 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Chloromethyltestosterone; CMT; 4-Chloro-17α-methyltestosterone; 4-Chloro-17α-methylandrost-4-en-17β-ol-3-one |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
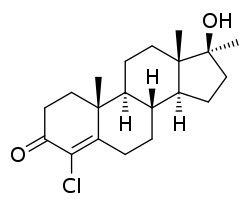
| Formula | C20H29ClO2 |
| Molar mass | 336.90 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Methylclostebol, also known as 4-chloro-17α-methyltestosterone or as 4-chloro-17α-methylandrost-4-en-17β-ol-3-one, is a synthetic, orally active anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) and designer steroid that has been sold on the Internet as a "dietary supplement",[1][2] but it has never been studied for medical use.[3] It is the 17α-alkylated variant of clostebol (4-chlorotestosterone).[4]
Rahnema, Crosnoe, and Kim (2015) reported that German athletes used methylclostebol as a performance enhancing drug in the 1960s and 1970s, but this has not been substantiated.[3] The compound is listed as a banned anabolic agent by the World Anti-Doping Agency.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ Rahnema CD, Crosnoe LE, Kim ED (March 2015). "Designer steroids - over-the-counter supplements and their androgenic component: review of an increasing problem". Andrology. 3 (2): 150–155. doi:10.1111/andr.307. PMID 25684733. S2CID 6999218.
- ↑ Pope HG, Wood RI, Rogol A, Nyberg F, Bowers L, Bhasin S (June 2014). "Adverse health consequences of performance-enhancing drugs: an Endocrine Society scientific statement". Endocrine Reviews. 35 (3): 341–375. doi:10.1210/er.2013-1058. PMC 4026349. PMID 24423981.
- 1 2 Rahnema CD, Crosnoe LE, Kim ED (March 2015). "Designer steroids - over-the-counter supplements and their androgenic component: review of an increasing problem". Andrology. 3 (2): 150–155. doi:10.1111/andr.307. PMID 25684733. S2CID 6999218.
- ↑ Lootens L, Van Eenoo P, Pozo Mendoza OJ, Meulemans P, Leroux-Roels G, Delbeke F (2010). "Application of in vivo urinary steroid detection in uPA+/+-SCID chimeric mice.". 28th Cologne workshop on Dope Analysis (Manfred Donike workshop). Vol. 18. pp. 52–61.
- ↑ "World Anti-Doping Code: International Standard Prohibited List" (PDF). January 2017.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.