihydrospirorenone) by the enzyme Δ1-hydrase, a transformation that occurs only in monkeys and humans.[4][5] Unlike spirorenone, drospirenone was found to be a highly potent progestin and antiandrogen in addition to antimineralocorticoid,[5] with 8-fold the potency of spironolactone as an antimineralocorticoid and 0.3 times the potency of cyproterone acetate as an antiandrogen.[6] Subsequently, investigation of spirorenone was discontinued and drospirenone was developed and eventually introduced instead as a contraceptive.[4][5]
See also
References
- ↑ Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 1112–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ↑ Morton IK, Hall JM (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 106–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- 1 2 3 James VH, Pasqualini JR (22 October 2013). Hormonal Steroids: Proceedings of the Sixth International Congress on Hormonal Steroids. Elsevier Science. pp. 776–. ISBN 978-1-4831-9067-9.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Fischer J, Ganellin CR (13 December 2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 396–. ISBN 978-3-527-60749-5.
- 1 2 3 4 Fischer J, Rotella DP (4 May 2015). Successful Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 8–. ISBN 978-3-527-33685-2.
- ↑ Pollow K, Juchem M, Elger W, Jacobi N, Hoffmann G, Möbus V (December 1992). "Dihydrospirorenone (ZK30595): a novel synthetic progestagen--characterization of binding to different receptor proteins". Contraception. 46 (6): 561–74. doi:10.1016/0010-7824(92)90121-9. PMID 1493716.