| |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 6,7-Dihydrocanrenone; 7-Desthioacetylspironolactone; 20-Spirox-4-ene-3,20-dione |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Antimineralocorticoid; Progestogen; Steroidal antiandrogen |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.321 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H30O3 |
| Molar mass | 342.479 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
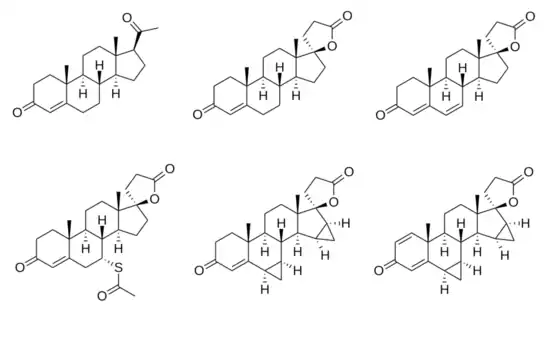
SC-5233, also known as 6,7-dihydrocanrenone or 20-spirox-4-ene-3,20-dione, is a synthetic, steroidal antimineralocorticoid of the spirolactone group which was developed by G. D. Searle & Company in the 1950s but was never marketed.[1][2] It was the first synthetic antagonist of the mineralocorticoid receptor to have been identified and tested in humans.[1][3] The drug was found to lack appreciable oral bioavailability and to be of low potency when administered parenterally,[4] but it nonetheless produced a mild diuretic effect in patients with congestive heart failure.[1] SC-8109, the 19-nor (19-demethyl) analogue, was developed and found to have improved oral bioavailability and potency, but still had low potency.[5] Spironolactone (SC-9420; Aldactone) followed and had both good oral bioavailability and potency, and was the first synthetic antimineralocorticoid to be marketed.[3] It has about 46-fold higher oral potency than SC-5233.[6]
SC-5233 is the propionic acid lactone of testosterone (androst-4-en-17β-ol-3-one) and is also known 3-(3-oxo-17β-hydroxyandrost-4-en-17α-yl)propionic acid γ-lactone or as 17α-(2-carboxyethyl)testosterone γ-lactone.[7] It is the unsubstituted parent or prototype compound of the spirolactone family of steroidal antimineralocorticoids.[2][8]
Similarly to other spirolactones like canrenone and spironolactone, SC-5233 has some antiandrogenic activity and antagonizes the effects of testosterone in animals.[7] In addition, along with SC-8109, it has been found to possess potent progestogenic activity.[9]
Chemical structures of spirolactones
|
References
- 1 2 3 Sherlock S (14 December 2013). "Diuretics in Liver Disease". In Buchborn E, Bock KD (eds.). Diuresis and Diuretics / Diurese und Diuretica: An International Symposium Herrenchiemsee, June 17th–20th, 1959 Sponsored by CIBA / Ein Internationales Symposium Herrenchiemsee, 17.–20. Juni 1959 Veranstaltet mit Unterstützung der CIBA. Springer-Verlag. pp. 224, 261. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-92756-0_11. ISBN 978-3-642-49716-2.
- 1 2 Szasz G, Budvari-Barany Z (19 December 1990). "Diuretics". Pharmaceutical Chemistry of Antihypertensive Agents. CRC Press. pp. 82–. ISBN 978-0-8493-4724-5.
- 1 2 Delcayre C, Fazal L, Ragot H, Prudhomme M, Azibani F, Samuel JL (6 November 2014). "The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System in Cardiovascular Disease". In Cokkinos DB (ed.). Introduction to Translational Cardiovascular Research. Springer. pp. 61–. ISBN 978-3-319-08798-6.
- ↑ "Spironolactone". The British Encyclopaedia of Medical Practice: Medical progress. Butterworth & Company. 1961. p. 302.
Cena and Kagawa first synthesized 3-(3-oxo-17β-hydroxy-4-androsten-17α-yl)-propionic acid-gamma-lactone and later prepared its 19-nor analogue. These compounds were designated SC-5233 and SC-8109, respectively. Both have anti-aldosterone activity and most of the early work on aldosterone antagonism was done with their aid. SC-5233 is not appreciably absorbed when given by mouth and the parenteral dose is large. As in the case of certain other steroids the 19-nor derivative was an improvement on the parent compound (Klyne, 1959). SC-8109 is well absorbed from the alimentary tract, but the dose is about 2 g daily.
- ↑ Brandon ML (1 January 1962). Corticosteroids in medical practice. Thomas. p. 310. ISBN 9780398002152.
- ↑ Kolkhof P, Bärfacker L (July 2017). "30 YEARS OF THE MINERALOCORTICOID RECEPTOR: Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists: 60 years of research and development". The Journal of Endocrinology. 234 (1): T125–T140. doi:10.1530/JOE-16-0600. PMC 5488394. PMID 28634268.
- 1 2 Kagawa CM, Sturtevant FM, Van Arman CG (June 1959). "Pharmacology of a new steroid that blocks salt activity of aldosterone and desoxycorticosterone". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 126 (2): 123–130. PMID 13665517.
[SC-5233] (total dose of 5 mg/rat) partially blocked the effects of testosterone propionate on the seminal vesicles and prostate in similar animals.
- ↑ Kalvoda J, de Gasparo M (24 August 2010). "Eplerenone: Selective Aldosterone Antagonist". In Fischer J, Ganellin CR (eds.). Analogue-based Drug Discovery II. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 361–. ISBN 978-3-527-63212-1.
- ↑ Hertz R, Tullner WW (November 1958). "Progestational activity of certain steroid-17-spirolactones". Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. 99 (2): 451–452. doi:10.3181/00379727-99-24380. PMID 13601900. S2CID 20150966.